Modelling
It’s really important to plan ahead before modeling. Quickly made models are fine during pre-production or for roughing out a space, but the moment you start finalizing an Asset to make a proper Scene, consider the following:
- Make every polygon count
- GameObject contribution to lighting
- Model UV layout strategy
- Details in geometry
- Smoothing groups (Hard/soft edges of polygons)
Make every polygon count
Despite modern hardware being more capable than ever, simple geometry is always beneficial in a Scene. Unnecessary tessellation and complex geometry is difficult to manage for a real-time setup, and it can impact performance and use memory unnecessarily. The following example demonstrates how geometry that is never seen by the players wastes resources such as lightmap and overdraw, and causes light leakage:

GameObject contribution to lighting
If you are using Baked lighting or Realtime GI with Light Probes, you need to decide whether a GameObject contributes to lighting in a Scene, or only receives indirect/baked lighting in the Scene.
GameObjects that contribute to lighting
To set a GameObject to contribute to lighting, make sure Lightmap Static in checked in the Inspector window. This provides simpler and smoother surface areas that produce better indirect bounces/baked lighting because of their efficiency in space usage for lightmap textures. Note that:
- You might need to author UV2 for the geometry when doing a light bake, if the auto lightmap UV provides inefficient chart or generate undesirable seams.
- You might need to author UV3 for the geometry for efficient results in Realtime GI.
Sometimes, in Realtime GI, you can simplify a UV of a Mesh to make the geometry use significantly less resources, and produce the best result with fewer artifacts.
GameObjects that only receive lighting in the scene
When GameObjects only receive lighting from real-time lights and Light Probes, the geometry doesn’t have a lightmap UV restriction. The geometry still needs special attention if it’s large, because it might not be lit properly with a single Light Probe, and might require a Light Probe Proxy Volume component to stitch together multiple probe light definitions.
You don’t always need to use a lightmap or use Realtime GI for non-moving GameObjects. If a GameObject is small, or it doesn’t have surfaces that bounce much light, it probably doesn’t need to be included in the lightmap. The bench and railings shown below are a good example:

Model UV layout strategy
The UV layout can help improve visual quality while using the same amount of memory for normal map baking (typically UV1), lightmaps baking (UV2) and real-time lightmaps (UV3), especially for geometry with non-tileable textures.
Here are a few tips to consider when making a UV layout strategy:
- For UV1 charts, split the UV shell only as necessary, and try to lay out the UV chart as efficiently as possible to prevent wasting texture space for normal map baking. To put it into perspective, a 1024 square texture uses the same amount of memory whether you place details in the texture or not.
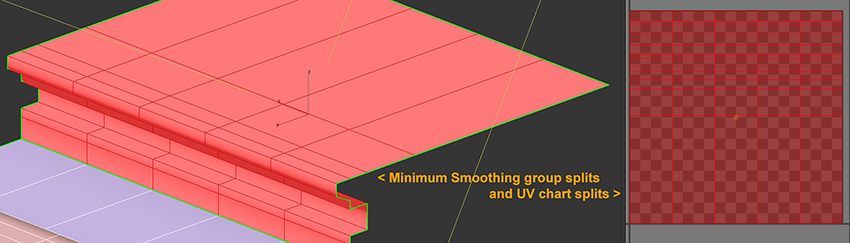
- For lightmaps (UV2), try to make unbroken lightmap charts with borders that touch but do not overlap, to avoid bleeding or seams in the light bake. Keeping a consistent scale between UV charts/shells is important for even distribution of lightmap texels across your model.
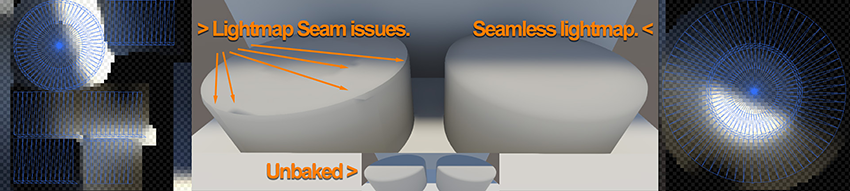
For Realtime GI (UV3), prioritize UV space for large areas that represent big surfaces in your model to reduce memory usage and avoid seams. In many cases, the automatic UV settings in the model can really help optimize the chart. For in-depth information on chart optimization for Realtime GI, see the Unity tutorial Optimizing Unity’s auto unwrapping.
For GameObjects that don’t require lightmaps, don’t waste memory and time by authoring additional UVs, unless custom shaders require them.
Details in geometry
Real world GameObjects are highly detailed. To author real-time geometry, you need to identify which details to place in geometry, and which to place in the normal map and textures. When developing Assets for real-time Scenes, it’s normal to bake high-polygon to low-polygon normal maps.

