Manual
- Unity User Manual (2018.3)
- Working in Unity
- Getting Started
- Unity Hub
- Installing Unity using the Hub
- Adding components to the Unity Editor
- Installing Unity without the hub
- Installing Unity offline without the Hub
- Unity Hub advanced deployment considerations
- 2D or 3D projects
- Project Templates
- Starting Unity for the first time
- Opening existing Projects
- Learning the interface
- Asset Workflow
- The Main Windows
- Creating Gameplay
- Editor Features
- 고급 개발
- 고급 에디터 토픽
- Licenses and Activation
- Upgrade Guides
- Using the Automatic API Updater
- Upgrading to Unity 2018.3
- Upgrading to Unity 2018.2
- Upgrading to Unity 2018.1
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.3
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.2
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.1
- Upgrading to Unity 5.6
- Upgrading to Unity 5.5
- Upgrading to Unity 5.4
- Upgrading to Unity 5.3
- Upgrading to Unity 5.2
- Upgrading to Unity 5.0
- Upgrading to Unity 4.0
- Upgrading to Unity 3.5
- Getting Started
- Importing
- 2D
- Gameplay in 2D
- 2D Sorting
- Sprites
- Tilemap
- Physics Reference 2D
- Graphics
- Graphics Overview
- Lighting
- Lighting overview
- Lighting Window
- Light Explorer
- Light sources
- Shadows
- Global Illumination
- Lightmapping
- Lightmap Parameters
- Baked ambient occlusion
- LOD for baked lightmaps
- Light Probes
- Reflection probes
- Lighting Modes
- GI visualizations in the Scene view
- Lighting Data Asset
- Lightmap Directional Modes
- Lightmaps: Technical information
- Material properties and the GI system
- Global Illumination UVs
- GI cache
- Light troubleshooting and performance
- Related topics
- Cameras
- Materials, Shaders & Textures
- Textures
- Creating and Using Materials
- Standard Shader
- Standard Particle Shaders
- Physically Based Rendering Material Validator
- Accessing and Modifying Material parameters via script
- Writing Shaders
- Legacy Shaders
- Video overview
- Terrain Engine
- Tree Editor
- Particle Systems
- Post-processing overview
- Advanced Rendering Features
- Procedural Mesh Geometry
- Optimizing graphics performance
- Layers
- Lighting
- Graphics Reference
- Cameras Reference
- Shader Reference
- Writing Surface Shaders
- Writing vertex and fragment shaders
- Vertex and fragment shader examples
- Shader semantics
- Accessing shader properties in Cg/HLSL
- Providing vertex data to vertex programs
- Built-in shader include files
- Predefined Shader preprocessor macros
- Built-in shader helper functions
- Built-in shader variables
- Making multiple shader program variants
- GLSL Shader programs
- Shading Language used in Unity
- Shader Compilation Target Levels
- Shader data types and precision
- Using sampler states
- ShaderLab Syntax
- Shader assets
- Advanced ShaderLab topics
- Unity's Rendering Pipeline
- Performance tips when writing shaders
- Rendering with Replaced Shaders
- Custom Shader GUI
- Using Depth Textures
- Camera's Depth Texture
- Platform-specific rendering differences
- Shader Level of Detail
- Texture arrays
- Debugging DirectX 11/12 shaders with Visual Studio
- Debugging DirectX 12 shaders with PIX
- Implementing Fixed Function TexGen in Shaders
- Particle Systems reference
- Particle System
- Particle System modules
- Particle System Main module
- Emission module
- Shape Module
- Velocity over Lifetime module
- Noise module
- Limit Velocity Over Lifetime module
- Inherit Velocity module
- Force Over Lifetime module
- Color Over Lifetime module
- Color By Speed module
- Size over Lifetime module
- Size by Speed module
- Rotation Over Lifetime module
- Rotation By Speed module
- External Forces module
- Collision module
- Triggers module
- Sub Emitters module
- Texture Sheet Animation module
- Lights module
- Trails module
- Custom Data module
- Renderer module
- Particle System Force Field
- Particle Systems (Legacy, prior to release 3.5)
- Visual Effects Reference
- Mesh Components
- Texture Components
- Rendering Components
- Rendering Pipeline Details
- Graphics HOWTOs
- How do I Import Alpha Textures?
- How do I Make a Skybox?
- How do I make a Mesh Particle Emitter? (Legacy Particle System)
- How do I make a Spot Light Cookie?
- How do I fix the rotation of an imported model?
- Water in Unity
- Art Asset best practice guide
- Importing models from 3D modeling software
- How to do Stereoscopic Rendering
- Graphics Tutorials
- Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Graphics Overview
- Physics
- Scripting
- Scripting Overview
- Creating and Using Scripts
- Variables and the Inspector
- Controlling GameObjects using components
- Event Functions
- Time and Framerate Management
- Creating and Destroying GameObjects
- Coroutines
- Namespaces
- Attributes
- Order of Execution for Event Functions
- Understanding Automatic Memory Management
- Platform dependent compilation
- Special folders and script compilation order
- Script compilation and assembly definition files
- Managed code stripping
- .NET profile support
- Referencing additional class library assemblies
- Stable scripting runtime: known limitations
- Generic Functions
- Scripting restrictions
- Script Serialization
- UnityEvents
- What is a Null Reference Exception?
- Important Classes
- Vector Cookbook
- Scripting Tools
- Event System
- C# Job System
- Scripting Overview
- Multiplayer and Networking
- Multiplayer Overview
- Setting up a multiplayer project
- Using the Network Manager
- Using the Network Manager HUD
- The Network Manager HUD in LAN mode
- The Network Manager HUD in Matchmaker mode
- Converting a single-player game to Unity Multiplayer
- Debugging Information
- The Multiplayer High Level API
- Multiplayer Component Reference
- Multiplayer Classes Reference
- UnityWebRequest
- Audio
- Audio Overview
- Audio files
- Tracker Modules
- Audio Mixer
- Native Audio Plugin SDK
- Audio Profiler
- 앰비소닉 오디오
- Audio Reference
- Audio Clip
- Audio Listener
- Audio Source
- Audio Mixer
- Audio Filters
- Audio Effects
- Audio Low Pass Effect
- Audio High Pass Effect
- Audio Echo Effect
- Audio Flange Effect
- Audio Distortion Effect
- Audio Normalize Effect
- Audio Parametric Equalizer Effect
- Audio Pitch Shifter Effect
- Audio Chorus Effect
- Audio Compressor Effect
- Audio SFX Reverb Effect
- Audio Low Pass Simple Effect
- Audio High Pass Simple Effect
- Reverb Zones
- Microphone
- Audio Settings
- Animation
- Animation System Overview
- Animation Clips
- Animator Controllers
- Retargeting of Humanoid animations
- Performance and optimization
- Animation Reference
- Animation FAQ
- Playables API
- A Glossary of animation terms
- Timeline
- UI
- Navigation and Pathfinding
- Navigation Overview
- Navigation System in Unity
- Inner Workings of the Navigation System
- Building a NavMesh
- NavMesh building components
- Advanced NavMesh Bake Settings
- Creating a NavMesh Agent
- Creating a NavMesh Obstacle
- Creating an Off-mesh Link
- Building Off-Mesh Links Automatically
- Building Height Mesh for Accurate Character Placement
- Navigation Areas and Costs
- Loading Multiple NavMeshes using Additive Loading
- Using NavMesh Agent with Other Components
- Navigation Reference
- Navigation How-Tos
- Navigation Overview
- Unity Services
- Setting up your project for Unity Services
- Unity Organizations
- Unity Ads
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Analytics Overview
- Setting Up Analytics
- Analytics Dashboard
- Analytics events
- Funnels
- Remote Settings
- Unity Analytics A/B Testing
- Monetization
- User Attributes
- Unity Analytics Raw Data Export
- Data reset
- Upgrading Unity Analytics
- COPPA Compliance
- Unity Analytics and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Analytics Metrics, Segments, and Terminology
- Unity Cloud Build
- Automated Build Generation
