Inserting clips
The TimelineGeneric term within Unity that refers to all features, windows, editors, and components related to creating, modifying, or reusing cut-scenes, cinematics, and game-play sequences. More info
See in Glossary window supports different methods of inserting clips depending on the type of track, where you click, and whether a clip or track is already selected. In the Timeline window, inserting clips refers to adding and making space for a clip without blending or replacing intersecting clips.
To accurately insert a clip, select Ripple mode as the Clip Edit mode, and position the Timeline PlayheadThe white marker and line that indicates the exact point in time being previewed in the Timeline Editor window. More info
See in Glossary to set the insertion point. Select Add From Animation ClipAnimation data that can be used for animated characters or simple animations. It is a simple “unit” piece of motion, such as (one specific instance of) “Idle”, “Walk” or “Run”. More info
See in Glossary from the Track menu for the track where you want to insert the clip.
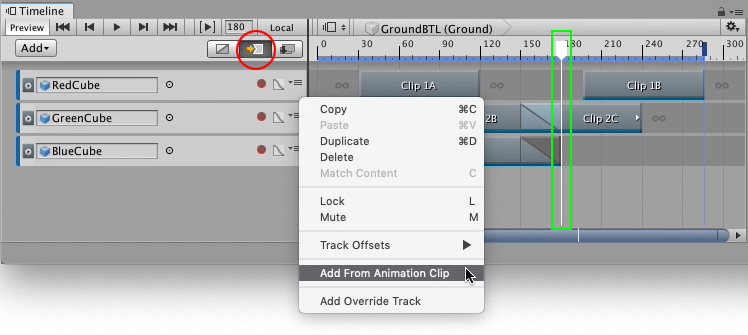
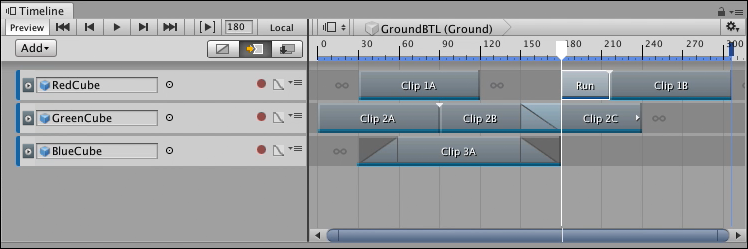
In the above example, the Timeline Playhead is the insertion point. You can specify the insertion point using these other methods:
Right-click within a gap and add a clip with the context menu. The insertion point is where you right-click.
Drag a Source AssetAny media or data that can be used in your game or Project. An asset may come from a file created outside of Unity, such as a 3D model, an audio file or an image. You can also create some asset types in Unity, such as an Animator Controller, an Audio Mixer or a Render Texture. More info
See in Glossary (animation or audio) to a track in the Clips viewThe area in the Timeline Editor window where you add, position, and manipulate clips. More info
See in Glossary. The insertion point is where you stop dragging.
The location of the insertion point determines where the clip is inserted and how it affects the other clips and gaps on the same track:
If the insertion point intersects a clip, the inserted clip is added at the insertion point. The intersected clip, and all subsequent clips and gaps, are rippled after the inserted clip.
If the insertion point is within a gap and there is enough space between the insertion point and the next clip, then the inserted clip is added to the gap. The other clips on the track are not affected.
If the insertion point is within a gap and the inserted clip overlaps the next clip, the inserted clips is added at the insertion point. The next clip, and all subsequent clips and gaps, are rippled to accommodate the inserted clip.
- 2019–08–20 Page published