One important detail to remember is the way edges on a GameObject catch highlights. It is unusual to find a real-life object with very sharp edges, with non bevelled edges, or without detailed edge definition. Replicating realistic edge effects improves the believability of the Scene.
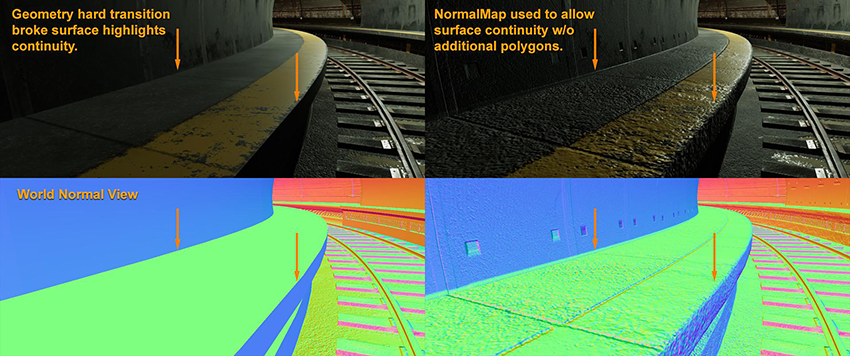
Smoothing groups (Hard/Soft edges of polygon)
You can improve the efficiency of models and normal maps by using proper smoothing groups. Here are some tips on using smoothing groups:
- When dealing with normal map baking from high polygon to low polygon, use a simple configuration for smoothing groups rather than multiple faceted polygons. This is because tangent normal maps need to bend the hard split of the surface normal from the low-poly geometry.
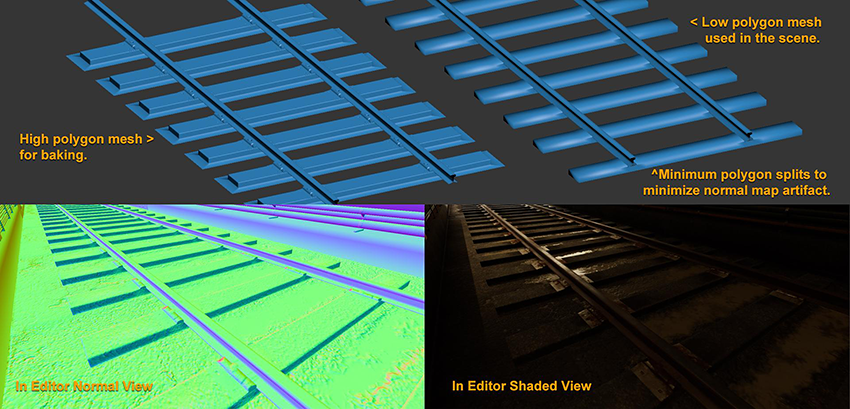
-
A smooth polygon with a good normal map saves on vertex count, which equates to more efficient geometry to render. Here’s a simple example that compares the following setups:
A single plane with split smoothing groups that is equal to 36 vertices.
A simple 18 triangle plane in 1 smoothing group that is equal to 16 vertices.

Single plane and triangle plane vertex count comparison
- A smooth polygon saves on chart splitting in Lightmap baking and Realtime GI that produces smoother visual result.
- 2018–03–21 Page published with limited editorial review
- Making believable visuals Best Practice Guide added in Unity 2017.3
Did you find this page useful? Please give it a rating: