Unity Manual
- Unity User Manual 2021.2
- New in Unity 2021.2
- Packages and feature sets
- Released packages
- 2D Animation
- 2D Pixel Perfect
- 2D PSD Importer
- 2D SpriteShape
- 2D Tilemap Extras
- Adaptive Performance
- Addressables
- Advertisement
- Alembic
- Analytics Library
- Android Logcat
- Animation Rigging
- AR Foundation
- ARCore XR Plugin
- ARKit Face Tracking
- ARKit XR Plugin
- Burst
- Cinemachine
- Code Coverage
- Editor Coroutines
- FBX Exporter
- In App Purchasing
- Input System
- iOS 14 Advertising Support
- JetBrains Rider Editor
- Live Capture
- Localization
- Magic Leap XR Plugin
- Mathematics
- ML Agents
- Mobile Notifications
- Oculus XR Plugin
- OpenXR Plugin
- Polybrush
- Post Processing
- ProBuilder
- Profile Analyzer
- Recorder
- Remote Config
- Scriptable Build Pipeline
- Sequences
- Terrain Tools
- Test Framework
- TextMeshPro
- Timeline
- Tutorial Authoring Tools
- Tutorial Framework
- Unity Distribution Portal
- Unity Profiling Core API
- Version Control
- Visual Scripting
- Visual Studio Code Editor
- Visual Studio Editor
- WebGL Publisher
- XR Plugin Management
- Release Candidates
- Pre-release packages
- Core packages
- Built-in packages
- AI
- Android JNI
- Animation
- Asset Bundle
- Audio
- Cloth
- Director
- Image Conversion
- IMGUI
- JSONSerialize
- NVIDIA
- Particle System
- Physics
- Physics 2D
- Screen Capture
- Terrain
- Terrain Physics
- Tilemap
- UI
- UIElements
- Umbra
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Web Request
- Unity Web Request Asset Bundle
- Unity Web Request Audio
- Unity Web Request Texture
- Unity Web Request WWW
- Vehicles
- Video
- VR
- Wind
- XR
- Experimental packages
- Packages by keywords
- Unity's Package Manager
- Concepts
- Configuration
- Package Manager window
- List view
- Details view
- Features (detail) view
- Finding packages and feature sets
- Adding and removing
- Installing a feature set
- Installing from a registry
- Installing a package from a local folder
- Installing a package from a local tarball file
- Installing from a Git URL
- Adding a registry package by name
- Removing an installed package
- Disabling a built-in package
- Importing an Asset Store package
- Switching to another package version
- Updating your Asset Store package
- Finding package documentation
- Inspecting packages
- Scripting API for packages
- Scoped Registries
- Resolution and conflict
- Project manifest
- Troubleshooting
- Creating custom packages
- Feature sets
- Released packages
- Working in Unity
- Installing Unity
- Upgrading Unity
- API updater
- Upgrading to Unity 2021.2
- Upgrading to Unity 2021.1
- Upgrading to Unity 2020 LTS
- Upgrading to Unity 2019 LTS
- Upgrading to Unity 2018 LTS
- Legacy Upgrade Guides
- Unity's interface
- Quickstart guides
- Creating Gameplay
- Editor Features
- 2D and 3D mode settings
- Preferences
- Shortcuts Manager
- Build Settings
- Incremental build pipeline
- Project Settings
- Visual Studio C# integration
- RenderDoc Integration
- Editor Analytics
- Check For Updates
- IME in Unity
- Version Control
- Plastic SCM plugin for Unity
- Upgrade from Collaborate to Plastic SCM
- Upgrade from Collaborate without moving the history
- Create projects
- Export Collaborate projects
- Plastic SCM plugin for Unity
- Add team members
- Reconnect Unity Cloud Build
- Add integrations
- Getting started with Plastic SCM
- Using external version control systems with Unity
- Smart merge
- Safe Mode
- Command line arguments
- Text-Based Scene Files
- Troubleshooting The Editor
- Analysis
- Memory in Unity
- Profiler overview
- Profiling your application
- Common Profiler markers
- The Profiler window
- Asset Loading Profiler module
- Audio Profiler module
- CPU Usage Profiler module
- File Access Profiler module
- Global Illumination Profiler module
- GPU Usage Profiler module
- Memory Profiler module
- Physics Profiler module
- 2D Physics Profiler module
- Rendering Profiler module
- UI and UI Details Profiler
- Video Profiler module
- Virtual Texturing Profiler module
- Customizing the Profiler
- Low-level native plug-in Profiler API
- Profiling tools
- Log files
- Understanding optimization in Unity
- Asset loading metrics
- Asset Workflow
- Input
- 2D
- 2D game development quickstart guide
- 2D Sorting
- Sprites
- Tilemap
- Physics Reference 2D
- Graphics
- Render pipelines
- Render pipelines introduction
- Render pipeline feature comparison
- How to get, set, and configure the active render pipeline
- Choosing and configuring a render pipeline and lighting solution
- Using the Built-in Render Pipeline
- Using the Universal Render Pipeline
- Using the High Definition Render Pipeline
- Scriptable Render Pipeline fundamentals
- Creating a custom render pipeline
- Cameras
- Lighting
- Introduction to lighting
- Light sources
- Shadows
- The Lighting window
- Lighting Settings Asset
- The Light Explorer window
- Lightmapping
- The Progressive Lightmapper
- Lightmapping using Enlighten Baked Global Illumination
- Lightmapping: Getting started
- Lightmap Parameters Asset
- Directional Mode
- Lightmaps and LOD
- Ambient occlusion
- Lightmaps: Technical information
- Lightmapping and shaders
- Lightmap UVs
- Lightmap seam stitching
- Custom fall-off
- Realtime Global Illumination using Enlighten
- Light Probes
- Reflection Probes
- Precomputed lighting data
- Scene View Draw Modes for lighting
- Models
- Meshes
- Textures
- Importing Textures
- Texture formats
- Mipmaps
- Render Texture
- Custom Render Textures
- Movie Textures
- 3D textures
- Texture arrays
- Cubemaps
- Cubemap arrays
- Streaming Virtual Texturing
- Streaming Virtual Texturing requirements and compatibility
- How Streaming Virtual Texturing works
- Enabling Streaming Virtual Texturing in your project
- Using Streaming Virtual Texturing in Shader Graph
- Cache Management for Virtual Texturing
- Marking textures as "Virtual Texturing Only"
- Virtual Texturing error material
- Sparse Textures
- Loading texture and mesh data
- Shaders
- Shaders core concepts
- Built-in shaders
- Standard Shader
- Standard Particle Shaders
- Autodesk Interactive shader
- Legacy Shaders
- Using Shader Graph
- Writing shaders
- Writing shaders overview
- ShaderLab
- ShaderLab: defining a Shader object
- ShaderLab: defining a SubShader
- ShaderLab: defining a Pass
- ShaderLab: adding shader programs
- ShaderLab: specifying package requirements
- ShaderLab: commands
- ShaderLab: grouping commands with the Category block
- ShaderLab command: AlphaToMask
- ShaderLab command: Blend
- ShaderLab command: BlendOp
- ShaderLab command: ColorMask
- ShaderLab command: Conservative
- ShaderLab command: Cull
- ShaderLab command: Offset
- ShaderLab command: Stencil
- ShaderLab command: UsePass
- ShaderLab command: GrabPass
- ShaderLab command: ZClip
- ShaderLab command: ZTest
- ShaderLab command: ZWrite
- ShaderLab legacy functionality
- HLSL in Unity
- GLSL in Unity
- Example shaders
- Writing Surface Shaders
- Writing shaders for different graphics APIs
- Understanding shader performance
- Materials
- Visual effects
- Post-processing and full-screen effects
- Particle systems
- Choosing your particle system solution
- Built-in Particle System
- Using the Built-in Particle System
- Particle System vertex streams and Standard Shader support
- Particle System GPU Instancing
- Particle System C# Job System integration
- Components and Modules
- Particle System
- Particle System modules
- Main module
- Emission module
- Shape module
- Velocity over Lifetime module
- Noise module
- Limit Velocity over Lifetime module
- Inherit Velocity module
- Lifetime by Emitter Speed module
- Force over Lifetime module
- Color over Lifetime module
- Color by Speed module
- Size over Lifetime module
- Size by Speed module
- Rotation over Lifetime module
- Rotation by Speed module
- External Forces module
- Collision module
- Triggers module
- Sub Emitters module
- Texture Sheet Animation module
- Lights module
- Trails module
- Custom Data module
- Renderer module
- Particle System Force Field
- Visual Effect Graph
- Decals and projectors
- Lens flares and halos
- Lines, trails, and billboards
- Sky
