Manual
- Unity User Manual (2019.4 LTS)
- Packages
- Verified packages
- 2D Animation
- 2D Common
- 2D Path
- 2D Pixel Perfect
- 2D PSD Importer
- 2D SpriteShape
- Adaptive Performance
- Adaptive Performance Samsung Android
- Addressables
- Advertisement
- Alembic
- Analytics Library
- Android Logcat
- AR Foundation
- AR Subsystems
- ARCore XR Plugin
- ARKit Face Tracking
- ARKit XR Plugin
- Asset Bundle Browser
- Barracuda
- Burst
- Core RP Library
- Custom NUnit
- Editor Coroutines
- Google Resonance Audio
- Google VR Android
- Google VR iOS
- High Definition RP
- High Definition RP Config
- In App Purchasing
- Input System
- Lightweight RP
- Magic Leap XR Plugin
- Mathematics
- Mobile Notifications
- Multiplayer HLAPI
- Oculus Android
- Oculus Desktop
- Oculus XR Plugin
- OpenVR Desktop
- Polybrush
- Post Processing
- ProBuilder
- Profile Analyzer
- Quick Search
- Remote Config
- Scriptable Build Pipeline
- Searcher
- Settings Manager
- Shader Graph
- Subsystem Registration
- Test Framework
- TextMesh Pro
- Timeline
- Unity Collaborate
- Universal RP
- Visual Effect Graph
- Vuforia Engine AR
- Windows Mixed Reality
- Windows XR Plugin
- XR Interaction Subsystems
- XR Legacy Input Helpers
- XR Plugin Management
- Preview packages
- 2D Entities
- 2D IK
- AI Planner
- Animation Rigging
- Asset Graph
- Build Report Inspector
- Cinemachine
- Code Coverage
- Collections
- Device Simulator
- DOTS Editor
- Entities
- FBX Exporter
- Film and TV Toolbox
- Game Foundation
- Havok Physics for Unity
- Hybrid Renderer
- Immediate Window
- Jobs
- Kinematica
- Область Memory
- MeshSync
- ML Agents
- MockHMD XR Plugin
- Package Development
- Package Validation Suite
- Performance testing API
- Platforms
- Platforms Android
- Platforms Linux
- Platforms macOS
- Platforms Web
- Platforms Windows
- PlayableGraph Visualizer
- ProGrids
- Project Tiny Full
- Streaming Image Sequence
- Terrain Tools
- UI Builder
- Unity AOV Recorder
- Unity Distribution Portal
- Unity NetCode
- Unity Physics
- Unity Recorder
- Unity Reflect
- Unity Render Streaming
- Unity Simulation Client
- Unity Simulation Core
- Unity Transport
- Unity User Reporting
- USD
- Vector Graphics
- WebGL Publisher
- WebRTC
- Xiaomi SDK
- XR Interaction Toolkit
- Built-in packages
- 2D Sprite
- 2D Tilemap Editor
- AI
- Android JNI
- Animation
- Asset Bundle
- Audio
- Cloth
- Director
- Image Conversion
- IMGUI
- JSONSerialize
- Particle System
- Physics
- Physics 2D
- Screen Capture
- Subsystems
- Terrain
- Terrain Physics
- Tilemap
- UI
- UIElements
- Umbra
- Unity Analytics
- Unity UI
- Unity Web Request
- Unity Web Request Asset Bundle
- Unity Web Request Audio
- Unity Web Request Texture
- Unity Web Request WWW
- Vehicles
- Video
- VR
- Wind
- XR
- Packages by keywords
- Unity's Package Manager
- Creating custom packages
- Verified packages
- New in Unity 2019
- Working in Unity
- Installing Unity
- Unity's interface
- Asset workflow
- Создание геймплея.
