Playables Examples
PlayableGraph Visualizer
All of the examples in this document use the PlayableGraph Visualizer (Pictured below) to illustrate the trees and nodes created by the PlayablesAn API that provides a way to create tools, effects or other gameplay mechanisms by organizing and evaluating data sources in a tree-like structure known as the PlayableGraph. More info
See in Glossary API. The Playable graphAn API for controlling Playables. Playable Graphs allow you to create, connect and destroy playables. More info
See in Glossary Visualizer is a tool available through GitHub.
To use the PlayableGraph Visualizer:
Download the PlayableGraph Visualizer that corresponds with your version of Unity from the GitHub repository
Open the tool by selecting Window > PlayableGraph Visualizer
Register your graph using GraphVisualizerClient.Show(PlayableGraph graph, string name).
Playables in the graph are represented by colored nodes. Wire color intensity indicates the weight of the blending. See GitHub for more information on this tool.
Playing a single animation clip on a GameObject
This example demonstrates a simple PlayableGraph with a single playable output that is linked to a single playable node. The playable node plays a single animation clipAnimation data that can be used for animated characters or simple animations. It is a simple “unit” piece of motion, such as (one specific instance of) “Idle”, “Walk” or “Run”. More info
See in Glossary (clip). An AnimationClipPlayable must wrap the animation clip to make it compatible with the Playables API.
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Playables;
using UnityEngine.Animations;
[RequireComponent(typeof(Animator))]
public class PlayAnimationSample : MonoBehaviour
{
public AnimationClip clip;
PlayableGraph playableGraph;
void Start()
{
playableGraph = PlayableGraph.Create();
playableGraph.SetTimeUpdateMode(DirectorUpdateMode.GameTime);
var playableOutput = AnimationPlayableOutput.Create(playableGraph, "Animation", GetComponent<Animator>());
// Wrap the clip in a playable
var clipPlayable = AnimationClipPlayable.Create(playableGraph, clip);
// Connect the Playable to an output
playableOutput.SetSourcePlayable(clipPlayable);
// Plays the Graph.
playableGraph.Play();
}
void OnDisable()
{
// Destroys all Playables and PlayableOutputs created by the graph.
playableGraph.Destroy();
}
}
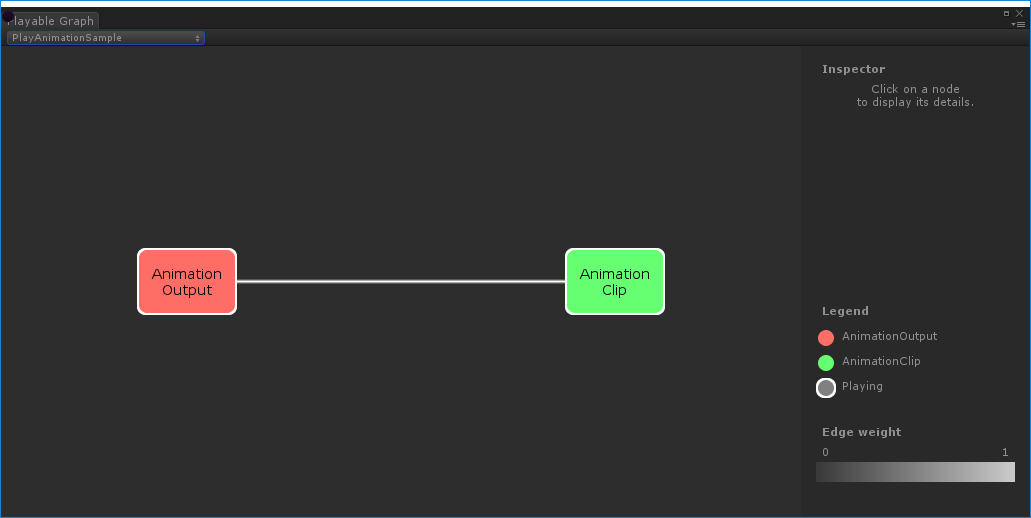
Use AnimationPlayableUtilities to simplify the creation and playback of animation playables, as shown in the following example:__
__
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Playables;
using UnityEngine.Animations;
[RequireComponent(typeof(Animator))]
public class PlayAnimationUtilitiesSample : MonoBehaviour
{
public AnimationClip clip;
PlayableGraph playableGraph;
void Start()
{
AnimationPlayableUtilities.PlayClip(GetComponent<Animator>(), clip, out playableGraph);
}
void OnDisable()
{
// Destroys all Playables and Outputs created by the graph.
playableGraph.Destroy();
}
}
Creating an animation blend tree
This example demonstrates how to use the AnimationMixerPlayable to blend two animation clips. Before blending the animation clips, they must be wrapped by playables. To do this, an AnimationClipPlayable (clipPlayable0 and clipPlayable1) wraps each AnimationClip (clip0 and clip1). The SetInputWeight() method dynamically adjusts the blend weight of each playable.
