- Unity User Manual (5.6)
- 플랫폼 특정
- Windows
- Windows Store Apps
- 스크립팅 백엔드
- Windows Store: IL2CPP scripting back end
- Windows Store Apps: Debugging on IL2CPP Scripting Backend
Windows Store Apps: Debugging on IL2CPP Scripting Backend
현재로서는 IL2CPP는 C# 디버거를 지원하지 않지만, Visual Studio를 사용하여 생성된 C++ 코드를 디버그할 수 있습니다.
생성된 C++ 코드의 클래스와 메서드 명명법
IL2CPP 클래스의 이름은 <ClassName>_t#number 형식을 가집니다. 여기서 <ClassName>은 클래스 이름이며, #number는 고유 타입 번호입니다. #number는 몇몇 코어 타입에는 없습니다. 아래의 예시를 참조하십시오.
String_t
Object_t
Type_t
Char_t34
StringBuilder_t26
GuidParser_t1539
IL2CPP 메서드의 이름은 <ClassName>_<MethodName>_m#number 형식을 가집니다. 여기서 <ClassName>은 메서드 선언 타입의 클래스 이름이며, <MethodName>은 메서드 이름이고, #number는 고유 메서드 번호입니다. 아래 예제를 참조하십시오.
GuidParser_ParseHex_m10003
ConfigurationSection_DoDeserializeSection_m1275
String_Format_m4102
Mathf_Sqrt_m289
Thing_Start_m1
정적 필드 구조는 <ClassName>_t#number_StaticFields 형식을 가집니다. 여기서 구조 이름의 첫 부분은 선언 타입과 동일합니다. 아래 예제를 참조하십시오.
StringBuilder_t26_StaticFields
Thing_t24_StaticFields
또한 각 클래스와 메서드 정의 위에는 전체 클래스와 메서드의 이름을 명시하는 C++ 코멘트가 있습니다. 아래 예제를 참조하십시오.
// System.String
struct String_t : public Object_t
{
// System.Int32 System.String::length
int32_t **_length_0;
// System.Char System.String::start_char
uint16_t **_start_char_1;
};
// System.Text.StringBuilder
struct StringBuilder_t26 : public Object_t
{
// System.Int32 System.Text.StringBuilder::_length
int32_t ****length_1;
// System.String System.Text.StringBuilder::_str
String_t* ****str_2;
// System.String System.Text.StringBuilder::_cached_str
String_t* ****cached_str_3;
// System.Int32 System.Text.StringBuilder::_maxCapacity
int32_t ****maxCapacity_4;
};
// System.Void MyData::.ctor()
extern "C" void MyData**ctor_m0 (MyData_t2 * **this, const MethodInfo* method)
{
...
}
// Thing
struct Thing_t24 : public MonoBehaviour_t25
{
// MyData Thing::m_Data
MyData_t2 * **_m_Data_2;
// System.Text.StringBuilder Thing::m_Builder
StringBuilder_t26 * **_m_Builder_3;
};
struct Thing_t24_StaticFields
{
// System.Int32 Thing::s_SomeStaticField
int32_t **_s_SomeStaticField_4;
};
변수 값 관측
디버깅의 중요한 부분 중 하나는 다양한 변수의 값을 관측하는 것입니다. Visual Studio를 사용하면 변수 위에 마우스를 올리거나 보기 창에 추가하는 방식으로 간단하게 할 수 있습니다. 아래의 예시를 참조하십시오.
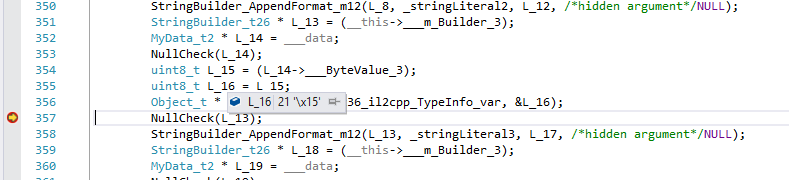
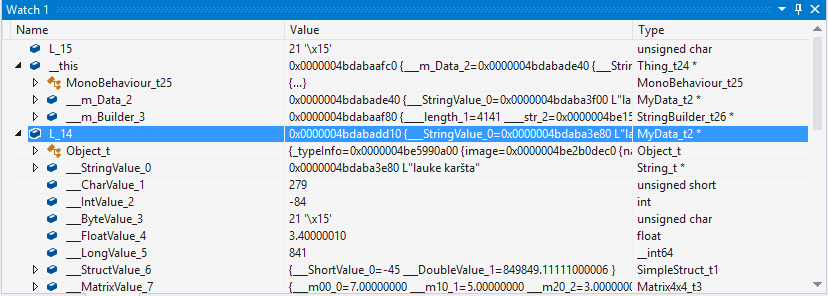
Observing static fields is a little bit harder. In IL2CPP, static fields are stored on a TypeInfo instance itself. So in order to observe a static field, we’ll first need a pointer to TypeInfo structure of that type. These pointers are in scope of methods that use them, but after observing it once, it will remain at the same memory address for the duration of application run. TypeInfo structure has “static_fields” field, which is a pointer to a memory block containing static fields for that particular type. To view the actual values, this pointer has to be cast to appropriate static field structure: each type has its own. For example, let’s observe the static fields of class Thing_t24:

예외 분석
IL2CPP는 .NET 예외를 구현하기 위해 네이티브 C++ 예외를 사용합니다. 예외 오류가 발생하는 경우 IL2CPP는 아래와 같이 정의되는 Il2CppExceptionWrapper 오브젝트를 발생시킵니다.
struct Il2CppExceptionWrapper
{
Il2CppException* ex;
Il2CppExceptionWrapper (Il2CppException* ex) : ex (ex) {}
};
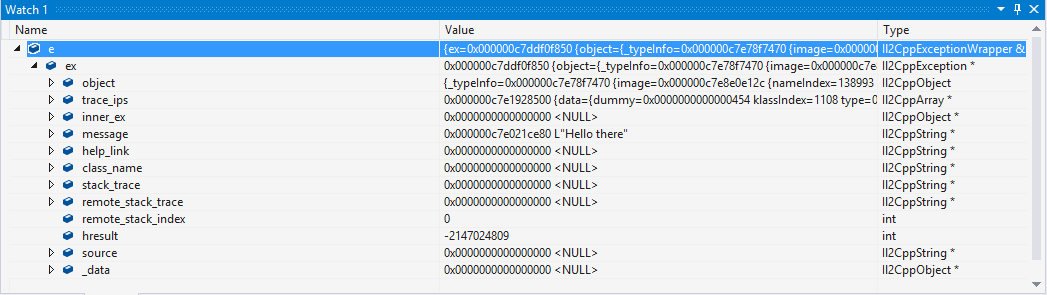
이러한 예외 오브젝트는 보기 창에서 아래와 같이 쉽게 분석할 수 있습니다.
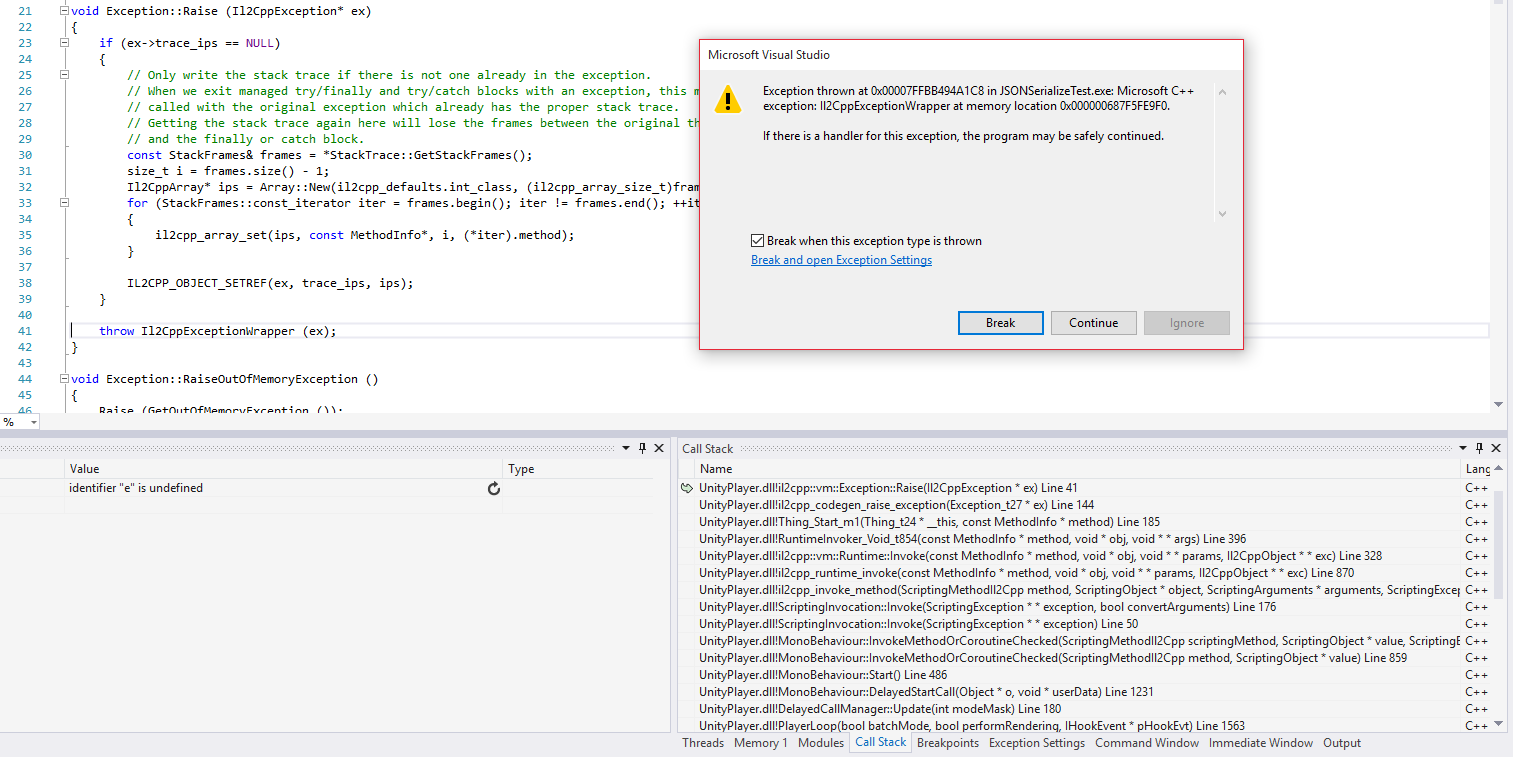
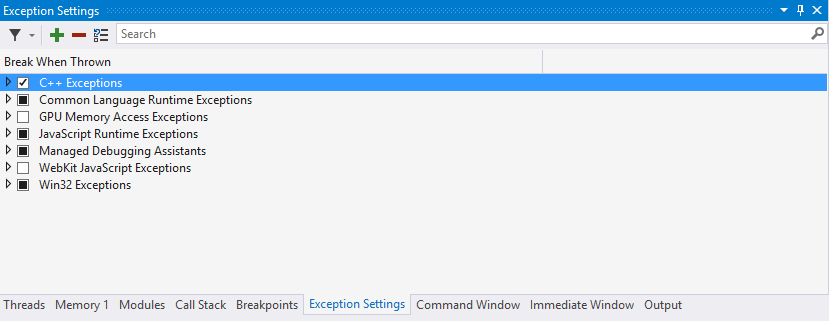
마지막으로 예외가 발생하면 디버거 브레이크를 활성화하는게 도움이 될 수 있습니다. 예외 원인을 바로 파악할 수 있기 때문입니다. Visual Studio에서 CTRL+ALT+E를 누르면 되며, 열린 창에서 C++ 예외 체크박스가 선택되어 있는지 확인해야 합니다.
이 설정을 활성화하면 Visual Studio는 아래와 같이 예외가 발생하면 자동으로 실행을 멈추게 됩니다.