- Editor Features
- 2D and 3D mode settings
- Preferences
- Presets
- Shortcuts Manager
- Build Settings
- Project Settings
- Visual Studio C# integration
- RenderDoc Integration
- Xcode Frame Debugger integration
- Editor Analytics
- Проверка обновлений
- IME в Unity
- Специальные Папки Проекта
- Reusing Assets between Projects
- Version Control
- Multi-Scene editing
- Command line arguments
- Support for custom Menu Item and Editor features
- Text-Based Scene Files
- Расширение редактора
- Configurable Enter Play Mode
- Решение проблем в редакторе
- Analysis
- Profiler overview
- Getting started with the Profiler window
- Profiling your application
- Audio Profiler module
- CPU Usage Profiler module
- Global Illumination Profiler module
- GPU Usage Profiler module
- Memory Profiler module
- Physics Profiler module
- 2D Physics Profiler module
- Область Rendering
- UI and UI Details Profiler
- Video Profiler module
- Profiler overview
- Upgrade Guides
- Using the API Updater
- Upgrading to Unity 2019 LTS
- Upgrading to Unity 2018 LTS
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.3
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.2
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.1
- Upgrading to Unity 5.6
- Upgrading to Unity 5.5
- Upgrading to Unity 5.4
- Upgrading to Unity 5.3
- Upgrading to Unity 5.2
- Upgrading to Unity 5.0
- Руководство по обновлению до Unity 4.0
- Обновление до Unity 3.5
- Importing
- Input
- 2D
- Геймплей в 2D
- 2D Sorting
- Sprites
- Tilemap
- Physics Reference 2D
- Графика
- Render pipelines
- Built-in Render Pipeline
- Universal Render Pipeline
- High Definition Render Pipeline
- Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Scriptable Render Pipeline introduction
- Creating a custom Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Creating a Render Pipeline Asset and Render Pipeline Instance
- Setting the active Render Pipeline Asset
- Scheduling and executing rendering commands in the Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Scriptable Render Pipeline (SRP) Batcher
- Камеры
- Post-processing
- Lighting
- Introduction to lighting
- Light sources
- Shadows
- The Lighting window
- The Light Explorer window
- Lightmapping
- The Progressive Lightmapper
- Lightmapping using Enlighten (deprecated)
- Lightmapping: Getting started
- Lightmap Parameters Asset
- Directional Mode
- Lightmaps and LOD
- Ambient occlusion
- Lightmaps: Technical information
- Lightmapping and the Shader Meta Pass
- Lightmap UVs
- UV overlap
- Lightmap seam stitching
- Custom fall-off
- Realtime Global Illumination using Enlighten (deprecated)
- Light Probes
- Reflection Probes
- Precomputed lighting data
- Scene View Draw Modes for lighting
- Meshes, Materials, Shaders and Textures
- Mesh Components
- Creating and Using Materials
- Текстуры
- Writing Shaders
- Standard Shader
- Standard Particle Shaders
- Legacy Shaders
- Shader Reference
- Writing Surface Shaders
- Writing vertex and fragment shaders
- Примеры вершинных и фрагментных шейдеров
- Shader semantics
- Accessing shader properties in Cg/HLSL
- Providing vertex data to vertex programs
- Встроенные подключаемые файлы для шейдеров
- Стандартные шейдерные предпроцессорные макросы
- Built-in shader helper functions
- Built-in shader variables
- Shader variants and keywords
- GLSL Shader programs
- Shading language used in Unity
- Shader Compilation Target Levels
- Shader data types and precision
- Using sampler states
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Shader
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: свойства
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: SubShader
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Pass
- ShaderLab culling and depth testing
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Blending
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: тэги Pass
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Stencil
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Name
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: цвет, материал, освещение
- ShaderLab: Legacy Texture Combiners
- Синтакс ShaderLab: Альфа тестинг (Alpha testing)
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: туман
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: BindChannels
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: UsePass
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: GrabPass
- ShaderLab: SubShader Tags
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Pass
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Fallback
- #Синтаксис ShaderLab: CustomEditor
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: другие команды
- Shader assets
- Расширенные возможности ShaderLab
- Optimizing shader variants
- Asynchronous Shader compilation
- Performance tips when writing shaders
- Rendering with Replaced Shaders
- Custom Shader GUI
- Использование текстур глубины
- Текстура глубины камеры
- Особенности рендеринга различных платформ
- ShaderLab: SubShader LOD value
- Using texture arrays in shaders
- Debugging DirectX 11/12 shaders with Visual Studio
- Debugging DirectX 12 shaders with PIX
- Implementing Fixed Function TexGen in Shaders
- Tutorial: ShaderLab and fixed function shaders
- Tutorial: vertex and fragment programs
- Particle systems
- Choosing your particle system solution
- Built-in Particle System
- Using the Built-in Particle System
- Particle System vertex streams and Standard Shader support
- Particle System GPU Instancing
- Particle System C# Job System integration
- Components and Modules
- Particle System
- Particle System modules
- Particle System Main module
- Emission module
- Shape Module
- Velocity over Lifetime module
- Noise module
- Limit Velocity Over Lifetime module
- Inherit Velocity module
- Force Over Lifetime module
- Color Over Lifetime module
- Color By Speed module
- Size over Lifetime module
- Size by Speed module
- Rotation Over Lifetime module
- Rotation By Speed module
- External Forces module
- Collision module
- Triggers module
- Sub Emitters module
- Texture Sheet Animation module
- Lights module
- Trails module
- Custom Data module
- Renderer module
- Particle System Force Field
- Built-in Particle System examples
- Visual Effect Graph
- Creating environments
- Sky
- Visual Effects Components
- Advanced rendering features
- Оптимизация производительности графики
- Color space
- Graphics tutorials
- Render pipelines
- Physics
- Скриптинг
- Обзор Скриптинга
- Создание и Использование Скриптов
- Variables and the Inspector
- Controlling GameObjects using components
- Функции событий
- Time and Framerate Management
- Создание и уничтожение игровых объектов (GameObjects)
- Coroutines
- Пространства имён
- Attributes
- Order of Execution for Event Functions
- Understanding Automatic Memory Management
- Platform dependent compilation
- Специальные папки и порядок компиляции скриптов
- Assembly Definitions
- Managed code stripping
- .NET profile support
- Referencing additional class library assemblies
- Stable scripting runtime: known limitations
- Generic Functions
- Scripting restrictions
- Script Serialization
- Unity События (UnityEvents)
- What is a Null Reference Exception?
- Important Classes
- Рецепты использования векторов
- JSON Serialization
- ScriptableObject
- Выполнение Editor скриптов при запуске редактора Unity
- Инструменты Скриптинга
- C# Job System
- Plug-ins
- Обзор Скриптинга
- Multiplayer and Networking
- Multiplayer Overview
- Setting up a multiplayer project
- Using the Network Manager
- Using the Network Manager HUD
- The Network Manager HUD in LAN mode
- The Network Manager HUD in Matchmaker mode
- Converting a single-player game to Unity Multiplayer
- Debugging Information
- The Multiplayer High Level API
- Multiplayer Component Reference
- Multiplayer Classes Reference
- Multiplayer Encryption Plug-ins
- UnityWebRequest
- Аудио
- Аудио. Обзор.
- Аудио файлы
- Трекерные модули
- Audio Mixer
- Native Audio Plugin SDK
- Audio Profiler
- Ambisonic Audio
- Справочник по аудио
- Audio Clip
- Audio Listener
- Audio Source
- Audio Mixer
- Аудио эффекты (только для Pro версии)
- Audio Effects
- Audio Low Pass Effect
- Audio High Pass Effect
- Audio Echo Effect
- Audio Flange Effect
- Audio Distortion Effect
- Audio Normalize Effect
- Audio Parametric Equalizer Effect
- Audio Pitch Shifter Effect
- Audio Chorus Effect
- Audio Compressor Effect
- Audio SFX Reverb Effect
- Audio Low Pass Simple Effect
- Audio High Pass Simple Effect
- Reverb Zones
- Микрофон
- Audio Settings
- Video overview
- Анимация
- Animation System Overview
- Анимационные клипы
- Animator Controllers (контроллеры аниматоров)
- Аниматор и контроллер аниматора
- The Animator Window
- Конечные автоматы в анимации
- Blend Trees (Деревья смешивания)
- Working with blend shapes
- Animator Override Controllers
- Переназначение гуманоидных анимаций
- Performance and optimization
- Animation Reference
- Кривые анимации и события
- Playables API
- Словарь терминов анимации и Mecanim.
- User interfaces (UI)
- UIElements Developer Guide
- Unity UI
- Сanvas (Полотно)
- Basic Layout
- Визуальные компоненты
- Компоненты взаимодействия
- Animation Integration
- Auto Layout
- Rich Text
- Event System
- Справка по пользовательским интерфейсам
- Rect Transform
- Canvas Components
- Visual Components
- Interaction Components
- Auto Layout
- Справка по системе событий
- Практические рекомендации по работе с UI (пользовательскими интерфейсами)
- Immediate Mode GUI (IMGUI)
- Навигация и поиск пути
- Navigation Overview
- Navigation System in Unity
- Inner Workings of the Navigation System
- Building a NavMesh
- NavMesh building components
- Advanced NavMesh Bake Settings
- Creating a NavMesh Agent
- Creating a NavMesh Obstacle
- Creating an Off-mesh Link
- Building Off-Mesh Links Automatically
- Building Height Mesh for Accurate Character Placement
- Navigation Areas and Costs
- Loading Multiple NavMeshes using Additive Loading
- Using NavMesh Agent with Other Components
- Справочник по навигации
- Navigation How-Tos
- Navigation Overview
- Unity Services
- Setting up your project for Unity Services
- Unity Organizations
- Unity Ads
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Analytics Overview
- Setting Up Analytics
- Analytics Dashboard
- Analytics events
- Funnels
- Remote Settings
- Unity Analytics A/B Testing
- Monetization
- User Attributes
- Unity Analytics Raw Data Export
- Data reset
- Upgrading Unity Analytics
- COPPA Compliance
- Unity Analytics and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Analytics Metrics, Segments, and Terminology
- Unity Cloud Build
- Automated Build Generation
- Supported platforms
- Supported versions of Unity
- Version control systems
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Using Apache Subversion (SVN) with Unity Cloud Build
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Perforce
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Perforce
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Plastic
- Building for iOS
- Advanced options
- Using Addressables in Unity Cloud Build
- Build manifest
- Cloud Build REST API
- Unity IAP
- Setting up Unity IAP
- Cross Platform Guide
- Codeless IAP
- Defining products
- Subscription Product support
- Initialization
- Browsing Product Metadata
- Initiating Purchases
- Processing Purchases
- Handling purchase failures
- Restoring Transactions
- Purchase Receipts
- Receipt validation
- Store Extensions
- Cross-store installation issues with Android in-app purchase stores
- Store Guides
- Implementing a Store
- Unity Collaborate
- Setting up Unity Collaborate
- Adding team members to your Unity Project
- Viewing history
- Enabling Cloud Build with Collaborate
- Managing Unity Editor versions
- Reverting files
- Resolving file conflicts
- Excluding Assets from publishing to Collaborate
- Publishing individual files to Collaborate
- Restoring previous versions of a project
- In-Progress edit notifications
- Managing cloud storage
- Moving your Project to another version control system
- Unity Accelerator
- Collaborate troubleshooting tips
- Unity Cloud Diagnostics
- Unity Integrations
- Multiplayer Services
- Unity Distribution Portal
- XR
- Open-source repositories
- Asset Store Publishing
- Creating your Publisher Account
- Creating a new package draft
- Deleting a package draft
- Uploading Assets to your package
- Filling in the package details
- Submitting your package for approval
- Viewing the status of your Asset Store submissions
- Collecting revenue
- Providing support to your customers
- Adding tags to published packages
- Connecting your account to Google Analytics
- Promoting your Assets
- Refunding your customers
- Upgrading packages
- Deprecating your Assets
- Issuing vouchers
- Managing your publishing team
- Asset Store Publisher portal
- Platform development
- Using Unity as a Library in other applications
- Enabling deep linking
- Автономный
- macOS
- Apple TV
- WebGL
- WebGL Player settings
- Getting started with WebGL development
- WebGL Browser Compatibility
- Building and running a WebGL project
- WebGL: Deploying compressed builds
- Server configuration for WebAssembly streaming
- Debugging and troubleshooting WebGL builds
- WebGL Graphics
- WebGL Networking
- Using Audio In WebGL
- WebGL performance considerations
- Embedded Resources on WebGL
- Memory in WebGL
- WebGL: Interacting with browser scripting
- Using WebGL Templates
- Cursor locking and full-screen mode in WebGL
- Input in WebGL
- iOS
- Integrating Unity into native iOS applications
- Первые шаги в iOS разработке
- iOS build settings
- iOS Player settings
- Продвинутые темы по iOS
- Troubleshooting on iOS devices
- Сообщение об ошибках, приводящих к "падениям" на iOS
- Android
- Windows
- Integrating Unity into Windows and UWP applications
- Windows General
- Universal Windows Platform
- Приложения Windows Store: Приступая к работе
- Universal Windows Platform: Deployment
- Universal Windows Platform (UWP) build settings
- Windows Device Portal Deployment
- Universal Windows Platform: Profiler
- Universal Windows Platform: Command line arguments
- Universal Windows Platform: Association launching
- Класс AppCallbacks
- Universal Windows Platform: WinRT API in C# scripts
- Universal Windows Platform Player Settings
- Universal Windows Platform: IL2CPP scripting back end
- ЧаВо
- Universal Windows Platform: Examples
- Universal Windows Platform: Code snippets
- Known issues
- Чеклист Мобильного Разработчика
- Experimental
- Legacy Topics
- Best practice guides
- Expert guides
- Glossary
- Unity User Manual (2019.4 LTS)
- Packages
- Unity's Package Manager
- Package conflicts
- Automatic conflict resolution
Automatic conflict resolution
When the Package Manager computes package dependencies, and finds requests for multiple versions of the same package, it automatically selects the package with the fewest dependency levels from the root. In the case of a tie, the Package Manager chooses the highest version among the versions that are tied. It then displays a description of the conflict in the Unity console.
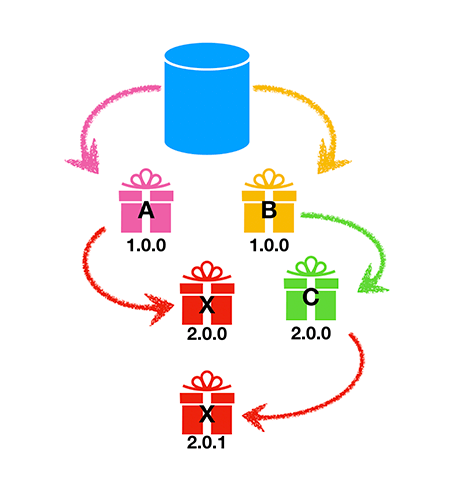
In this example, the higher version (2.0.1) of Package X appears as a dependency three levels away from the project (via Package B and Package C). The Package Manager loads version 2.0.0 of Package X because its dependency is two levels away from the project (via only Package A).
Note: Even if the Package Manager can resolve which package to load, Unity still writes a conflict report to the Unity log file if Unity requests different major versions of the same package, such as 1.0.0 and 2.0.0.