Description
Projects a vector onto another vector.
To understand vector projection, imagine that onNormal is resting on a line pointing in its
direction. Somewhere along that line will be the nearest point to the tip of vector. The
projection is just onNormal rescaled so that it reaches that point on the line.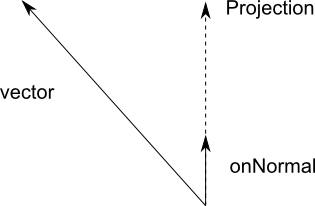
The function will return a zero vector if onNormal is almost zero.
An example of the usage of projection is a rail-mounted gun that should slide so that it gets
as close as possible to a target object. The projection of the target heading along the
direction of the rail can be used to move the gun by applying a force to a rigidbody, say.
function Slide(target: Transform, railDirection: Vector3) { var heading = target.position - transform.position; var force = Vector3.Project(heading, railDirection); GetComponent.<Rigidbody>().AddForce(force); }
using UnityEngine; using System.Collections;
public class ExampleClass : MonoBehaviour { void Slide(Transform target, Vector3 railDirection) { Vector3 heading = target.position - transform.position; Vector3 force = Vector3.Project(heading, railDirection); GetComponent<Rigidbody>().AddForce(force); } }
Did you find this page useful? Please give it a rating: