Manual
- Unity User Manual (2018.2)
- Working in Unity
- Getting Started
- Unity Hub
- Installing Unity using the Hub
- Adding components to the Unity Editor
- Installing Unity without the hub
- Installing Unity offline without the Hub
- Unity Hub advanced deployment considerations
- 2D или 3D проекты
- Project Templates
- Starting Unity for the first time
- Opening existing Projects
- Learning the interface
- Asset Workflow (работа с ассетами)
- The Main Windows
- Создание геймплея.
- Editor Features
- Advanced Development
- Advanced Editor Topics
- Licenses and Activation
- Upgrade Guides
- Использование автоматического обновления API
- Upgrading to Unity 2018.2
- Upgrading to Unity 2018.1
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.3
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.2
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.1
- Upgrading to Unity 5.6
- Upgrading to Unity 5.5
- Upgrading to Unity 5.4
- Upgrading to Unity 5.3
- Upgrading to Unity 5.2
- Upgrading to Unity 5.0
- Руководство по обновлению до Unity 4.0
- Обновление до Unity 3.5
- Getting Started
- Importing
- 2D
- Графика
- Обзор графических возможностей
- Освещение
- Lighting overview
- Lighting Window
- Light Explorer
- Light sources
- Shadows
- Global Illumination
- Enlighten
- Progressive Lightmapper
- Lightmap Parameters
- Baked ambient occlusion
- LOD for baked lightmaps
- Light Probes
- Reflection probes
- Lighting Modes
- GI visualizations in the Scene view
- Lighting Data Asset
- Lightmap Directional Modes
- Lightmaps: Technical information
- Material properties and the GI system
- Global Illumination UVs
- GI cache
- Light troubleshooting and performance
- Related topics
- Камеры
- Materials, Shaders & Textures
- Текстуры
- Creating and Using Materials
- Standard Shader
- Standard Particle Shaders
- Physically Based Rendering Material Validator
- Accessing and Modifying Material parameters via script
- Writing Shaders
- Legacy Shaders
- Video overview
- Ландшафтный движок
- Tree Editor
- Системы Частиц
- Post-processing overview
- Расширенные возможности рендеринга
- Procedural Mesh Geometry
- Оптимизация производительности графики
- Слои
- Освещение
- Справка по графическим возможностям
- Справочник по камерам
- Shader Reference
- Writing Surface Shaders
- Программирование вершинных и фрагментных (пиксельных) шейдеров
- Примеры вершинных и фрагментных шейдеров
- Shader semantics
- Accessing shader properties in Cg/HLSL
- Providing vertex data to vertex programs
- Встроенные подключаемые файлы для шейдеров
- Стандартные шейдерные предпроцессорные макросы
- Built-in shader helper functions
- Built-in shader variables
- Создание программ с несколькими вариантами шейдеров
- GLSL Shader programs
- Shading Language used in Unity
- Shader Compilation Target Levels
- Shader data types and precision
- Using sampler states
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Shader
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: свойства
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: SubShader
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Pass
- ShaderLab: Culling & Depth Testing
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Blending
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: тэги Pass
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Stencil
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Name
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: цвет, материал, освещение
- ShaderLab: Legacy Texture Combiners
- Синтакс ShaderLab: Альфа тестинг (Alpha testing)
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: туман
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: BindChannels
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: UsePass
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: GrabPass
- ShaderLab: SubShader Tags
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Pass
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: Fallback
- #Синтаксис ShaderLab: CustomEditor
- Синтаксис ShaderLab: другие команды
- Shader assets
- Расширенные возможности ShaderLab
- Unity's Rendering Pipeline
- Performance tips when writing shaders
- Rendering with Replaced Shaders
- Custom Shader GUI
- Использование текстур глубины
- Текстура глубины камеры
- Особенности рендеринга различных платформ
- Уровень детализации шейдера (Level Of Detail)
- Texture arrays
- Debugging DirectX 11/12 shaders with Visual Studio
- Debugging DirectX 12 shaders with PIX
- Implementing Fixed Function TexGen in Shaders
- Particle Systems reference
- Particle System
- Particle System modules
- Particle System Main module
- Emission module
- Particle System Shape Module
- Velocity over Lifetime module
- Noise module
- Limit Velocity Over Lifetime module
- Inherit Velocity module
- Force Over Lifetime module
- Color Over Lifetime module
- Color By Speed module
- Size over Lifetime module
- Size by Speed module
- Rotation Over Lifetime module
- Rotation By Speed module
- External Forces module
- Collision module
- Triggers module
- Sub Emitters module
- Texture Sheet Animation module
- Lights module
- Trails module
- Custom Data module
- Renderer module
- Системы частиц (Более старая система, используемая до версии 3.5)
- Справка по Визуальным Эффектам
- Mesh Components
- Текстурные компоненты
- Компоненты рендеринга
- Rendering Pipeline Details
- Подборка уроков по графике
- How do I Import Alpha Textures?