Although not shown in this example, you can also use AnimationMixerPlayable to blend playable mixers and other playables.
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Playables;
using UnityEngine.Animations;
[RequireComponent(typeof(Animator))]
public class MixAnimationSample : MonoBehaviour
{
public AnimationClip clip0;
public AnimationClip clip1;
public float weight;
PlayableGraph playableGraph;
AnimationMixerPlayable mixerPlayable;
void Start()
{
// Creates the graph, the mixer and binds them to the Animator.
playableGraph = PlayableGraph.Create();
var playableOutput = AnimationPlayableOutput.Create(playableGraph, "Animation", GetComponent<Animator>());
mixerPlayable = AnimationMixerPlayable.Create(playableGraph, 2);
playableOutput.SetSourcePlayable(mixerPlayable);
// Creates AnimationClipPlayable and connects them to the mixer.
var clipPlayable0 = AnimationClipPlayable.Create(playableGraph, clip0);
var clipPlayable1 = AnimationClipPlayable.Create(playableGraph, clip1);
playableGraph.Connect(clipPlayable0, 0, mixerPlayable, 0);
playableGraph.Connect(clipPlayable1, 0, mixerPlayable, 1);
// Plays the Graph.
playableGraph.Play();
}
void Update()
{
weight = Mathf.Clamp01(weight);
mixerPlayable.SetInputWeight(0, 1.0f-weight);
mixerPlayable.SetInputWeight(1, weight);
}
void OnDisable()
{
// Destroys all Playables and Outputs created by the graph.
playableGraph.Destroy();
}
}
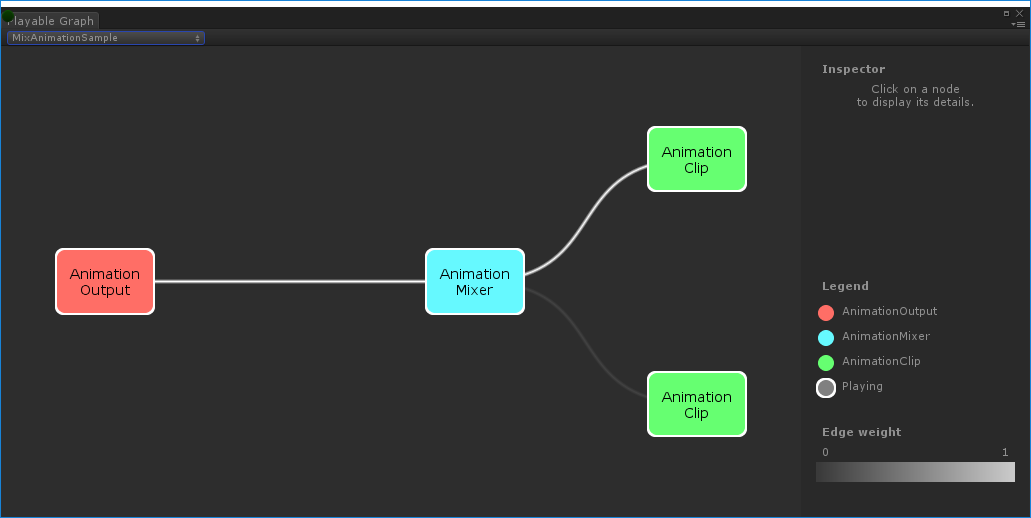
PlayableGraph generated by `MixAnimationSampleBlending an AnimationClip and AnimatorController
This example demonstrates how to use an AnimationMixerPlayable to blend an AnimationClip with an AnimatorController.
Before blending the AnimationClip and AnimatorController, they must be wrapped by playables. To do this, an AnimationClipPlayable (clipPlayable) wraps the AnimationClip (clip) and an AnimatorControllerPlayable (ctrlPlayable) wraps the RuntimeAnimatorController (controller). The SetInputWeight() method dynamically adjusts the blend weight of each playable.
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Playables;
using UnityEngine.Animations;
[RequireComponent(typeof(Animator))]
public class RuntimeControllerSample : MonoBehaviour
{
public AnimationClip clip;
public RuntimeAnimatorController controller;
public float weight;
PlayableGraph playableGraph;
AnimationMixerPlayable mixerPlayable;
void Start()
{
// Creates the graph, the mixer and binds them to the Animator.
playableGraph = PlayableGraph.Create();
var playableOutput = AnimationPlayableOutput.Create(playableGraph, "Animation", GetComponent<Animator>());
mixerPlayable = AnimationMixerPlayable.Create(playableGraph, 2);
playableOutput.SetSourcePlayable(mixerPlayable);
// Creates AnimationClipPlayable and connects them to the mixer.
var clipPlayable = AnimationClipPlayable.Create(playableGraph, clip);
var ctrlPlayable = AnimatorControllerPlayable.Create(playableGraph, controller);
playableGraph.Connect(clipPlayable, 0, mixerPlayable, 0);
playableGraph.Connect(ctrlPlayable, 0, mixerPlayable, 1);
// Plays the Graph.
playableGraph.Play();
}
void Update()
{
weight = Mathf.Clamp01(weight);
mixerPlayable.SetInputWeight(0, 1.0f-weight);
mixerPlayable.SetInputWeight(1, weight);
}
void OnDisable()
{
// Destroys all Playables and Outputs created by the graph.
playableGraph.Destroy();
}
}
Creating a PlayableGraph with several outputs
This example demonstrates how to create a PlayableGraph with two different playable output types: an AudioPlayableOutput and an AnimationPlayableOutput. A PlayableGraph can have many playable outputs of different types.
This example also demonstrates how to play an AudioClip through an AudioClipPlayable that is connected to an AudioPlayableOutput.
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Animations;
using UnityEngine.Audio;
using UnityEngine.Playables;
[RequireComponent(typeof(Animator))]
[RequireComponent(typeof(AudioSource))]
public class MultiOutputSample : MonoBehaviour
{
public AnimationClip animationClip;
public AudioClip audioClip;
PlayableGraph playableGraph;
void Start()
{
playableGraph = PlayableGraph.Create();
// Create the outputs.
var animationOutput = AnimationPlayableOutput.Create(playableGraph, "Animation", GetComponent<Animator>());
var audioOutput = AudioPlayableOutput.Create(playableGraph, "Audio", GetComponent<AudioSource>());
// Create the playables.
var animationClipPlayable = AnimationClipPlayable.Create(playableGraph, animationClip);
var audioClipPlayable = AudioClipPlayable.Create(playableGraph, audioClip, true);
// Connect the playables to an output
animationOutput.SetSourcePlayable(animationClipPlayable);
audioOutput.SetSourcePlayable(audioClipPlayable);
// Plays the Graph.
playableGraph.Play();
}
void OnDisable()
{
// Destroys all Playables and Outputs created by the graph.
