Manual
Version:
2020.1
- Unity User Manual (2020.1)
- Packages
- Verified packages
- 2D Animation
- 2D Pixel Perfect
- 2D PSD Importer
- 2D SpriteShape
- Adaptive Performance
- Adaptive Performance Samsung Android
- Addressables
- Advertisement
- Alembic
- Analytics Library
- Android Logcat
- AR Foundation
- ARCore XR Plugin
- ARKit Face Tracking
- ARKit XR Plugin
- Burst
- Cinemachine
- Editor Coroutines
- High Definition RP
- In App Purchasing
- Input System
- JetBrains Rider Editor
- Magic Leap XR Plugin
- ML Agents
- Mobile Notifications
- Multiplayer HLAPI
- Oculus XR Plugin
- Polybrush
- Post Processing
- ProBuilder
- Profile Analyzer
- Quick Search
- Remote Config
- Scriptable Build Pipeline
- Shader Graph
- Test Framework
- TextMeshPro
- Timeline
- Unity Collaborate
- Unity Distribution Portal
- Unity Recorder
- Universal RP
- Visual Effect Graph
- Visual Studio Code Editor
- Visual Studio Editor
- Windows XR Plugin
- Xiaomi SDK
- XR Plugin Management
- Preview packages
- Core packages
- Built-in packages
- AI
- Android JNI
- Animation
- Asset Bundle
- Audio
- Cloth
- Director
- Image Conversion
- IMGUI
- JSONSerialize
- Particle System
- Physics
- Physics 2D
- Screen Capture
- Terrain
- Terrain Physics
- Tilemap
- UI
- UIElements
- Umbra
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Web Request
- Unity Web Request Asset Bundle
- Unity Web Request Audio
- Unity Web Request Texture
- Unity Web Request WWW
- Vehicles
- Video
- VR
- Wind
- XR
- Packages by keywords
- Unity's Package Manager
- Creating custom packages
- Verified packages
- Working in Unity
- Installing Unity
- Upgrading Unity
- Using the API Updater
- Upgrading to Unity 2020.2
- Upgrading to Unity 2020.1
- Upgrading to Unity 2019 LTS
- Upgrading to Unity 2018 LTS
- Legacy Upgrade Guides
- Unity's interface
- Asset workflow
- Creación del Gameplay
- Características del Editor
- 2D and 3D mode settings
- Preferences
- Presets
- Shortcuts Manager
- Build Settings
- Project Settings
- Integración Visual Studio C#
- Integración con RenderDoc
- Using the Xcode frame debugger
- Analiticas del Editor
- Buscar Actualizaciones
- IME en Unity
- Nombres de carpetas de especiales
- Reusing Assets between Projects
- Control de Versiones
- Multi-Scene editing
- Command line arguments
- Support for custom Menu Item and Editor features
- Archivos de escena basados en texto
- Solución de Problemas del Editor
- Analysis
- Importing
- Input
- 2D
- Experiencia de Juego en 2D
- asdf
- Sprites
- Tilemap
- Physics Reference 2D
- Gráficos
- Render pipelines
- Built-in Render Pipeline
- Universal Render Pipeline
- High Definition Render Pipeline
- Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Scriptable Render Pipeline introduction
- Creating a custom Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Creating a Render Pipeline Asset and Render Pipeline Instance
- Setting the active Render Pipeline Asset
- Creating a simple render loop in a custom Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Scheduling and executing rendering commands in the Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Scriptable Render Pipeline (SRP) Batcher
- Cameras
- Post-processing
- Lighting
- Introduction to lighting
- Light sources
- Shadows
- The Lighting window
- Lighting Settings Asset
- The Light Explorer window
- Lightmapping
- The Progressive Lightmapper
- Lightmapping using Enlighten (deprecated)
- Lightmapping: Getting started
- Lightmap Parameters Asset
- Directional Mode
- Lightmaps and LOD
- Ambient occlusion
- Lightmaps: Technical information
- Lightmapping and the Shader Meta Pass
