Audio Clip
Switch to ScriptingAudio clips contain the audio data used by Audio SourcesA component which plays back an Audio Clip in the scene to an audio listener or through an audio mixer. More info
See in Glossary. Unity supports mono, stereo, and multichannel audio assets up to eight channels.
You can import the following audio file formats in Unity: .aif, .wav, .mp3, and .ogg. Unity also supports importing of tracker modules in the .xm, .mod, .it, and .s3m formats. The tracker module assets behave the same way as any other audio assets in Unity although no waveform preview is available in the asset import inspectorA Unity window that displays information about the currently selected GameObject, asset or project settings, allowing you to inspect and edit the values. More info
See in Glossary.
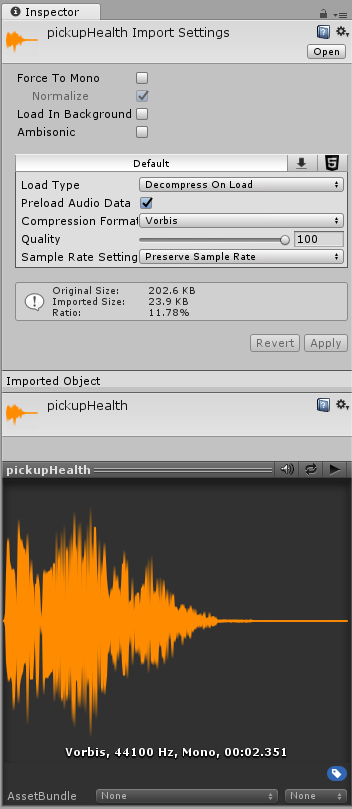
Options
Force To Mono
When this option is enabled, multi-channel audio will be mixed down to a mono track before packing.
Normalize
When this option is enabled, audio will be normalized during the “Force To Mono” mixing down process.
Load In Background
When this option is enabled, the loading of the clip will happen at a delayed time on a separate thread, without blocking the main thread.
Ambisonic
Ambisonic audio sources store audio in a format which represents a soundfield that can be rotated based on the listener’s orientation. It’s useful for 360-degree videos and XRAn umbrella term encompassing Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR) applications. Devices supporting these forms of interactive applications can be referred to as XR devices. More info
See in Glossary applications. Enable this option if your audio file contains Ambisonic-encoded audio.
Properties
| Property: | Function: | |
|---|---|---|
| Load Type | The method Unity uses to load audio assets at runtime. | |
| Decompress On Load | Audio files are decompressed as soon as they’re loaded. Use this option for smaller compressed sounds to avoid the performance overhead of decompressing on the fly. Be aware that decompressing Vorbis-encoded sounds on load will use about ten times more memory than keeping them compressed (for ADPCM encoding it’s about 3.5 times), so don’t use this option for large files. | |
| Compressed In Memory | Keep audio compressed in memory and decompress while playing. This option has a slight performance overhead, especially for Ogg/Vorbis compressed files. Use it only for files that consume excess memory for the Decompressed on Load. The decompression happens on the mixer thread, which can be monitored in the DSP CPU section in the Audio pane of the ProfilerA window that helps you to optimize your game. It shows how much time is spent in the various areas of your game. For example, it can report the percentage of time spent rendering, animating, or in your game logic. More info See in Glossary window. |
|
| Streaming | Decode continuous audio. This method uses a minimal amount of memory to buffer compressed data that’s incrementally read from the disk and decoded spontaneously. The decompression happens on a separate streaming thread whose CPU usage can be monitored in the Streaming CPU section in the Audio pane of the profiler window. Note: Streaming clips have an overhead of approximately 200KB, even if none of the audio data is loaded. | |
| Compression Format | The specific format that will be used for the sound at runtime. Note that the options available depend on the currently selected build target. | |
| PCM | This option offers higher quality at the expense of larger file size and is best for short sound effects. | |
| ADPCM | This format is useful for sounds that contain a fair bit of noise and need to be played in large quantities, such as footsteps, impacts, weapons. The compressionA method of storing data that reduces the amount of storage space it requires. See Texture Compression, Animation Compression, Audio Compression, Build Compression. See in Glossary ratio is 3.5 times smaller than PCM, but CPU usage is much lower than the MP3/Vorbis formats which makes it the preferrable choice for the aforementioned categories of sounds. |
|
| Vorbis/MP3 | The compression results in smaller files but with somewhat lower quality compared to PCM audio. The amount of compression is configurable via the Quality slider. This format is best for medium length sound effects and music. | |
| Sample Rate Setting | PCM and ADPCM compression formats allow automatically optimized or manual sample rate reduction. | |
| Preserve Sample Rate | This setting keeps the sample rate unmodified (default). | |
| Optimize Sample Rate | This setting automatically optimizes the sample rate according to the highest frequency content analyzed. | |
| Override Sample Rate | This setting allows manual overriding of the sample rate, so effectively this might be used to discard frequency content. | |