playableGraph.Destroy();
}
}
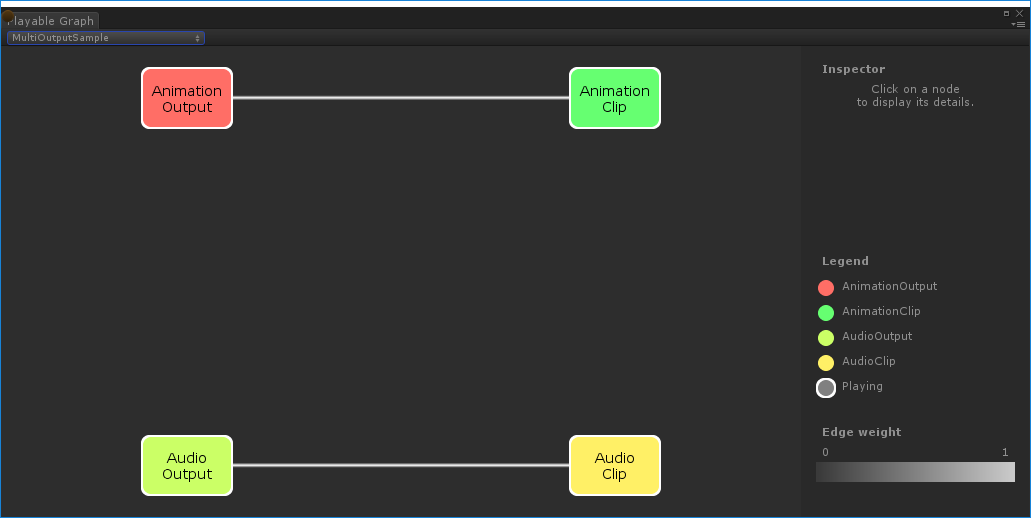
PlayableGraph generated by `MultiOutputSampleControlling the play state of the tree
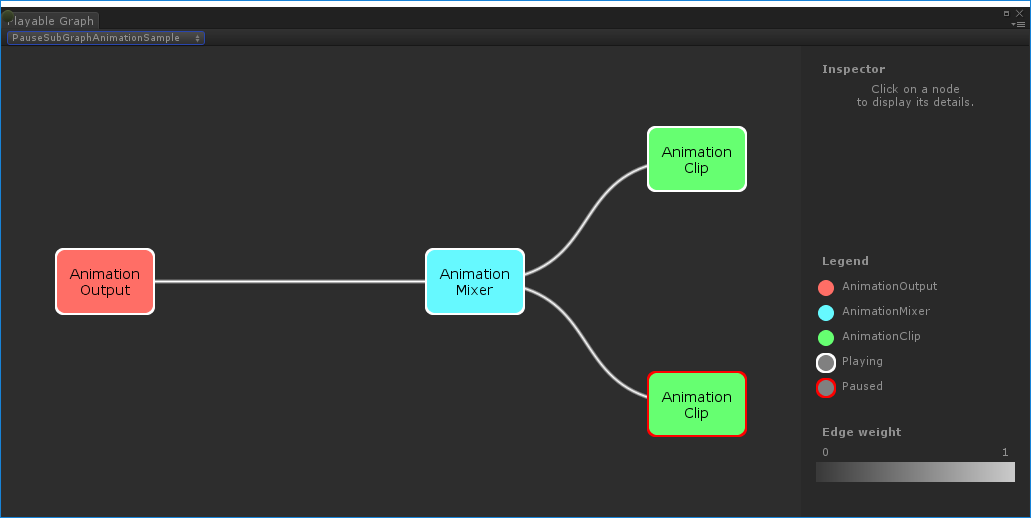
This example demonstrates how to use the Playable.SetPlayState() method to control the play state of node on the PlayableGraph tree. The SetPlayState method controls the play state of the entire tree, one of its branches, or a single node.
When setting the play state of a node, the state propagates to all its children, regardless of their play states. For example, if a child node is explicitly paused, setting a parent node to “playing” also sets all its child nodes to “playing.”
In this example, the PlayableGraph contains a mixer that blends two animation clips. An AnimationClipPlayable wraps each animation clip and the SetPlayState() method explicitly pauses the second playable. The second AnimationClipPlayable is explicitly paused, so its internal time does not advance and outputs the same value. The exact value depends on the specific time when the AnimationClipPlayable was paused.
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Playables;
using UnityEngine.Animations;
[RequireComponent(typeof(Animator))]
public class PauseSubGraphAnimationSample : MonoBehaviour
{
public AnimationClip clip0;
public AnimationClip clip1;
PlayableGraph playableGraph;
AnimationMixerPlayable mixerPlayable;
void Start()
{
// Creates the graph, the mixer and binds them to the Animator.
playableGraph = PlayableGraph.Create();
var playableOutput = AnimationPlayableOutput.Create(playableGraph, "Animation", GetComponent<Animator>());
mixerPlayable = AnimationMixerPlayable.Create(playableGraph, 2);
playableOutput.SetSourcePlayable(mixerPlayable);
// Creates AnimationClipPlayable and connects them to the mixer.
var clipPlayable0 = AnimationClipPlayable.Create(playableGraph, clip0);
var clipPlayable1 = AnimationClipPlayable.Create(playableGraph, clip1);
playableGraph.Connect(clipPlayable0, 0, mixerPlayable, 0);
playableGraph.Connect(clipPlayable1, 0, mixerPlayable, 1);
mixerPlayable.SetInputWeight(0, 1.0f);
mixerPlayable.SetInputWeight(1, 1.0f);
clipPlayable1.SetPlayState(PlayState.Paused);
// Plays the Graph.
playableGraph.Play();
}
void OnDisable()
{
// Destroys all Playables and Outputs created by the graph.
playableGraph.Destroy();
}
}
Controlling the timing of the tree
This example demonstrates how to use the Play() method to play a PlayableGraph, how to use the SetPlayState() method to pause a playable, and how to use the SetTime() method to manually set the local time of a playable with a variable.