- Lightmap UVs
- UV overlap
- Lightmap seam stitching
- Custom fall-off
- Realtime Global Illumination using Enlighten (deprecated)
- Light Probes
- Reflection Probes
- Precomputed lighting data
- Scene View Draw Modes for lighting
- Meshes, Materials, Shaders and Textures
- Componentes Mesh
- Materials
- Texturas 2D
- Sombreadores(Shaders) con Funciones Fijas
- Standard Shader
- Standard Particle Shaders
- Autodesk Interactive shader
- Legacy Shaders (Shaders de Legado)
- Referencia del Shader
- Writing Surface Shaders
- Writing vertex and fragment shaders
- Ejemplos del Vertex y Fragment Shader
- Semánticas de Shader
- Accediendo propiedades shader en Cg/HLSL
- Proporcionar datos del vértice a programas vertex
- El Sombreador integrado incluye archivos
- Macros del preprocesador Shader predefinidas
- Funciones Shader integradas de ayuda
- Variables shader integradas
- Shader variants and keywords
- GLSL Shader programs
- Shading language used in Unity
- Niveles Objetivo de Compilación Shader
- Tipos de dato Shader y precisión
- Using sampler states
- Sintaxis ShaderLab
- Assets Shader
- Temas Avanzados de ShaderLab
- Optimizing shader variants
- Asynchronous Shader compilation
- Consejos de rendimiento al escribir shaders
- Rendering con Shaders Remplazados
- Custom Shader GUI (GUI Shader Personalizado)
- Utilizando Depth Textures (Texturas de profundidad)
- La Depth Texture (Textura de Profundidad) de la cámara
- Diferencias especificas de rendering por plataforma
- ShaderLab: SubShader LOD value
- Using texture arrays in shaders
- Debugging DirectX 11/12 shaders with Visual Studio
- Debugging DirectX 12 shaders with PIX
- Implementando la Función Fija TexGen en Shaders
- Tutorial: ShaderLab and fixed function shaders
- Tutorial: vertex and fragment programs
- Particle systems
- Choosing your particle system solution
- Built-in Particle System
- Using the Built-in Particle System
- Particle System vertex streams and Standard Shader support
- Particle System GPU Instancing
- Particle System C# Job System integration
- Components and Modules
- Particle System
- Módulos del Sistema de Partículas
- Particle System Main module
- Emission module
- Módulo Shape (forma)
- Velocity over Lifetime module
- Noise module
- Limit Velocity Over Lifetime module
- Inherit Velocity module
- Lifetime by Emitter Speed
- Force Over Lifetime module
- Color Over Lifetime module
- Color By Speed module
- Módulo Size Over Lifetime
- Módulo Size By Speed
- Rotation Over Lifetime module
- Rotation By Speed module
- External Forces module
- Collision module
- Módulo Triggers
- Sub Emitters module
- Texture Sheet Animation module
- Lights module
- Trails module
- Módulo de datos personalizados
- Renderer module
- Particle System Force Field
- Built-in Particle System examples
- Visual Effect Graph
- Creating environments
- Sky
- Visual Effects Components
- Advanced rendering features
- High dynamic range
- Level of Detail (LOD) for meshes
- Graphics API support
- Streaming Virtual Texturing
- Streaming Virtual Texturing requirements and compatibility
- How Streaming Virtual Texturing works
- Enabling Streaming Virtual Texturing in your project
- Using Streaming Virtual Texturing in Shader Graph
- Cache Management for Virtual Texturing
- Marking textures as "Virtual Texturing Only"
- Virtual Texturing error material
- Compute shaders
- GPU instancing
- Sparse Textures (Texturas Dispersas)
- CullingGroup API
- Loading texture and mesh data
- Optimizando el Rendimiento Gráfico
- Color space
- Graphics tutorials
- Cómo arreglo la rotación de un modelo importado?
- Art Asset best practice guide
- Importing models from 3D modeling software
- Hacer imágenes visuales creíbles en Unity
- Update: believable visuals in URP and HDRP
- Believable visuals: preparing assets
- Believable visuals: render settings
- Believable visuals: lighting strategy
- Believable visuals: models
- Believable visuals: materials and shaders
- Believable visuals: outdoor lighting
- Believable visuals: indoor and local lighting
- Believable visuals: post-processing
- Believable visuals: dynamic lighting
- Setting up the Rendering Pipeline and Lighting in Unity
- Render pipelines
- Física
- 3D Physics for object-oriented projects
- Referencia de física en 3D
- Articulation Body
- Box Collider
- Capsule Collider
- El Character Controller ( Controlador del personaje)
- Character Joint
- Configurable Joint
- Constant Force (fuerza constante)
- Fixed Joint
- Hinge Joint
- Mesh Collider
- Rigidbody
- Sphere Collider
- Spring Joint
- Cloth
- Wheel Collider
- Terrain Collider
- Physic Material (Material de Física)
- Los cómos de la Física
- Scripting
- Setting Up Your Scripting Environment
- Scripting concepts
- Important Classes
- Important Classes - GameObject
- Important Classes - MonoBehaviour
- Important Classes - Object
- Important Classes - Transform
- Important Classes - Vectors
- Important Classes - Quaternion
- ScriptableObject
- Important Classes - Time and Framerate Management
- Important Classes - Mathf
- Important Classes - Random
- Important Classes - Debug
- Important Classes - Gizmos & Handles
- Unity architecture
- Plug-ins
- C# Job System
- Multijugador y Networking (redes)
- Multiplayer Overview
- Configurando un proyecto multijugador
- Using the Network Manager
- Using the Network Manager HUD
- The Network Manager HUD in LAN mode
- The Network Manager HUD in Matchmaker mode
- Converting a single-player game to Unity Multiplayer
- Debugging Information
- La API de Alto Nivel Multijugador
- Multiplayer Component Reference
- Clases Multijugador de referencia
- Multiplayer Encryption Plug-ins
- UnityWebRequest
- Audio
- Vista General del Audio
- Archivos de Audio
- Tracker Modules
- Audio Mixer (Mezclador de Audio)
- Plugin SDK del Audio Nativo de Unity
- Audio Profiler (Perfilador de Audio)
- Ambisonic Audio
- Referencias de Audio
- Audio Clip
- Audio Listener
- Audio Source (Fuente de Audio)
- Audio Mixer (Mezclador de Audio)
- Audio Filters (Filtros de Audio)
- Audio Effects (Efectos de audio)
- Audio Low Pass Effect
- Audio High Pass Effect
- Audio Echo Effect
- Audio Flange Effect
- Audio Distortion Effect
- Audio Normalize Effect
- Audio Parametric Equalizer Effect
- Audio Pitch Shifter Effect
- Audio Chorus Effect
- Audio Compressor Effect
- Audio SFX Reverb Effect
- Audio Low Pass Simple Effect
- Audio High Pass Simple Effect
- Reverb Zones (Zonas de reverberación)
- Micrófono
- Configuraciones de Audio
- Descripción general de video
- Animación
- Visión general del Sistema de Animación
- Clips de Animación (Animation Clips)
- Animator Controllers
- El Asset del Animator Controller
- La Ventana Animator
- Animation State Machines (Máquinas de Estado de Animación)
- Lo básico de los Estados de Maquina
- Parámetros de animación
- Transiciones de State Machine (Estados de Maquina)
- State Machine Behaviours (Comportamientos de Maquinas de Estado)
- Sub-State Machines (Sub-Estados de Maquina)
- Capas de Animación
- Funcionalidad "Solo" y "Mute"
- Target Matching (Haciendo que coincida con un objetivo)
- Inverse Kinematics (Cinemática Inversa)
- Root Motion - Cómo funciona
- Blend Trees (Árboles de Mezcla)
- Working with blend shapes
- Animator Override Controllers
- Retargeting de Animaciones Humanoides
- Performance and optimization
- Animation Reference
- Preguntas más frecuentes de Animación
- Playables API
