Description
Use Transform.Rotate to rotate GameObjects in a variety of ways. The rotation is often provided as a Euler angle and not a Quaternion.
You can specify a rotation in world axes or local axes.
World axis rotation uses the coordinate system of the Scene, so when you start rotate a GameObject, its x, y, and z axes are aligned with the x, y, and z world axes. So if you randomly rotate a cube in world space, its axes align with the world. When you select a cube in the Unity Editor’s Scene view, rotation Gizmos appear for the left/right, up/down and forward/back rotation axes. Moving these Gizmos rotates the cube around the axes. If you de-select and then re-select the cube, the axes restart in world alignment.
Local rotation uses the coordinate system of the GameObject itself. So, a newly created cube uses its x, y, and z axis set to zero rotation. Rotating the cube updates the rotation axes. If you de-select and the re-select the cube, the axes will be shown in the orientation they were before.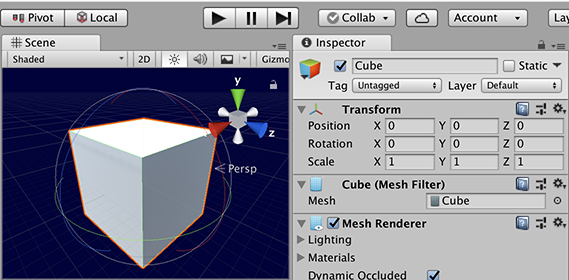
A cube not rotated in Local Gizmo Toggle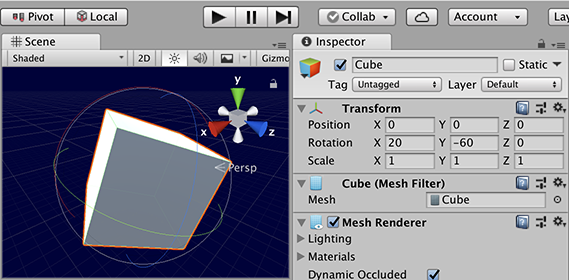
A cube rotated in Local Gizmo Toggle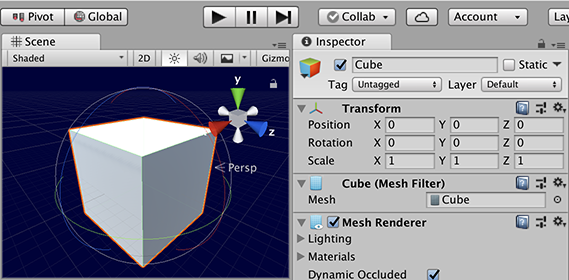
A cube not rotated in Global Gizmo Toggle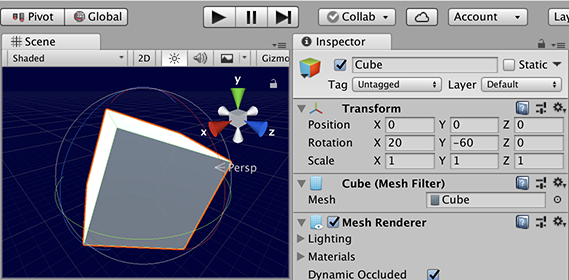
A cube rotated in Global Gizmo Toggle
Parameters
| eulers | The rotation to apply in euler angles. |
| relativeTo | Determines whether to rotate the GameObject either locally to the GameObject or relative to the Scene in world space. |
Description
Applies a rotation of eulerAngles.z degrees around the z-axis, eulerAngles.x degrees around the x-axis, and eulerAngles.y degrees around the y-axis (in that order).
Rotate takes a Vector3 argument as a euler angle. The second argument is the rotation axes, which can be set to local axis (Space.Self) or global axis (Space.World). The rotation is by the Euler amount.
Declaration
public void Rotate(float xAngle, float yAngle, float zAngle, Space relativeTo = Space.Self);Parameters
| relativeTo | Determines whether to rotate the GameObject either locally to the GameObject or relative to the Scene in world space. |
| xAngle | Degrees to rotate the GameObject around the X axis. |
| yAngle | Degrees to rotate the GameObject around the Y axis. |
| zAngle | Degrees to rotate the GameObject around the Z axis. |
Description
Applies a rotation of zAngle degrees around the z axis, xAngle degrees around the x axis, and yAngle degrees around the y axis (in that order).
Rotate can have the euler angle specified in 3 floats for x, y, and z.
The example shows two cubes: one cube uses Space.Self (the local space and axes of the GameObject) and the other uses Space.World (the space and axes in relation to the Scene). Both cubes have the same angle using 3 Scenes. When two or three of the Scenes are given values of approximately 0.25f, both cubes will rotate. The X ValueSceneZ Value Inspector fields store the rotation values. The cubes rotate in different ways. To see the difference, add the script to your Scene and take a look at the Scene view as the Game is running. In the Scene view, make sure that Local is set by the Gizmo Toggle, and select the Self cube. The Self cube rotates with the x, y and z arrows continuing their direction through the cube faces. Now change the Gizmo Toggle to Global and select the World cube. The is aligned with the world x, y and z axes.
using UnityEngine;
// Transform.Rotate example // // Two cubes are created. One (red) is rendered using Space.Self. The // other (green) uses Space.World. The rotation is controlled using xAngle, // yAngle and zAngle. Over time, the cubes rotate differently.
public class ExampleScript : MonoBehaviour { public float xAngle, yAngle, zAngle; public Material selfMat, worldMat;
private GameObject cube1, cube2;
void Awake() { cube1 = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube); cube1.transform.position = new Vector3(0.75f, 0.0f, 0.0f); cube1.GetComponent<Renderer>().material = selfMat; cube1.name = "Self";
cube2 = GameObject.CreatePrimitive(PrimitiveType.Cube); cube2.transform.position = new Vector3(-0.75f, 0.0f, 0.0f); cube2.GetComponent<Renderer>().material = worldMat; cube2.name = "World"; }
void Update() { cube1.transform.Rotate(xAngle, yAngle, zAngle, Space.Self); cube2.transform.Rotate(xAngle, yAngle, zAngle, Space.World); } }
Parameters
| angle | The degrees of rotation to apply. |
| axis | The axis to apply rotation to. |
| relativeTo | Determines whether to rotate the GameObject either locally to the GameObject or relative to the Scene in world space. |
Description
Rotates the object around the given axis by the number of degrees defined by the given angle.
Rotate has an axis, angle and the local or global parameters. The rotation axis can be in any direction.
Parameters
| eulers | The rotation to apply in euler angles. |
Description
Applies a rotation of eulerAngles.z degrees around the z-axis, eulerAngles.x degrees around the x-axis, and eulerAngles.y degrees around the y-axis (in that order).
The rotation is relative to the GameObject's local space (Space.Self).
Declaration
public void Rotate(float xAngle, float yAngle, float zAngle);Parameters
| xAngle | Degrees to rotate the GameObject around the X axis. |
| yAngle | Degrees to rotate the GameObject around the Y axis. |
| zAngle | Degrees to rotate the GameObject around the Z axis. |
Description
The implementation of this method applies a rotation of zAngle degrees around the z axis, xAngle degrees around the x axis, and yAngle degrees around the y axis (in that order).
The rotation is relative to the GameObject's local space (Space.Self).
Parameters
| axis | The axis to apply rotation to. |
| angle | The degrees of rotation to apply. |
Description
Rotates the object around the given axis by the number of degrees defined by the given angle.
Rotate has an axis, angle and the local or global parameters. The rotation axis can be in any direction. The rotation is relative to the GameObject's local space (Space.Self).