- Unity User Manual (2019.4 LTS)
- Графика
- Камеры
- Dynamic resolution
Dynamic resolution
Dynamic resolution is a Camera setting that allows you to dynamically scale individual render targets, to reduce workload on the GPU. In cases where the application’s frame rate reduces, you can gradually scale down the resolution to maintain a consistent frame rate instead. Unity triggers this scaling if performance data suggests that the frame rate is about to decrease as a result of the application being GPU-bound. You can also trigger the scaling manually by preempting a particularly GPU-intensive section of the application and controlling the scaling via a script. If scaled gradually, dynamic resolution can be almost unnoticeable.
Поддерживаемые платформы Unity supports dynamic resolution on Xbox One, PS4, Nintendo Switch, iOS, macOS and tvOS (Metal only), Android (Vulkan only), Windows Standalone and UWP (DirectX 12 only).
Impact on render targets
With dynamic resolution, Unity does not re-allocate render targets. Conceptually, Unity scales the render target; however, in reality, Unity uses aliasing, and the scaled-down render target only uses a small portion of the original render target. Unity allocates the render targets at their full resolution, and then the dynamic resolution system scales them down and back up again, using a portion of the original target instead of re-allocating a new target.
Scaling render targets
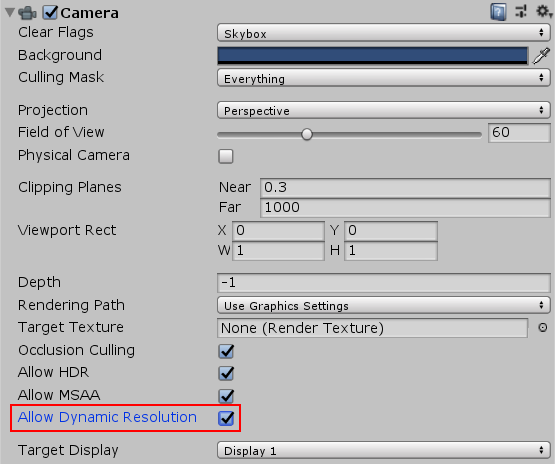
With dynamic resolution, render targets have the DynamicallyScalable flag. You can set this to state whether Unity should scale this render texture as part of the dynamic resolution process or not. Cameras also have the allowDynamicResolution flag, which you can use to set up dynamic resolution so that there is no need to override the render target if you just want to apply dynamic resolution to a less complex Scene.
MRT buffers
When you enable Allow Dynamic Resolution on the Camera, Unity scales all of that Camera’s targets.
Controlling the scaling
You can control the scale through the ScalableBufferManager. The ScalableBufferManager gives you control of the dynamic width and height scale for all render targets you have marked for the dynamic resolution system to scale.
As an example, assume your application is running at a desirable frame rate, but under some circumstances the GPU performance decreases, due to a combination of increased particles, post-effects and screen complexity. The Unity FrameTimingManager allows you to detect when the CPU or GPU performance start to decrease. So you can use the FrameTimingManager to calculate a new desired width and height scale to keep the frame rate within your desired range, and bring the scale down to that value to keep performance stable (either instantly or gradually over a set amount of frames). When the screen complexity reduces and the GPU is performing consistently, you may then raise the width and height scale back to a value that you’ve calculated the GPU can handle.
Пример
This example script demonstrates basic use of the API. Add it to a Camera in your Scene, and check Allow Dynamic Resolution in the Camera settings. You also need to open the Player settings (menu: Edit > Project Settings, then select the Player category) and check the Enable Frame Timing Stats checkbox.
Clicking the mouse, or tapping the screen with one finger, lowers the height and width resolution by the amount in the scaleWidthIncrement and scaleHeightIncrement variables respectively. Tapping with two fingers raises the resolutions by the same increment.
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using UnityEngine;
using UnityEngine.UI;
public class DynamicResolutionTest : MonoBehaviour
{
public Text screenText;
FrameTiming[] frameTimings = new FrameTiming[3];
public float maxResolutionWidthScale = 1.0f;
public float maxResolutionHeightScale = 1.0f;
public float minResolutionWidthScale = 0.5f;
public float minResolutionHeightScale = 0.5f;
public float scaleWidthIncrement = 0.1f;
public float scaleHeightIncrement = 0.1f;
float m_widthScale = 1.0f;
float m_heightScale = 1.0f;
// Variables for dynamic resolution algorithm that persist across frames
uint m_frameCount = 0;
const uint kNumFrameTimings = 2;
double m_gpuFrameTime;
double m_cpuFrameTime;
// Use this for initialization
void Start()
{
int rezWidth = (int)Mathf.Ceil(ScalableBufferManager.widthScaleFactor * Screen.currentResolution.width);
int rezHeight = (int)Mathf.Ceil(ScalableBufferManager.heightScaleFactor * Screen.currentResolution.height);
screenText.text = string.Format("Scale: {0:F3}x{1:F3}\nResolution: {2}x{3}\n",
m_widthScale,
m_heightScale,
rezWidth,
rezHeight);
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
float oldWidthScale = m_widthScale;
float oldHeightScale = m_heightScale;
// One finger lowers the resolution
if (Input.GetButtonDown("Fire1"))
{
m_heightScale = Mathf.Max(minResolutionHeightScale, m_heightScale - scaleHeightIncrement);
m_widthScale = Mathf.Max(minResolutionWidthScale, m_widthScale - scaleWidthIncrement);
}
// Two fingers raises the resolution
if (Input.GetButtonDown("Fire2"))
{
m_heightScale = Mathf.Min(maxResolutionHeightScale, m_heightScale + scaleHeightIncrement);
m_widthScale = Mathf.Min(maxResolutionWidthScale, m_widthScale + scaleWidthIncrement);
}
if (m_widthScale != oldWidthScale || m_heightScale != oldHeightScale)
{
ScalableBufferManager.ResizeBuffers(m_widthScale, m_heightScale);
}
DetermineResolution();
int rezWidth = (int)Mathf.Ceil(ScalableBufferManager.widthScaleFactor * Screen.currentResolution.width);
int rezHeight = (int)Mathf.Ceil(ScalableBufferManager.heightScaleFactor * Screen.currentResolution.height);
screenText.text = string.Format("Scale: {0:F3}x{1:F3}\nResolution: {2}x{3}\nScaleFactor: {4:F3}x{5:F3}\nGPU: {6:F3} CPU: {7:F3}",
m_widthScale,
m_heightScale,
rezWidth,
rezHeight,
ScalableBufferManager.widthScaleFactor,
ScalableBufferManager.heightScaleFactor,
m_gpuFrameTime,
m_cpuFrameTime);
}
// Estimate the next frame time and update the resolution scale if necessary.
private void DetermineResolution()
{
++m_frameCount;
if (m_frameCount <= kNumFrameTimings)
{
return;
}
FrameTimingManager.CaptureFrameTimings();
FrameTimingManager.GetLatestTimings(kNumFrameTimings, frameTimings);
if (frameTimings.Length < kNumFrameTimings)
{
Debug.LogFormat("Skipping frame {0}, didn't get enough frame timings.",
m_frameCount);
return;
}
m_gpuFrameTime = (double)frameTimings[0].gpuFrameTime;
m_cpuFrameTime = (double)frameTimings[0].cpuFrameTime;
}
}
Смотрите так же
- FrameTimingManager scripting class reference.
- ScalableBufferManager scripting class reference.
2018–09–20 Page published
Documentation on dynamic resolution added in 2017.4
Dynamic Resolution support for macOS (Metal only), Windows Standalone and UWP (DirectX 12 only) added in 2019.1