- Un Glosario de términos de Animación
- Creating user interfaces (UI)
- Comparison of UI systems in Unity
- UI Toolkit
- Unity UI
- Canvas
- Diseño Básico
- Componentes Visuales
- Componentes de Interacción
- Integración de Animación
- Diseño Automático
- Rich Text
- Event System
- Referencia UI
- Rect Transform
- Canvas Components (Componentes del Canvas)
- Componentes Visuales
- Componentes de Interacción
- Auto Layout (Diseño Automático)
- Referencia al Event System (Sistema de Eventos)
- Los cómos del UI
- Immediate Mode GUI (IMGUI)
- Navegación y Pathfinding (Búsqueda de Caminos)
- Visión General de la Navegación
- Sistema de Navegación de Unity
- Trabajos interiores del Sistema de Navegación
- Construyendo un NavMesh
- Componentes de construcción del NavMesh
- Ajustes Bake Avanzados del NavMesh
- Creando un Agente NavMesh
- Creando un NavMesh Obstacle (Obstáculo NavMesh)
- Creando un Off-mesh Link (Enlace Off-mesh)
- Construyendo Off-Mesh Links (Enlaces Off-mesh) Automáticamente
- Construyendo un Height Mesh (Mesh de altura) para una colocación precisa del personaje
- Áreas de Navegación y Costos
- Cargar Múltiples NavMeshes utilizando el Additive Loading
- Utilizando el NavMesh Agent con otros componentes
- Navigation Reference
- Los 'Cómos' de la Navegación
- Visión General de la Navegación
- Servicios de Unity
- Setting up your project for Unity services
- Unity Organizations
- Unity Ads
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Analytics Overview
- Configurando Analytics
- Analytics Dashboard
- Eventos de analítica
- Funnels
- Configuración remota
- Unity Analytics A/B Testing
- Monetization (Monetización)
- User Attributes (Atributos de Usuario)
- Unity Analytics Raw Data Export (Exportación de datos sin procesar)
- Restablecimiento de datos
- Actualizando Unity Analytics
- COPPA Compliance
- Unity Analytics and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Métricas, segmentos y terminología de Analytics
- Unity Cloud Build
- Automated Build Generation
- Supported platforms
- Versiones soportadas de Unity
- Share links
- Sistemas de control de versiones
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Utilizar Apache Subversion (SVN) con Unity Cloud Build
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Perforce
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Plastic
- Construyendo para iOS
- Opciones Avanzadas
- Using Addressables in Unity Cloud Build
- Manifest de la construcción
- Scheduled builds
- Cloud Build REST API
- Unity Cloud Content Delivery
- Unity IAP
- Configurando el Unity IAP
- Guia Multi Plataforma
- Codeless IAP
- Definiendo productos
- Subscription Product support
- Inicialización
- Mirando Metadata del Producto
- Iniciando Compras
- Procesando Compras
- Manejando fallas en las compras
- Recuperando Transacciones
- Recibos de Compra
- Validación de Recibo
- Extensiones de la Store (tienda)
- Cross-store installation issues with Android in-app purchase stores
- Guías de Tiendas
- Implementando una Tienda
- Unity Collaborate
- Setting up Unity Collaborate
- Adding team members to your Unity project
- Ver el historial
- Enabling Cloud Build with Collaborate
- Gestión de versiones del ediitor de Unity
- Reverting files
- Resolving file conflicts
- Excluding Assets from publishing to Collaborate
- Publicar archivos individuales a Collaborate
- Restoring previous versions of a project
- Notificaciones de edición en progreso
- Managing cloud storage
- Moving your Project to another version control system
- Unity Accelerator
- Collaborate troubleshooting tips
- Unity Cloud Diagnostics
- Unity Integrations
- Servicios Multiplayer
- Unity Distribution Portal
- XR
- Getting started with AR development in Unity
- Getting started with VR development in Unity
- XR Plug-in Framework
- Configuring your Unity Project for XR