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Playables;
using UnityEngine.Animations;
[RequireComponent(typeof(Animator))]
public class PlayWithTimeControlSample : MonoBehaviour
{
public AnimationClip clip;
public float time;
PlayableGraph playableGraph;
AnimationClipPlayable playableClip;
void Start()
{
playableGraph = PlayableGraph.Create();
var playableOutput = AnimationPlayableOutput.Create(playableGraph, "Animation", GetComponent<Animator>());
// Wrap the clip in a playable
playableClip = AnimationClipPlayable.Create(playableGraph, clip);
// Connect the Playable to an output
playableOutput.SetSourcePlayable(playableClip);
// Plays the Graph.
playableGraph.Play();
// Stops time from progressing automatically.
playableClip.SetPlayState(PlayState.Paused);
}
void Update ()
{
// Control the time manually
playableClip.SetTime(time);
}
void OnDisable()
{
// Destroys all Playables and Outputs created by the graph.
playableGraph.Destroy();
}
}
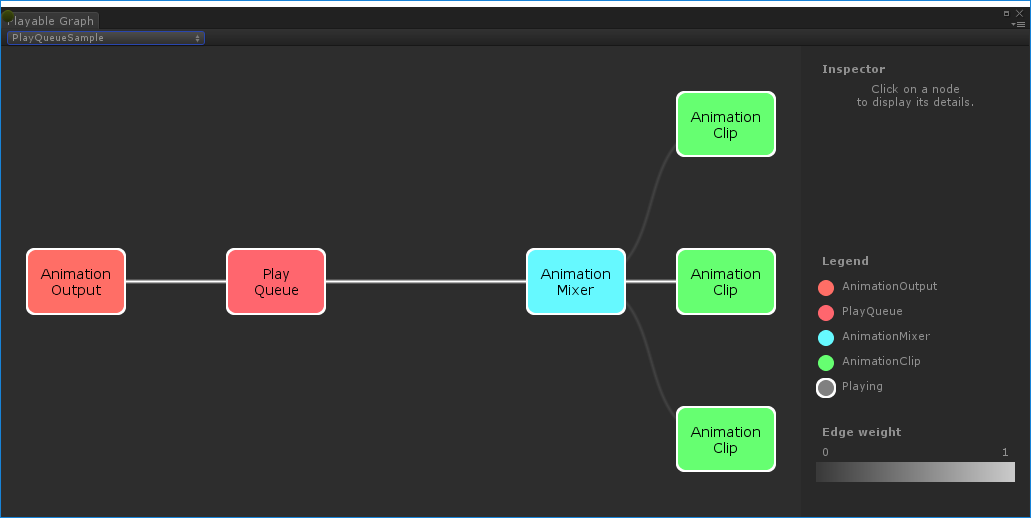
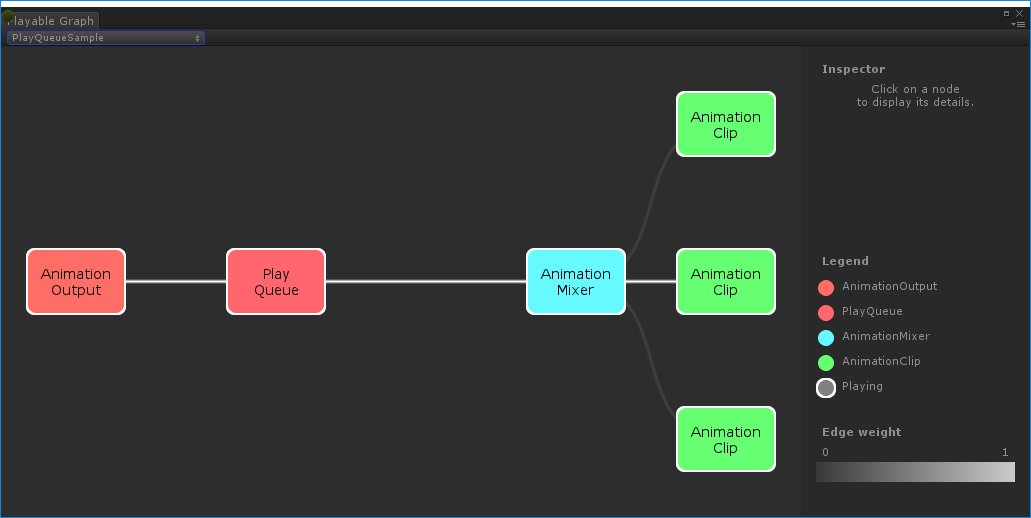
Creating PlayableBehaviour
This example demonstrates how to create custom playables with the PlayableBehaviour public class. This example also demonstrate how to override the PrepareFrame() virtual method to control nodes on the PlayableGraph. Custom playables can override any of the other virtual methods of the PlayableBehaviour class.