- Как я могу создать Skybox?
- Как сделать эмиттер частиц в форме меша (Устаревшая система частиц)
- Как добавить Spot Light Cookie (Cookie текстура для Точечного Источника Света)?
- Как мне исправить вращение импортированной модели?
- Water in Unity
- Art Asset best practice guide
- Importing models from 3D modeling software
- How to do Stereoscopic Rendering
- Уроки по графике
- Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Обзор графических возможностей
- Physics
- Скриптинг
- Обзор Скриптинга
- Создание и Использование Скриптов
- Variables and the Inspector
- Controlling GameObjects using components
- Функции событий
- Time and Framerate Management
- Создание и уничтожение игровых объектов (GameObjects)
- Coroutines
- Пространства имён
- Attributes
- Порядок выполнения функций событий
- Понимание автоматического управления памятью
- Platform dependent compilation
- Специальные папки и порядок компиляции скриптов
- Script compilation and assembly definition files
- .NET profile support
- Referencing additional class library assemblies
- Stable scripting runtime: known limitations
- Generic Functions
- Scripting restrictions
- Script Serialization
- Unity События (UnityEvents)
- What is a Null Reference Exception?
- Important Classes
- Рецепты использования векторов
- Инструменты Скриптинга
- Система событий (EventSystem)
- C# Job System
- Обзор Скриптинга
- Multiplayer and Networking
- Multiplayer Overview
- Setting up a multiplayer project
- Using the Network Manager
- Using the Network Manager HUD
- The Network Manager HUD in LAN mode
- The Network Manager HUD in Matchmaker mode
- Converting a single-player game to Unity Multiplayer
- Debugging Information
- The Multiplayer High Level API
- Multiplayer Component Reference
- Multiplayer Classes Reference
- UnityWebRequest
- Аудио
- Аудио. Обзор.
- Аудио файлы
- Трекерные модули
- Audio Mixer
- Native Audio Plugin SDK
- Audio Profiler
- Ambisonic Audio
- Справочник по аудио
- Audio Clip
- Audio Listener
- Audio Source
- Audio Mixer
- Аудио эффекты (только для Pro версии)
- Audio Effects
- Audio Low Pass Effect
- Audio High Pass Effect
- Audio Echo Effect
- Audio Flange Effect
- Audio Distortion Effect
- Audio Normalize Effect
- Audio Parametric Equalizer Effect
- Audio Pitch Shifter Effect
- Audio Chorus Effect
- Audio Compressor Effect
- Audio SFX Reverb Effect
- Audio Low Pass Simple Effect
- Audio High Pass Simple Effect
- Reverb Zones
- Микрофон
- Audio Settings
- Анимация
- Animation System Overview
- Анимационные клипы
- Animator Controllers (контроллеры аниматоров)
- Аниматор и контроллер аниматора
- The Animator Window
- Конечные автоматы в анимации
- Blend Trees (Деревья смешивания)
- Применение Blend Shapes (форм смешивания) для анимации
- Animator Override Controllers
- Переназначение гуманоидных анимаций
- Performance and optimization
- Animation Reference
- Кривые анимации и события
- Playables API
- Словарь терминов анимации и Mecanim.
- Timeline
- Пользовательский интерфейс
- Сanvas (Полотно)
- Basic Layout
- Визуальные компоненты
- Компоненты взаимодействия
- Animation Integration
- Auto Layout
- «Обогащенный» текст (Rich Text)
- Справка по пользовательским интерфейсам
- Практические рекомендации по работе с UI (пользовательскими интерфейсами)
- Immediate Mode GUI (IMGUI)
- Навигация и поиск пути
- Navigation Overview
- Navigation System in Unity
- Inner Workings of the Navigation System
- Building a NavMesh
- NavMesh building components
- Advanced NavMesh Bake Settings
- Creating a NavMesh Agent
- Creating a NavMesh Obstacle
- Creating an Off-mesh Link
- Building Off-Mesh Links Automatically
- Building Height Mesh for Accurate Character Placement
- Navigation Areas and Costs
- Loading Multiple NavMeshes using Additive Loading
- Using NavMesh Agent with Other Components
- Справочник по навигации
- Navigation How-Tos
- Navigation Overview
- Unity Services
- Setting up your project for Unity Services
- Unity Organizations
- Unity Ads
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Analytics Overview
- Setting Up Analytics
- Analytics Dashboard
- Analytics events
- Funnels
- Remote Settings
- Unity Analytics A/B Testing
- Monetization
- User Attributes
- Unity Analytics Raw Data Export
- Data reset
- Upgrading Unity Analytics
- COPPA Compliance
- Unity Analytics and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Analytics Metrics, Segments, and Terminology
- Unity Cloud Build
- Automated Build Generation
- Supported platforms
- Supported versions of Unity
- Version control systems
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Using Apache Subversion (SVN) with Unity Cloud Build
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Perforce
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Perforce
- Building for iOS
- Advanced options
- Build manifest
- Cloud Build REST API
- Unity IAP
- Setting up Unity IAP
- Cross Platform Guide
- Codeless IAP
- Defining products
- Subscription Product support
- Initialization
- Browsing Product Metadata
- Initiating Purchases
- Processing Purchases
- Handling purchase failures
- Restoring Transactions
- Purchase Receipts
- Receipt validation
- Store Extensions
- Cross-store installation issues with Android in-app purchase stores
- Store Guides
- Implementing a Store
- IAP Promo
- Unity Collaborate
- Setting up Unity Collaborate
- Adding team members to your Unity Project
- Viewing history
- Enabling Cloud Build with Collaborate
- Managing Unity Editor versions
- Reverting files
- Resolving file conflicts
- Excluding Assets from publishing to Collaborate
- Publishing individual files to Collaborate
- Restoring previous versions of a project
- In-Progress edit notifications
- Managing cloud storage
- Moving your Project to another version control system
- Collaborate troubleshooting tips
- Unity Cloud Diagnostics
- Unity Integrations
- Multiplayer Services
- XR
- XR SDKs
- Google VR
- Vuforia
- Windows Mixed Reality
- Unity XR input
- XR API reference
- Mixed Reality Devices
- Обзор
- VR devices
- Single Pass Stereo rendering (Double-Wide rendering)
- VR Audio Spatializers
- XR SDKs
- Open-source repositories
- Asset Store Publishing
- Специфичные платформы
- Автономный
- macOS
- Apple TV
- WebGL
- WebGL Player Settings
- Getting started with WebGL development
- WebGL Browser Compatibility
- Building and running a WebGL project
- WebGL: Deploying compressed builds
- Debugging and troubleshooting WebGL builds
- WebGL Graphics
- WebGL Networking
- Using Audio In WebGL
- WebGL performance considerations
- Memory in WebGL
- WebGL: Interacting with browser scripting
- Using WebGL Templates
- Cursor locking and full-screen mode in WebGL
- Input in WebGL
- iOS
- Первые шаги в iOS разработке
- iOS Player Settings
- iOS 2D Texture Overrides
- Upgrading to 64-bit iOS
- Продвинутые темы по iOS
- Features currently not supported by Unity iOS
- Решение проблем на iOS устройствах
- Сообщение об ошибках, приводящих к "падениям" на iOS
- Android
- Getting started with Android development
- Android environment setup
- Unity Remote
- Android Remote (УСТАРЕВШЕЕ)
- Troubleshooting Android development
- Building apps for Android
- Reporting crash bugs under Android
- Support for APK expansion files (OBB)
- Написание кода для Android
- Building and using plug-ins for Android
- Кастомизация экрана приветствия (Splash Screen) на Android
- Single-Pass Stereo Rendering for Android
- Android Player Settings
- Android 2D Textures Overrides
- Gradle for Android
- Android Manifest
- Getting started with Android development
- Windows
- Windows General
- Universal Windows Platform
- Приложения Windows Store: Приступая к работе
- Universal Windows Platform: Deployment
- Universal Windows Platform: Profiler
- Universal Windows Platform: Command line arguments
- Universal Windows Platform: Association launching
- Класс AppCallbacks
- Universal Windows Platform: WinRT API in C# scripts
- Universal Windows Platform Player Settings
- Scripting Backends
- ЧаВо
- Universal Windows Platform: Examples
- Universal Windows Platform: Code snippets
- Known issues
- Web Player
- Чеклист Мобильного Разработчика
- Experimental
- Legacy Topics
- Best practice guides
- Expert guides
- New in Unity 2018.2
- Packages Documentation
- Glossary
- Unity User Manual (2018.2)
- Анимация
- Animation System Overview
Animation System Overview
Unity has a rich and sophisticated animation system (sometimes referred to as ‘Mecanim’). It provides:
- Easy workflow and setup of animations for all elements of Unity including objects, characters, and properties.
- Support for imported animation clips and animation created within Unity
- Humanoid animation retargeting - the ability to apply animations from one character model onto another.
- Simplified workflow for aligning animation clips.
- Удобный предпросмотр анимационных клипов, переходов и взаимодействий между ними. Это позволяет аниматорам работать более независимо от программистов, прототипировать и просматривать анимации до подключения игрового кода.
- Управление сложными взаимодействиями между анимациями с помощью инструмента визуального программирования.
- Animating different body parts with different logic.
- Layering and masking features
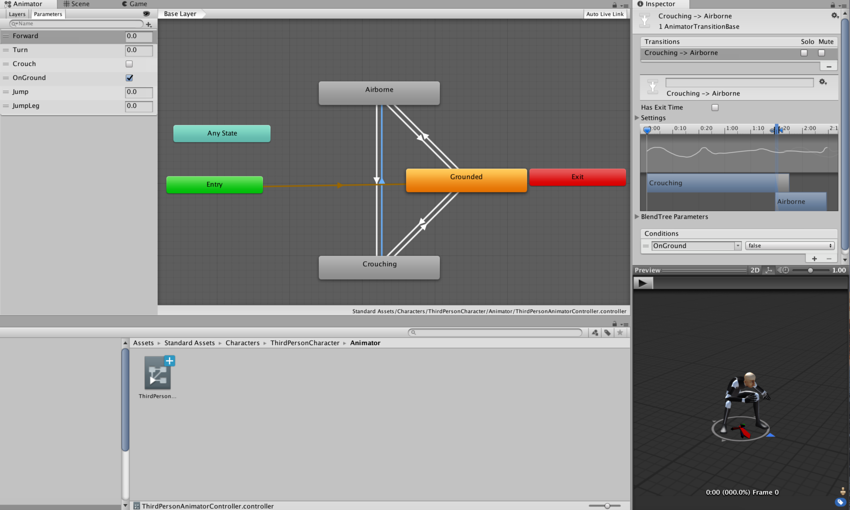
Обзор анимации
Unity’s animation system is based on the concept of Animation Clips, which contain information about how certain objects should change their position, rotation, or other properties over time. Each clip can be thought of as a single linear recording. Animation clips from external sources are created by artists or animators with 3rd party tools such as Max or Maya, or come from motion capture studios or other sources.
Animation Clips are then organised into a structured flowchart-like system called an Animator Controller. The Animator Controller acts as a “State Machine” which keeps track of which clip should currently be playing, and when the animations should change or blend together.
A very simple Animator Controller might only contain one or two clips, for example to control a powerup spinning and bouncing, or to animate a door opening and closing at the correct time. A more advanced Animator Controller might contain dozens of humanoid animations for all the main character’s actions, and might blend between multiple clips at the same time to provide a fluid motion as the player moves around the scene.
Unity’s Animation system also has numerous special features for handling humanoid characters which give you the ability to retarget humanoid animation from any source (for example: motion capture; the Asset Store; or some other third-party animation library) to your own character model, as well as adjusting muscle definitions. These special features are enabled by Unity’s Avatar system, where humanoid characters are mapped to a common internal format.
Each of these pieces - the Animation Clips, the Animator Controller, and the Avatar, are brought together on a GameObject via the Animator Component. This component has a reference to an Animator Controller, and (if required) the Avatar for this model. The Animator Controller, in turn, contains the references to the Animation Clips it uses.
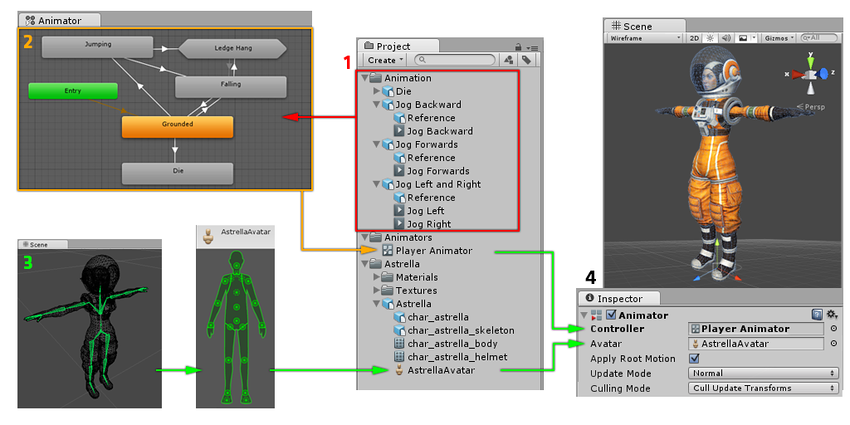
The above diagram shows the following:
- Animation clips are imported from an external source or created within Unity. In this example, they are imported motion captured humanoid animations.
- The animation clips are placed and arranged in an Animator Controller. This shows a view of an Animator Controller in the Animator window. The States (which may represent animations or nested sub-state machines) appear as nodes connected by lines. This Animator Controller exists as an asset in the Project window.
- The rigged character model (in this case, the astronaut “Astrella”) has a specific configuration of bones which are mapped to Unity’s common Avatar format. This mapping is stored as an Avatar asset as part of the imported character model, and also appears in the Project window as shown.
- When animating the character model, it has an Animator component attached. In the Inspector view shown above, you can see the Animator Component which has both the Animator Controller and the Avatar assigned. The animator uses these together to animate the model. The Avatar reference is only necessary when animating a humanoid character. For other types of animation, only an Animator Controller is required.
Unity’s animation system comes with a lot of concepts and terminology. If at any point, you need to find out what something means, go to our Animation Glossary.
Унаследованная анимационная система
While Mecanim is recommended for use in most situations, Unity has retained its legacy animation system which existed before Unity 4. You may need to use when working with older content created before Unity 4. For information on the Legacy animation system, see this section
- 2018–04–25 Page amended with limited editorial review