- Universal Render Pipeline compatibility in XR
- XR API reference
- Single Pass Stereo rendering (Double-Wide rendering)
- VR Audio Spatializers
- VR frame timing
- Unity XR SDK
- Repositorios Open-source
- Cómo contribuir a Unity
- Paso 1: Obtener una cuenta de Bitbucket
- Paso 2: Fork el repositorio al cual usted quiere contribuir
- Step 3: Clone Su Fork
- Paso 4: Aplique las modificaciones a su fork
- Paso 5: Abra una solicitud Pull en Bitbucket
- Paso 6: Espere al Feedback (retroalimentación)
- Lecturas Adicionales
- FAQ (Preguntas más frecuentes)
- Cómo contribuir a Unity
- Asset Store Publishing
- Creating your Publisher Account
- Creating a new package draft
- Deleting a package draft
- Uploading Assets to your package
- Filling in the package details
- Submitting your package for approval
- Viewing the status of your Asset Store submissions
- Collecting revenue
- Providing support to your customers
- Adding tags to published packages
- Connecting your account to Google Analytics
- Promoting your Assets
- Refunding your customers
- Upgrading packages
- Deprecating your Assets
- Issuing vouchers
- Managing your publishing team
- Asset Store Publisher portal
- Platform development
- Using Unity as a Library in other applications
- Enabling deep linking
- Standalone
- macOS
- Apple TV
- WebGL
- Empezar con el desarrollo de WebGL
- WebGL Player settings
- Building and running a WebGL project
- WebGL: Compressed builds and server configuration
- WebGL: Server configuration code samples
- Compatibilidad del navegador con WebGL
- Gráficas WebGL
- Utilizando Audio en WebGL
- Embedded Resources on WebGL
- Using WebGL templates
- Bloqueo del cursor y modo de pantalla completa en WebGL
- Input en WebGL
- WebGL: Interacting with browser scripting
- Consideraciones de rendimiento WebGL
- Memory in WebGL
- Debugging and troubleshooting WebGL builds
- WebGL Networking (redes)
- Empezar con el desarrollo de WebGL
- iOS
- Integrating Unity into native iOS applications
- Iniciando con desarrollo iOS
- iOS build settings
- iOS Player settings
- Temas Avanzados de iOS
- Troubleshooting on iOS devices
- Reportando bugs de falla en iOS
- Android
- Android environment setup
- Integrating Unity into Android applications
- Unity Remote
- Android Player settings
- Android Keystore Manager
- Building apps for Android
- Un Solo Pase de Stereo Rendering para Android
- Building and using plug-ins for Android
- Android mobile scripting
- Troubleshooting Android development
- Reporting crash bugs under Android
- Windows
- Integrating Unity into Windows and UWP applications
- Windows General
- Universal Windows Platform
- Cómo empezar
- Universal Windows Platform: Deployment
- Universal Windows Platform (UWP) build settings
- Windows Device Portal Deployment
- Universal Windows Platform: Profiler
- Universal Windows Platform: Command line arguments
- Universal Windows Platform: Association launching
- Clase AppCallbacks
- Universal Windows Platform: WinRT API in C# scripts
- Universal Windows Platform Player Settings
- Universal Windows Platform: IL2CPP scripting back end
- FAQ (Preguntas más frecuentes)
- Universal Windows Platform: Ejemplos
- Universal Windows Platform: Code snippets
- Known issues
- Lista de Verificación para Desarrolladores en Móviles
- Experimental
- Tópicos de legado
- Expert guides
- New in Unity 2020.1
- Glossary
- Unity User Manual (2020.1)
- Working in Unity
- Creación del Gameplay
- Restricciones
- Aim Constraints
Aim Constraints
An Aim Constraint rotates a GameObject to face its source GameObjects. It can also maintain a consistent orientation for another axis. For example, you can add an Aim Constraint to a Camera. To keep the Camera upright while the Constraint aims it, specify the up axis of the Camera and an up direction to align it to.
Use the Up Vector to specify the up axis of a constrained GameObject. Use the World Up Vector to specify the upward direction. As the Aim Constraint rotates the GameObject to face its source GameObjects, the Constraint also aligns the up axis of the constrained GameObject with the upward direction.
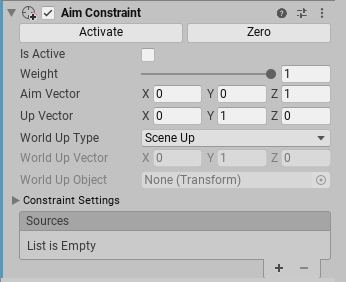
Propiedades
| Property: | Función: | |
|---|---|---|
| Activate | After you rotate the constrained GameObject and move its source GameObjects, click Activate to save this information. Activate saves the current offset from the source GameObjects in Rotation At Rest and Rotation Offset, then checks Is Active and Lock. | |
| Zero | Sets the rotation of the constrained GameObject to the source GameObjects. Zero resets the Rotation At Rest and Rotation Offset fields, then checks Is Active and Lock. | |
| Is Active | Toggles whether or not to evaluate the Constraint. To also apply the Constraint, make sure Lock is checked. | |
| Weight | The strength of the Constraint. A weight of 1 causes the Constraint to rotate the GameObject at the same rate that its source GameObjects move. A weight of 0 removes the effect of the Constraint completely. This weight affects all source GameObjects. Each GameObject in the Sources list also has a weight. | |
| Aim Vector | Specifies the axis which faces the direction of its source GameObjects. For example, to specify that the GameObject should orient only its positive Z axis to face the source GameObjects, enter an Aim Vector of 0, 0, 1 for the X, Y, and Z axes, respectively. | |
| Up Vector | Specifies the up axis of this GameObject. For example, to specify that the GameObject should always keep its positive Y axis pointing upward, enter an Up Vector of 0, 1, 0 for the X, Y, and Z axes, respectively. | |
| World Up Type | Specifies the axis for the upward direction. The Aim Constraint uses this vector to align the up axis of the GameObject the upward direction. | |
| Scene Up | The Y axis of the scene. | |
| Object Up | The Y axis of the GameObject referred to by World Up Object. | |
| Object Up Rotation | The axis specified by World Up Vector of the GameObject referred to by World Up Object. | |
| Vector | The World Up Vector. | |
| Ninguno | Do not use a World Up vector. | |
| World Up Vector | Specifies the vector to use for the Object Up Rotation and Vector choices in World Up Type. | |
| World Up Object | Specifies the GameObject to use for the Object Up and Object Up Rotation choices in World Up Type. | |
| Constraint Settings | ||
| Lock | Enable this setting to let the Constraint rotate the GameObject. Uncheck this property to edit the rotation of this GameObject. You can also edit the Rotation At Rest and Rotation Offset properties. If Is Active is checked, the Constraint updates the Rotation At Rest or Rotation Offset properties for you as you rotate the GameObject or its source GameObjects. When you are satisfied with your changes, check Lock to let the Constraint control this GameObject. This property has no effect in Play Mode. | |
| Rotation At Rest | The X, Y, and Z values to use when Weight is 0 or when the corresponding Freeze Rotation Axes are not checked. To edit these fields, uncheck Lock. | |
| Rotation Offset | The X, Y, and Z offset from the rotation that is calculated by the Constraint. To edit these fields, uncheck Lock. | |
| Freeze Rotation Axes | Check X, Y, or Z to allow the Constraint to control the corresponding axes. Uncheck an axis to stop the Constraint from controlling it. This allows you to edit, animate, or script the unfrozen axis. | |
| Sources | The list of GameObjects that constrain this GameObject. Unity evaluates source GameObjects in the order that they appear in this list. This order affects how this Constraint rotates the constrained GameObject. To get the result you want, drag and drop items in this list. Each source has a weight from 0 to 1. | |
Copyright © 2020 Unity Technologies. Publication 2020.1