In this example, the nodes being controlled are a series of animation clips (clipsToPlay). The SetInputMethod() modifies the blend weight of each animation clip, ensuring that only one clip plays at a time, and the SetTime() method adjusts the local time so playback starts at the moment the animation clip is activated.
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.Animations;
using UnityEngine.Playables;
public class PlayQueuePlayable : PlayableBehaviour
{
private int m_CurrentClipIndex = -1;
private float m_TimeToNextClip;
private Playable mixer;
public void Initialize(AnimationClip[] clipsToPlay, Playable owner, PlayableGraph graph)
{
owner.SetInputCount(1);
mixer = AnimationMixerPlayable.Create(graph, clipsToPlay.Length);
graph.Connect(mixer, 0, owner, 0);
owner.SetInputWeight(0, 1);
for (int clipIndex = 0 ; clipIndex < mixer.GetInputCount() ; ++clipIndex)
{
graph.Connect(AnimationClipPlayable.Create(graph, clipsToPlay[clipIndex]), 0, mixer, clipIndex);
mixer.SetInputWeight(clipIndex, 1.0f);
}
}
override public void PrepareFrame(Playable owner, FrameData info)
{
if (mixer.GetInputCount() == 0)
return;
// Advance to next clip if necessary
m_TimeToNextClip -= (float)info.deltaTime;
if (m_TimeToNextClip <= 0.0f)
{
m_CurrentClipIndex++;
if (m_CurrentClipIndex >= mixer.GetInputCount())
m_CurrentClipIndex = 0;
var currentClip = (AnimationClipPlayable)mixer.GetInput(m_CurrentClipIndex);
// Reset the time so that the next clip starts at the correct position
currentClip.SetTime(0);
m_TimeToNextClip = currentClip.GetAnimationClip().length;
}
// Adjust the weight of the inputs
for (int clipIndex = 0 ; clipIndex < mixer.GetInputCount(); ++clipIndex)
{
if (clipIndex == m_CurrentClipIndex)
mixer.SetInputWeight(clipIndex, 1.0f);
else
mixer.SetInputWeight(clipIndex, 0.0f);
}
}
}
[RequireComponent(typeof (Animator))]
public class PlayQueueSample : MonoBehaviour
{
public AnimationClip[] clipsToPlay;
PlayableGraph playableGraph;
void Start()
{
playableGraph = PlayableGraph.Create();
var playQueuePlayable = ScriptPlayable<PlayQueuePlayable>.Create(playableGraph);
var playQueue = playQueuePlayable.GetBehaviour();
playQueue.Initialize(clipsToPlay, playQueuePlayable, playableGraph);
var playableOutput = AnimationPlayableOutput.Create(playableGraph, "Animation", GetComponent<Animator>());
playableOutput.SetSourcePlayable(playQueuePlayable);
playableOutput.SetSourceInputPort(0);
playableGraph.Play();
}
void OnDisable()
{
// Destroys all Playables and Outputs created by the graph.
playableGraph.Destroy();
}
}
2017–07–04 Page published with limited editorial review
New in Unity 2017.1 NewIn20171
Did you find this page useful? Please give it a rating: