Unity Manual
- Unity User Manual (2018.3)
- Working in Unity
- Getting Started
- Unity Hub
- Installing Unity using the Hub
- Adding components to the Unity Editor
- Installing Unity without the hub
- Installing Unity offline without the Hub
- Unity Hub advanced deployment considerations
- 2D or 3D projects
- Project Templates
- Starting Unity for the first time
- Opening existing Projects
- Learning the interface
- Asset Workflow
- The Main Windows
- Creating Gameplay
- Editor Features
- Advanced Development
- Advanced Editor Topics
- Licenses and Activation
- Upgrade Guides
- Using the Automatic API Updater
- Upgrading to Unity 2018.3
- Upgrading to Unity 2018.2
- Upgrading to Unity 2018.1
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.3
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.2
- Upgrading to Unity 2017.1
- Upgrading to Unity 5.6
- Upgrading to Unity 5.5
- Upgrading to Unity 5.4
- Upgrading to Unity 5.3
- Upgrading to Unity 5.2
- Upgrading to Unity 5.0
- Upgrading to Unity 4.0
- Upgrading to Unity 3.5
- Getting Started
- Importing
- 2D
- Gameplay in 2D
- 2D Sorting
- Sprites
- Tilemap
- Physics Reference 2D
- Graphics
- Graphics Overview
- Lighting
- Lighting overview
- Lighting Window
- Light Explorer
- Light sources
- Shadows
- Global Illumination
- Lightmapping
- Lightmap Parameters
- Baked ambient occlusion
- LOD for baked lightmaps
- Light Probes
- Reflection probes
- Lighting Modes
- GI visualizations in the Scene view
- Lighting Data Asset
- Lightmap Directional Modes
- Lightmaps: Technical information
- Material properties and the GI system
- Global Illumination UVs
- GI cache
- Light troubleshooting and performance
- Related topics
- Cameras
- Materials, Shaders & Textures
- Textures
- Creating and Using Materials
- Standard Shader
- Standard Particle Shaders
- Physically Based Rendering Material Validator
- Accessing and Modifying Material parameters via script
- Writing Shaders
- Legacy Shaders
- Video overview
- Terrain Engine
- Tree Editor
- Particle Systems
- Post-processing overview
- Advanced Rendering Features
- Procedural Mesh Geometry
- Optimizing graphics performance
- Layers
- Lighting
- Graphics Reference
- Cameras Reference
- Shader Reference
- Writing Surface Shaders
- Writing vertex and fragment shaders
- Vertex and fragment shader examples
- Shader semantics
- Accessing shader properties in Cg/HLSL
- Providing vertex data to vertex programs
- Built-in shader include files
- Predefined Shader preprocessor macros
- Built-in shader helper functions
- Built-in shader variables
- Making multiple shader program variants
- GLSL Shader programs
- Shading Language used in Unity
- Shader Compilation Target Levels
- Shader data types and precision
- Using sampler states
- ShaderLab Syntax
- Shader assets
- Advanced ShaderLab topics
- Unity's Rendering Pipeline
- Performance tips when writing shaders
- Rendering with Replaced Shaders
- Custom Shader GUI
- Using Depth Textures
- Camera's Depth Texture
- Platform-specific rendering differences
- Shader Level of Detail
- Texture arrays
- Debugging DirectX 11/12 shaders with Visual Studio
- Debugging DirectX 12 shaders with PIX
- Implementing Fixed Function TexGen in Shaders
- Particle Systems reference
- Particle System
- Particle System modules
- Particle System Main module
- Emission module
- Shape Module
- Velocity over Lifetime module
- Noise module
- Limit Velocity Over Lifetime module
- Inherit Velocity module
- Force Over Lifetime module
- Color Over Lifetime module
- Color By Speed module
- Size over Lifetime module
- Size by Speed module
- Rotation Over Lifetime module
- Rotation By Speed module
- External Forces module
- Collision module
- Triggers module
- Sub Emitters module
- Texture Sheet Animation module
- Lights module
- Trails module
- Custom Data module
- Renderer module
- Particle System Force Field
- Particle Systems (Legacy, prior to release 3.5)
- Visual Effects Reference
- Mesh Components
- Texture Components
- Rendering Components
- Rendering Pipeline Details
- Graphics HOWTOs
- How do I Import Alpha Textures?
- How do I Make a Skybox?
- How do I make a Mesh Particle Emitter? (Legacy Particle System)
- How do I make a Spot Light Cookie?
- How do I fix the rotation of an imported model?
- Water in Unity
- Art Asset best practice guide
- Importing models from 3D modeling software
- How to do Stereoscopic Rendering
- Graphics Tutorials
- Scriptable Render Pipeline
- Graphics Overview
- Physics
- Scripting
- Scripting Overview
- Creating and Using Scripts
- Variables and the Inspector
- Controlling GameObjects using components
- Event Functions
- Time and Framerate Management
- Creating and Destroying GameObjects
- Coroutines
- Namespaces
- Attributes
- Order of Execution for Event Functions
- Understanding Automatic Memory Management
- Platform dependent compilation
- Special folders and script compilation order
- Script compilation and assembly definition files
- Managed code stripping
- .NET profile support
- Referencing additional class library assemblies
- Stable scripting runtime: known limitations
- Generic Functions
- Scripting restrictions
- Script Serialization
- UnityEvents
- What is a Null Reference Exception?
- Important Classes
- Vector Cookbook
- Scripting Tools
- Event System
- C# Job System
- Scripting Overview
- Multiplayer and Networking
- Multiplayer Overview
- Setting up a multiplayer project
- Using the Network Manager
- Using the Network Manager HUD
- The Network Manager HUD in LAN mode
- The Network Manager HUD in Matchmaker mode
- Converting a single-player game to Unity Multiplayer
- Debugging Information
- The Multiplayer High Level API
- Multiplayer Component Reference
- Multiplayer Classes Reference
- UnityWebRequest
- Audio
- Audio Overview
- Audio files
- Tracker Modules
- Audio Mixer
- Native Audio Plugin SDK
- Audio Profiler
- Ambisonic Audio
- Audio Reference
- Audio Clip
- Audio Listener
- Audio Source
- Audio Mixer
- Audio Filters
- Audio Effects
- Audio Low Pass Effect
- Audio High Pass Effect
- Audio Echo Effect
- Audio Flange Effect
- Audio Distortion Effect
- Audio Normalize Effect
- Audio Parametric Equalizer Effect
- Audio Pitch Shifter Effect
- Audio Chorus Effect
- Audio Compressor Effect
- Audio SFX Reverb Effect
- Audio Low Pass Simple Effect
- Audio High Pass Simple Effect
- Reverb Zones
- Microphone
- Audio Settings
- Animation
- Animation System Overview
- Animation Clips
- Animator Controllers
- Retargeting of Humanoid animations
- Performance and optimization
- Animation Reference
- Animation FAQ
- Playables API
- A Glossary of animation terms
- Timeline
- UI
- Navigation and Pathfinding
- Navigation Overview
- Navigation System in Unity
- Inner Workings of the Navigation System
- Building a NavMesh
- NavMesh building components
- Advanced NavMesh Bake Settings
- Creating a NavMesh Agent
- Creating a NavMesh Obstacle
- Creating an Off-mesh Link
- Building Off-Mesh Links Automatically
- Building Height Mesh for Accurate Character Placement
- Navigation Areas and Costs
- Loading Multiple NavMeshes using Additive Loading
- Using NavMesh Agent with Other Components
- Navigation Reference
- Navigation How-Tos
- Navigation Overview
- Unity Services
- Setting up your project for Unity Services
- Unity Organizations
- Unity Ads
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Analytics Overview
- Setting Up Analytics
- Analytics Dashboard
- Analytics events
- Funnels
- Remote Settings
- Unity Analytics A/B Testing
- Monetization
- User Attributes
- Unity Analytics Raw Data Export
- Data reset
- Upgrading Unity Analytics
- COPPA Compliance
- Unity Analytics and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Analytics Metrics, Segments, and Terminology
- Unity Cloud Build
- Automated Build Generation
- Supported platforms
- Supported versions of Unity
- Version control systems
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Using Apache Subversion (SVN) with Unity Cloud Build
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Perforce
- Using the Unity Editor to configure Unity Cloud Build for Perforce
- Building for iOS
- Advanced options
- Build manifest
- Cloud Build REST API
- Unity IAP
- Setting up Unity IAP
- Cross Platform Guide
- Codeless IAP
- Defining products
- Subscription Product support
- Initialization
- Browsing Product Metadata
- Initiating Purchases
- Processing Purchases
- Handling purchase failures
- Restoring Transactions
- Purchase Receipts
- Receipt validation
- Store Extensions
- Cross-store installation issues with Android in-app purchase stores
- Store Guides
- Implementing a Store
- IAP Promo
- Unity Collaborate
- Setting up Unity Collaborate
- Adding team members to your Unity Project
- Viewing history
- Enabling Cloud Build with Collaborate
- Managing Unity Editor versions
- Reverting files
- Resolving file conflicts
- Excluding Assets from publishing to Collaborate
- Publishing individual files to Collaborate
- Restoring previous versions of a project
- In-Progress edit notifications
- Managing cloud storage
- Moving your Project to another version control system
- Collaborate troubleshooting tips
- Unity Cloud Diagnostics
- Unity Integrations
- Multiplayer Services
- XR
- XR SDKs
- Google VR
- Vuforia
- Windows Mixed Reality
- Unity XR input
- XR API reference
- Mixed Reality Devices
- VR overview
- VR devices
- Single Pass Stereo rendering (Double-Wide rendering)
- VR Audio Spatializers
- VR frame timing
- XR SDKs
- Open-source repositories
- Asset Store Publishing
- Platform-specific
- Standalone
- macOS
- Apple TV
- WebGL
- Player settings for the WebGL platform
- Getting started with WebGL development
- WebGL Browser Compatibility
- Building and running a WebGL project
- WebGL: Deploying compressed builds
- Debugging and troubleshooting WebGL builds
- WebGL Graphics
- WebGL Networking
- Using Audio In WebGL
- WebGL performance considerations
- Memory in WebGL
- WebGL: Interacting with browser scripting
- Using WebGL Templates
- Cursor locking and full-screen mode in WebGL
- Input in WebGL
- iOS
- Getting started with iOS development
- Player settings for the iOS platform
- iOS 2D Texture Overrides
- Upgrading to 64-bit iOS
- iOS Advanced Topics
- Features currently not supported by Unity iOS
- Troubleshooting on iOS devices
- Reporting crash bugs on iOS
- Android
- Getting started with Android development
- Android environment setup
- Unity Remote
- Android Remote (DEPRECATED)
- Troubleshooting Android development
- Building apps for Android
- Reporting crash bugs under Android
- Support for APK expansion files (OBB)
- Android Scripting
- Building and using plug-ins for Android
- Customizing an Android Splash Screen
- Single-Pass Stereo Rendering for Android
- Player settings for the Android platform
- Android 2D Textures Overrides
- Gradle for Android
- Android Manifest
- Getting started with Android development
- Windows
- Windows General
- Universal Windows Platform
- Getting Started
- Universal Windows Platform: Deployment
- Universal Windows Platform: Profiler
- Universal Windows Platform: Command line arguments
- Universal Windows Platform: Association launching
- AppCallbacks class
- Universal Windows Platform: WinRT API in C# scripts
- Player settings for the Universal Windows platform
- Scripting Backends
- FAQ
- Universal Windows Platform: Examples
- Universal Windows Platform: Code snippets
- Known issues
- Web Player
- Mobile Developer Checklist
- Experimental
- Legacy Topics
- Best practice guides
- Expert guides
- New in Unity 2018.3
- Packages Documentation
- Glossary
GameObject
Switch to Scripting
GameObjects are the fundamental objects in Unity that represent characters, props and scenery. They do not accomplish much in themselves but they act as containers for ComponentsA functional part of a GameObject. A GameObject can contain any number of components. Unity has many built-in components, and you can create your own by writing scripts that inherit from MonoBehaviour. More info
See in Glossary, which implement the real functionality.
For example, a Light object is created by attaching a Light component to a GameObject.