- Color
- Graphics API support
- Graphics performance and profiling
- Render pipelines
- World building
- Physics
- Scripting
- Setting Up Your Scripting Environment
- Scripting concepts
- Important Classes
- Important Classes - GameObject
- Important Classes - MonoBehaviour
- Important Classes - Object
- Important Classes - Transform
- Important Classes - Vectors
- Important Classes - Quaternion
- ScriptableObject
- Important Classes - Time
- Important Classes - Mathf
- Important Classes - Random
- Important Classes - Debug
- Important Classes - Gizmos & Handles
- Unity architecture
- Plug-ins
- C# Job System
- Multiplayer and Networking
- Multiplayer Overview
- Setting up a multiplayer project
- Using the Network Manager
- Using the Network Manager HUD
- The Network Manager HUD in LAN mode
- The Network Manager HUD in Matchmaker mode
- Converting a single-player game to Unity Multiplayer
- Debugging Information
- Multiplayer Component Reference
- Multiplayer Classes Reference
- Multiplayer Encryption Plug-ins
- UnityWebRequest
- Audio
- Audio Overview
- Audio files
- Tracker Modules
- Audio Mixer
- Native Audio Plugin SDK
- Audio Profiler
- Ambisonic Audio
- Audio Reference
- Audio Clip
- Audio Listener
- Audio Source
- Audio Mixer
- Audio Filters
- Audio Effects
- Audio Low Pass Effect
- Audio High Pass Effect
- Audio Echo Effect
- Audio Flange Effect
- Audio Distortion Effect
- Audio Normalize Effect
- Audio Parametric Equalizer Effect
- Audio Pitch Shifter Effect
- Audio Chorus Effect
- Audio Compressor Effect
- Audio SFX Reverb Effect
- Audio Low Pass Simple Effect
- Audio High Pass Simple Effect
- Reverb Zones
- Microphone
- Audio Settings
- Video overview
- Animation
- Animation System Overview
- Rotation in animations
- Animation Clips
- Animator Controllers
- Retargeting of Humanoid animations
- Performance and optimization
- Animation Reference
- Animation FAQ
- Playables API
- A Glossary of animation terms
- Create user interfaces (UI)
- Comparison of UI systems in Unity
- UI Toolkit
- Get started with UI Toolkit
- The Visual Tree
- The Layout Engine
- UI Builder
- Structure UI with UXML
- Style UI with USS
- Control behavior with Events
- Controls
- Bindings
- ViewData persistence
- Manage UI asset references from C# scripts
- Examples
- Migration guides
- Unity UI
- Immediate Mode GUI (IMGUI)
- Navigation and Pathfinding
- Navigation Overview
- Navigation System in Unity
- Inner Workings of the Navigation System
- Building a NavMesh
- NavMesh building components
- Advanced NavMesh Bake Settings
- Creating a NavMesh Agent
- Creating a NavMesh Obstacle
- Creating an Off-mesh Link
- Building Off-Mesh Links Automatically
- Building Height Mesh for Accurate Character Placement
- Navigation Areas and Costs
- Loading Multiple NavMeshes using Additive Loading
- Using NavMesh Agent with Other Components
- Navigation Reference
- Navigation How-Tos
- Navigation Overview
- Unity Services
- Setting up your project for Unity services
- Unity Organizations
- Unity Ads
- Legacy Analytics
- Legacy Analytics Overview
- Setting Up Legacy Analytics
- Legacy Analytics Dashboard
- Legacy Analytics Events
- Funnels
- Remote Settings
- Unity Analytics A/B Testing
- Monetization
- User Attributes
- Unity Analytics Raw Data Export
- Data reset
- Upgrading Unity Analytics
- COPPA Compliance
- Unity Analytics and the EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
- Unity Analytics and PIPL
- Analytics Metrics, Segments, and Terminology
- Unity Cloud Build
- Setting up Cloud Build
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Cloud Build for Git
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Cloud Build for Mercurial
- Using Apache Subversion (SVN) with Unity Cloud Build
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Cloud Build for Perforce
- Using the Unity Developer Dashboard to configure Unity Cloud Build for Plastic
- Building for iOS
- Advanced options
- Using Addressables in Unity Cloud Build
- Build manifest
- Scheduled builds
- Cloud Build REST API
- Setting up Cloud Build