| Force To Mono | When enabled, the audio clip is down-mixed to a single channel sound. After the down-mixing the signal is peak-normalized, because the down-mixing process typically results in signals that are more quiet than the original. The peak-normalized signal provides headroom for later adjustments through the volume property of AudioSource. | |
| Load In Background | When enabled, the audio clip loads in the background without causing stalls on the main thread. This is disabled by default to ensure the standard Unity behavior where all AudioClips complete loading as soon as the sceneA Scene contains the environments and menus of your game. Think of each unique Scene file as a unique level. In each Scene, you place your environments, obstacles, and decorations, essentially designing and building your game in pieces. More info See in Glossary starts playing. Play requests on AudioClips that are still loading in the background are deferred until the clip is loaded. You can query the load state through the AudioClip.loadState property. |
|
| Preload Audio Data | When enabled, the audio clip is pre-loaded after the scene is loaded. This is enabled by default to reflect standard Unity behavior where all AudioClips complete loading as soon as the scene starts playing. If this flag isn’t set, the audio data will either be loaded on the first AudioSource.Play AudioSource.PlayOneShot, or it can be loaded through AudioClip.LoadAudioData and unloaded again through AudioClip.UnloadAudioData. | |
| Quality | Determines the amount of Compression to be applied to a compressed clip. Doesn’t apply to PCM/ADPCM/HEVAG formats. Statistics about the file size can be seen in the inspector. A good approach to tuning this value is to drag the slider to a place that leaves the playback “good enough” while keeping the file small enough for your distribution requirements. Note that the original size relates to the original file, so if this was an MP3 file and Compression Format is set to PCM (uncompressed), the resulting Ratio will be bigger than 100% because the file is now stored uncompressed and taking up more space than the source MP3 that it came from. | |
Preview Window
The Preview window contains the following icons:
 - When Auto Play is on, the clips play as soon as they’re selected.
- When Auto Play is on, the clips play as soon as they’re selected. - When Loop is on, the clips play in a continuous loop.
- When Loop is on, the clips play in a continuous loop. - Plays the selected clip.
- Plays the selected clip.
If Unity Audio is disabled in Project SettingsA broad collection of settings which allow you to configure how Physics, Audio, Networking, Graphics, Input and many other areas of your project behave. More info
See in Glossary, preview is unavailable.
Importing Audio Assets
Unity supports a wide range of source file formats. Whenever importing a file, Unity transcodes to a format suitable for the build target and the type of sound. You can select this via the Compression Format setting in the inspector.
Typically, the PCM and Vorbis/MP3 formats are preferrable for keeping the sound as close to the original as possible. PCM is lightweight on the CPU requirements, because the sound is uncompressed and can just be read from memory. Vorbis/MP3 allows adaptive discarding with less audible information via the Quality slider.
ADPCM falls between memory and CPU usage as it uses only slightly more CPU than the uncompressed PCM option, but yields a constant 3.5 compression factor, which is in general about 3 times worse than the compression that can be achieved with Vorbis or MP3 compression. Furthermore ADPCM (like PCM) allows automatically optimized or manually set sample rates to be used, which – depending on the frequency content of the sound and the acceptable loss of quality – can further shrink the size of the packed sound assets.
Module files (.mod,.it,.s3m..xm) can deliver high quality with an extremely low footprint. When using module files, unless you specifically want this, make sure that the Load Type is set to Compressed In Memory, because if it’s set to Decompress On Load, the whole song will be decompressed.
As a general rule of thumb, Compressed audio (or modules) are best for long files like background music or dialog, while PCM and ADPCM is better for short sound effects that contain some noise, as the artefacts of ADPCM are too apparent on smooth signals. You should tweak the amount of Compression using the compression slider. Start with high-quality compression and gradually reduce the setting to the point where the loss of sound quality is perceptible. Then, increase it again slightly until the perceived loss of quality disappears.
Platform specific details
- Unity supports importing a variety of source format sound files. However, when importing these files (except tracker files), they’re always re-encoded to the build target format. By default, this format is Vorbis, though this can be overridden per platform to other formats (ADPCM, MP3 etc) if required.
- For audio clip support on Centos 7, make sure you’ve installed the ffmpeg package.
AudioClip