- Supported platforms
- Supported versions of Unity
- Version control systems
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Using Apache Subversion (SVN) with Unity Cloud Build
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Perforce
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Perforce
- Building for iOS
- Advanced options
- Build manifest
- Cloud Build REST API
- Unity IAP
- Setting up Unity IAP
- Cross Platform Guide
- Codeless IAP
- Defining products
- Subscription Product support
- Initialization
- Browsing Product Metadata
- Initiating Purchases
- Processing Purchases
- Handling purchase failures
- Restoring Transactions
- Purchase Receipts
- Receipt validation
- Store Extensions
- Cross-store installation issues with Android in-app purchase stores
- Store Guides
- Implementing a Store
- IAP Promo
- Unity Collaborate
- Setting up Unity Collaborate
- Adding team members to your Unity Project
- Viewing history
- Enabling Cloud Build with Collaborate
- Managing Unity Editor versions
- Reverting files
- Resolving file conflicts
- Excluding Assets from publishing to Collaborate
- Publishing individual files to Collaborate
- Restoring previous versions of a project
- In-Progress edit notifications
- Managing cloud storage
- Moving your Project to another version control system
- Collaborate troubleshooting tips
- Unity Cloud Diagnostics
- Unity Integrations
- Multiplayer Services
- XR
- XR SDKs
- Google VR
- Vuforia
- Windows Mixed Reality
- Unity XR input
- XR API reference
- Mixed Reality Devices
- VR overview
- VR devices
- Single Pass Stereo rendering (Double-Wide rendering)
- VR Audio Spatializers
- VR frame timing
- XR SDKs
- Open-source repositories
- Asset Store Publishing
- Platform-specific
- Standalone
- macOS
- Apple TV
- WebGL
- Player settings for the WebGL platform
- Getting started with WebGL development
- WebGL Browser Compatibility
- Building and running a WebGL project
- WebGL: Deploying compressed builds
- Debugging and troubleshooting WebGL builds
- WebGL Graphics
- WebGL Networking
- Using Audio In WebGL
- WebGL performance considerations
- Memory in WebGL
- WebGL: Interacting with browser scripting
- Using WebGL Templates
- Cursor locking and full-screen mode in WebGL
- Input in WebGL
- iOS
- Getting started with iOS development
- Player settings for the iOS platform
- iOS 2D Texture Overrides
- Upgrading to 64-bit iOS
- iOS Advanced Topics
- Features currently not supported by Unity iOS
- Troubleshooting on iOS devices
- Reporting crash bugs on iOS
- Android
- Android용 개발 시작
- Player settings for the Android platform
- Android 2D Textures Overrides
- Android용 Gradle
- Android 매니페스트
- Windows
- Windows General
- Universal Windows Platform
- Getting Started
- Universal Windows Platform: Deployment
- Universal Windows Platform: Profiler
- Universal Windows Platform: Command line arguments
- Universal Windows Platform: Association launching
- AppCallbacks class
- Universal Windows Platform: WinRT API in C# scripts
- Player settings for the Universal Windows platform
- Scripting Backends
- FAQ
- Universal Windows Platform: Examples
- Universal Windows Platform: Code snippets
- Known issues
- Web Player
- Mobile Developer Checklist
- Experimental
- Legacy Topics
- Best practice guides
- Expert guides
- New in Unity 2018.3
- Packages Documentation
- Glossary
Camera
Cameras are the devices that capture and display the world to the player. By customizing and manipulating cameras, you can make the presentation of your game truly unique. You can have an unlimited number of cameras in a scene. They can be set to render in any order, at any place on the screen, or only certain parts of the screen.
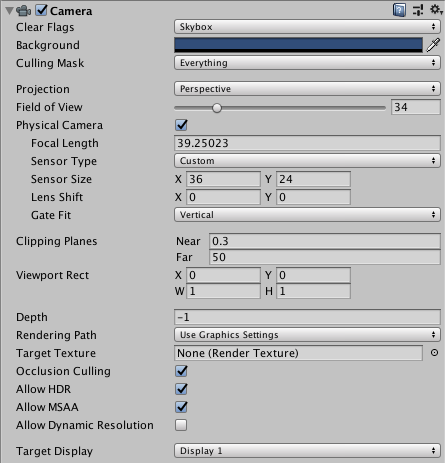
Properties
| Property: | Function: |
|---|---|
| Clear Flags | Determines which parts of the screen will be cleared. This is handy when using multiple Cameras to draw different game elements. |
| Background | The color applied to the remaining screen after all elements in view have been drawn and there is no skybox. |
| Culling Mask | Includes or omits layers of objects to be rendered by the Camera. Assigns layers to your objects in the Inspector. |
| Projection | Toggles the camera’s capability to simulate perspective. |
| Perspective | Camera will render objects with perspective intact. |
| Orthographic | Camera will render objects uniformly, with no sense of perspective. NOTE: Deferred rendering is not supported in Orthographic mode. Forward rendering is always used. |
| Size (when Orthographic is selected) | The viewport size of the Camera when set to Orthographic. |
| Field of view (when Perspective is selected) | The width of the Camera’s view angle, measured in degrees along the local Y axis. |
| Physical Camera | Tick this box to enable the Physical Camera properties for this camera. When the Physical Camera properties are enabled, Unity calculates the Field of View using the properties that simulate real-world camera attributes: Focal Length, Sensor Size, and Lens Shift. Physical Camera properties are not visible in the Inspector until you tick this box. |
| Focal Length | Set the distance, in millimeters, between the camera sensor and the camera lens. Lower values result in a wider Field of View, and vice versa. When you change this value, Unity automatically updates the Field of View property accordingly. |
| Sensor Type | Specify the real-world camera format you want the camera to simulate. Choose the desired format from the list. When you choose a camera format, Unity sets the the Sensor Size > X and Y properties to the correct values automatically. If you change the Sensor Size values manually, Unity automatically sets this property to Custom. |
| Sensor Size | Set the size, in millimeters, of the camera sensor. Unity sets the X and Y values automatically when you choose the Sensor Type. You can enter custom values if needed. |
| X | The width of the sensor. |
| Y | The height of the sensor. |
| Lens Shift | Shift the lens horizontally or vertically from center. Values are multiples of the sensor size; for example, a shift of 0.5 along the X axis offsets the sensor by half its horizontal size. You can use lens shifts to correct distortion that occurs when the camera is at an angle to the subject (for example, converging parallel lines). Shift the lens along either axis to make the camera frustum oblique. |
| X | The horizontal sensor offset. |
| Y | The vertical sensor offset. |
| Gate Fit | Options for changing the size of the resolution gate (size/aspect ratio of the game view) relative to the film gate (size/aspect ratio of the Physical Camera sensor). For further information about resolution gate and film gate, see documentation on Physical Cameras. |
| Vertical | Fits the resolution gate to the height of the film gate. If the sensor aspect ratio is larger than the game view aspect ratio, Unity crops the rendered image at the sides. If the sensor aspect ratio is smaller than the game view aspect ratio, Unity overscans the rendered image at the sides. When you choose this setting, changing the sensor width (Sensor Size > X property) has no effect on the rendered image. |
| Horizontal | Fits the resolution gate to the width of the film gate. If the sensor aspect ratio is larger than the game view aspect ratio, Unity overscans the rendered image on the top and bottom. If the sensor aspect ratio is smaller than the game view aspect ratio, Unity crops the rendered image on the top and bottom. When you choose this setting, changing the sensor height (Sensor Size > Y property) has no effect on the rendered image. |
| Fill | Fits the resolution gate to either the width or height of the film gate, whichever is smaller. This crops the rendered image. |
| Overscan | Fits the resolution gate to either the width or height of the film gate, whichever is larger. This overscans the rendered image. |
| None | Ignores the resolution gate and uses the film gate only. This stretches the rendered image to fit the game view aspect ratio. |
| Clipping Planes | Distances from the camera to start and stop rendering. |
| Near | The closest point relative to the camera that drawing will occur. |
| Far | The furthest point relative to the camera that drawing will occur. |
| Viewport Rect | Four values that indicate where on the screen this camera view will be drawn. Measured in Viewport Coordinates (values 0–1). |
| X | The beginning horizontal position that the camera view will be drawn. |
| Y | The beginning vertical position that the camera view will be drawn. |
| W (Width) | Width of the camera output on the screen. |
| H (Height) | Height of the camera output on the screen. |
| Depth | The camera’s position in the draw order. Cameras with a larger value will be drawn on top of cameras with a smaller value. |
| Rendering Path | Options for defining what rendering methods will be used by the camera. |
| Use Player Settings | This camera will use whichever Rendering Path is set in the Player Settings. |
| Vertex Lit | All objects rendered by this camera will be rendered as Vertex-Lit objects. |
| Forward | All objects will be rendered with one pass per material. |
| Deferred Lighting | All objects will be drawn once without lighting, then lighting of all objects will be rendered together at the end of the render queue. NOTE: If the camera’s projection mode is set to Orthographic, this value is overridden, and the camera will always use Forward rendering. |
| Target Texture | Reference to a Render Texture that will contain the output of the Camera view. Setting this reference will disable this Camera’s capability to render to the screen. |
| Occlusion Culling | Enables High Dynamic Range rendering for this camera. See Occlusion Culling for details |
| Allow HDR | Enables High Dynamic Range rendering for this camera. See High Dynamic Range Rendering for details. |
| Allow MSAA | Enables multi sample antialiasing for this camera. |
| Allow Dynamic Resolution | Enables Dynamic Resolution rendering for this camera. See Dynamic Resolution for details. |
| Target Display | Defines which external device to render to. Between 1 and 8. |
Details
Cameras are essential for displaying your game to the player. They can be customized, scripted, or parented to achieve just about any kind of effect imaginable. For a puzzle game, you might keep the Camera static for a full view of the puzzle. For a first-person shooter, you would parent the Camera to the player character, and place it at the character’s eye level. For a racing game, you’d probably have the Camera follow your player’s vehicle.
You can create multiple Cameras and assign each one to a different Depth. Cameras are drawn from low Depth to high Depth. In other words, a Camera with a Depth of 2 will be drawn on top of a Camera with a depth of 1. You can adjust the values of the Normalized View Port Rectangle property to resize and position the Camera’s view onscreen. This can create multiple mini-views like missile cams, map views, rear-view mirrors, etc.
Render path
Unity supports different rendering paths. You should choose which one you use depending on your game content and target platform / hardware. Different rendering paths have different features and performance characteristics that mostly affect lights and shadows. The rendering path used by your Project is chosen in the Player settings. Additionally, you can override it for each Camera.
For more information on rendering paths, check the rendering paths page.
Clear Flags
Each Camera stores color and depth information when it renders its view. The portions of the screen that are not drawn in are empty, and will display the skybox by default. When you are using multiple Cameras, each one stores its own color and depth information in buffers, accumulating more data as each Camera renders. As any particular Camera in your scene renders its view, you can set the Clear Flags to clear different collections of the buffer information. To do this, choose one of the following four options:
Skybox
This is the default setting. Any empty portions of the screen will display the current Camera’s skybox. If the current Camera has no skybox set, it will default to the skybox chosen in the Lighting Window (menu: Window > Rendering > Lighting Settings). It will then fall back to the Background Color. Alternatively a Skybox component can be added to the camera. If you want to create a new Skybox, you can use this guide.
Solid color
Any empty portions of the screen will display the current Camera’s Background Color.
Depth only
If you want to draw a player’s gun without letting it get clipped inside the environment, set one Camera at Depth 0 to draw the environment, and another Camera at Depth 1 to draw the weapon alone. Set the weapon Camera’s Clear Flags to depth only. This will keep the graphical display of the environment on the screen, but discard all information about where each object exists in 3-D space. When the gun is drawn, the opaque parts will completely cover anything drawn, regardless of how close the gun is to the wall.
Don’t clear
This mode does not clear either the color or the depth buffer. The result is that each frame is drawn over the next, resulting in a smear-looking effect. This isn’t typically used in games, and would more likely be used with a custom shader.
Note that on some GPUs (mostly mobile GPUs), not clearing the screen might result in the contents of it being undefined in the next frame. On some systems, the screen may contain the previous frame image, a solid black screen, or random colored pixels.
Clip Planes
The Near and Far Clip Plane properties determine where the Camera’s view begins and ends. The planes are laid out perpendicular to the Camera’s direction and are measured from its position. The Near plane is the closest location that will be rendered, and the Far plane is the furthest.
The clipping planes also determine how depth buffer precision is distributed over the scene. In general, to get better precision you should move the Near plane as far as possible.
Note that the near and far clip planes together with the planes defined by the field of view of the camera describe what is popularly known as the camera frustum. Unity ensures that when rendering your objects those which are completely outside of this frustum are not displayed. This is called Frustum Culling. Frustum Culling happens irrespective of whether you use Occlusion Culling in your game.
For performance reasons, you might want to cull small objects earlier. For example, small rocks and debris could be made invisible at much smaller distance than large buildings. To do that, put small objects into a separate layer and set up per-layer cull distances using Camera.layerCullDistances script function.
Culling Mask
The Culling Mask is used for selectively rendering groups of objects using Layers. More information on using layers can be found here.
Normalized Viewport Rectangles
Normalized Viewport Rectangle is specifically for defining a certain portion of the screen that the current camera view will be drawn upon. You can put a map view in the lower-right hand corner of the screen, or a missile-tip view in the upper-left corner. With a bit of design work, you can use Viewport Rectangle to create some unique behaviors.
It’s easy to create a two-player split screen effect using Normalized Viewport Rectangle. After you have created your two cameras, change both camera’s H values to be 0.5 then set player one’s Y value to 0.5, and player two’s Y value to 0. This will make player one’s camera display from halfway up the screen to the top, and player two’s camera start at the bottom and stop halfway up the screen.

Orthographic
Marking a Camera as Orthographic removes all perspective from the Camera’s view. This is mostly useful for making isometric or 2D games.
Note that fog is rendered uniformly in orthographic camera mode and may therefore not appear as expected. This is because the Z coordinate of the post-perspective space is used for the fog “depth”. This is not strictly accurate for an orthographic camera but it is used for its performance benefits during rendering.
Render Texture
This will place the camera’s view onto a Texture that can then be applied to another object. This makes it easy to create sports arena video monitors, surveillance cameras, reflections etc.
Target display
A camera has up to 8 target display settings. The camera can be controlled to render to one of up to 8 monitors. This is supported only on PC, Mac and Linux. In Game View the chosen display in the Camera Inspector will be shown.
Hints
- Cameras can be instantiated, parented, and scripted just like any other GameObject.
- To increase the sense of speed in a racing game, use a high Field of View.
- Cameras can be used in physics simulation if you add a Rigidbody Component.
- There is no limit to the number of Cameras you can have in your scenes.
- Orthographic cameras are great for making 3D user interfaces.
- If you are experiencing depth artifacts (surfaces close to each other flickering), try setting Near Plane to as large as possible.
- Cameras cannot render to the Game Screen and a Render Texture at the same time, only one or the other.
- There’s an option of rendering a Camera’s view to a texture, called Render-to-Texture, for even more interesting effects.
- Unity comes with pre-installed Camera scripts, found in Components > Camera Control. Experiment with them to get a taste of what’s possible.
- 2018–10–05 Page amended with limited editorial review
- Physical Camera options added in Unity 2018.2
- Gate Fit options added in Unity 2018.3