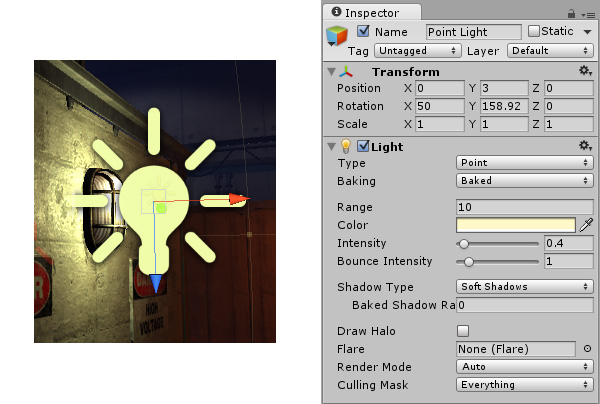
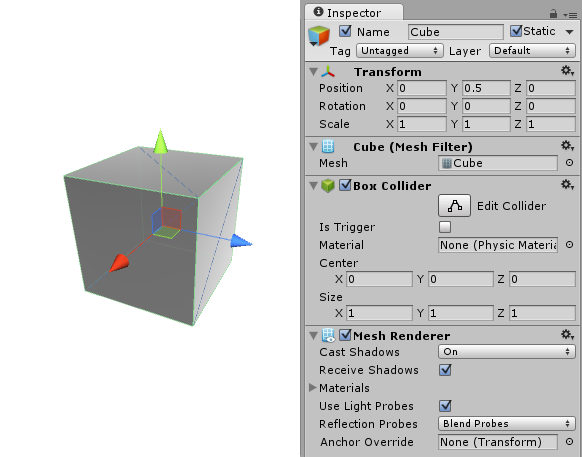
A solid cube object has a Mesh FilterA mesh component that takes a mesh from your assets and passes it to the Mesh Renderer for rendering on the screen. More info
See in Glossary and MeshThe main graphics primitive of Unity. Meshes make up a large part of your 3D worlds. Unity supports triangulated or Quadrangulated polygon meshes. Nurbs, Nurms, Subdiv surfaces must be converted to polygons. More info
See in Glossary Renderer component, to draw the surface of the cube, and a Box ColliderAn invisible shape that is used to handle physical collisions for an object. A collider doesn’t need to be exactly the same shape as the object’s mesh - a rough approximation is often more efficient and indistinguishable in gameplay. More info
See in Glossary component to represent the object’s solid volume in terms of physics.
Details
A GameObject always has a Transform component attached (to represent position and orientation) and it is not possible to remove this. The other components that give the object its functionality can be added from the editor’s Component menu or from a script. There are also many useful pre-constructed objects (primitive shapes, Cameras, etc) available on the GameObject > 3D Object menu, see Primitive Objects.
Since GameObjects are a very important part of Unity, there is a GameObjects section in the manual with extensive detail about them. You can find out more about controlling GameObjects from scriptsA piece of code that allows you to create your own Components, trigger game events, modify Component properties over time and respond to user input in any way you like. More info
See in Glossary on the GameObject scripting reference page.
Did you find this page useful? Please give it a rating:
Thanks for rating this page!
What kind of problem would you like to report?
- This page needs code samples
- Code samples do not work
- Information is missing
- Information is incorrect
- Information is unclear or confusing
- There is a spelling/grammar error on this page
- Something else
Is something described here not working as you expect it to? It might be a Known Issue. Please check with the Issue Tracker at issuetracker.unity3d.com.
Thanks for letting us know! This page has been marked for review based on your feedback.
If you have time, you can provide more information to help us fix the problem faster.
Provide more information
You've told us this page needs code samples. If you'd like to help us further, you could provide a code sample, or tell us about what kind of code sample you'd like to see:
You've told us there are code samples on this page which don't work. If you know how to fix it, or have something better we could use instead, please let us know:
You've told us there is information missing from this page. Please tell us more about what's missing:
You've told us there is incorrect information on this page. If you know what we should change to make it correct, please tell us:
You've told us this page has unclear or confusing information. Please tell us more about what you found unclear or confusing, or let us know how we could make it clearer:
You've told us there is a spelling or grammar error on this page. Please tell us what's wrong:
You've told us this page has a problem. Please tell us more about what's wrong:
Thanks for helping to make the Unity documentation better!