- Unity Cloud Content Delivery
- Unity IAP
- Setting up Unity IAP
- Cross Platform Guide
- Codeless IAP
- Defining products
- Subscription Product support
- Initialization
- Browsing Product Metadata
- Initiating Purchases
- Processing Purchases
- Handling purchase failures
- Restoring Transactions
- Purchase Receipts
- Receipt validation
- Store Extensions
- Cross-store installation issues with Android in-app purchase stores
- Store Guides
- Implementing a Store
- Unity Collaborate
- Setting up Unity Collaborate
- Adding team members to your Unity project
- Viewing history
- Enabling Cloud Build with Collaborate
- Managing Unity Editor versions
- Reverting files
- Resolving file conflicts
- Excluding Assets from publishing to Collaborate
- Publishing individual files to Collaborate
- Restoring previous versions of a project
- In-Progress edit notifications
- Managing cloud storage
- Moving your Project to another version control system
- Unity Accelerator
- Collaborate troubleshooting tips
- Unity Cloud Diagnostics
- Unity Integrations
- Multiplayer Services
- Unity Distribution Portal
- XR
- Getting started with AR development in Unity
- Getting started with VR development in Unity
- XR Plug-in Framework
- Configuring your Unity Project for XR
- Universal Render Pipeline compatibility in XR
- Unity VR project template
- Unity AR project template
- XR API reference
- Single Pass Stereo rendering (Double-Wide rendering)
- VR Audio Spatializers
- VR frame timing
- Unity XR SDK
- Open-source repositories
- Unity's Asset Store
- Asset Store packages
- Publishing to the Asset Store
- Creating your Publisher Account
- Creating a new package draft
- Deleting a package draft
- Uploading assets to your package
- Filling in the package details
- Submitting your package for approval
- Viewing the status of your Asset Store submissions
- Collecting revenue
- Providing support to your customers
- Adding tags to published packages
- Connecting your account to Google Analytics
- Promoting your Assets
- Refunding your customers
- Upgrading packages
- Deprecating your Assets
- Issuing vouchers
- Managing your publishing team
- Asset Store Publisher portal
- Platform development
- Using Unity as a Library in other applications
- Deep linking
- Xcode frame debugger Unity integration
- Android
- Introducing Android
- Getting started with Android
- Developing for Android
- Android mobile scripting
- Input for Android devices
- Android application size restrictions
- Graphics for Android
- Testing and debugging
- Building and using plug-ins for Android
- Integrating Unity into Android applications
- Deep linking on Android
- Android thread configuration
- Device features and permissions
- Building and delivering for Android
- Troubleshooting Android development
- Reporting crash bugs under Android
- Chrome OS
- iOS
- Integrating Unity into native iOS applications
- Getting started with iOS development
- iOS build settings
- iOS Player settings
- iOS Advanced Topics
- Troubleshooting on iOS devices
- Reporting crash bugs on iOS
- Linux
- macOS
- tvOS
- WebGL
- Windows
- Universal Windows Platform
- Getting Started
- Universal Windows Platform: Deployment
- Universal Windows Platform (UWP) build settings
- Windows Device Portal Deployment
- Universal Windows Platform: Profiler
- Universal Windows Platform: Command line arguments
- Universal Windows Platform: Association launching
- AppCallbacks class
- Universal Windows Platform: WinRT API in C# scripts
- Universal Windows Platform Player Settings
- Deep linking on Universal Windows Platform
- Universal Windows Platform: IL2CPP scripting back end
- FAQ
- Universal Windows Platform: Examples
- Universal Windows Platform: Code snippets
- Known issues
- Unity Search
- Legacy Topics
- Glossary
- Unity User Manual 2021.2
- Unity Search
- Search usage
- Filter searches
Filter searches
Filtering narrows the scope of your searches to specific providers. You can filter searches in the following ways:
Set up persistent search filters to control which providers Search uses for regular searches.
Use a Search Provider’s search token in the search field to only display results from that provider.
Limit your search results by using sub-filters and query operators and using the keywords available for your index.
See a list of additional search filters here.
Persistent search filters
You can temporarily toggle Search Providers on and off from the Filters pane. This can help reduce the number of items that a search returns, which is convenient if you already know what type of item you are looking for. The providers that are toggled on at any given time are the active Search Providers.
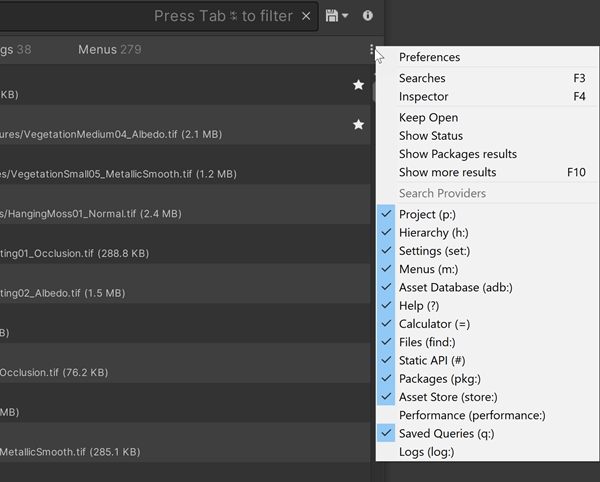
Search Providers drop-down menu
When you toggle Search Providers off in the Search Providers menu, Search “mutes” them rather than disabling them completely. Search Providers that perform background indexing or other hidden operations continue to do so when muted.
Note: To permanently toggle Search Providers on and off, change them in Search preferences.
To set persistent search filters:
- Choose Edit > Search All to launch Search, and in the Search Providers area select More Options (:)
- Enable or disable any Search Providers you want to include/exclude from subsequent searches.
Tip: You can use ↑ (up arrow) and ↓ (down arrow) to cycle through the available filters, and Space to toggle a filter.
Search tokens
Every Search Provider has a unique text string called a search token, also called a filter ID. When you prefix a search query with a provider’s search token, Search limits the scope of the search to that provider.
For example, p: is the search token for the Asset Search Provider. When you enter p:Player in the search field, Search searches for Assets that match the term “Player” (for example, assets with “Player” in their names).
See Search Providers for a list of search tokens for Search Providers.
See Additional search tokens for a list of search tokens for PrefabsAn asset type that allows you to store a GameObject complete with components and properties. The prefab acts as a template from which you can create new object instances in the scene. More info
See in Glossary
, Files, Types, Properties, and DependenciesIn the context of the Package Manager, a dependency is a specific package version (expressed in the form package_name@package_version) that a project or another package requires in order to work. Projects and packages use the dependencies attribute in their manifests to define the set of packages they require. For projects, these are considered direct dependencies; for packages, these are indirect, or transitive, dependencies. More info
See in Glossary searches.
Combining search tokens
You can combine search tokens to create more complex queries.
- The queries are written on one line with one character space between tokens.
- The character space between each new token is an “And” operation, so both filters must be true for the query to return a result. Add another operator (or, <, >) to return different results.
- If a Search Provider filter token (h:, p:) is used, it must be the first component in the query.
Here are a few examples:
| Query | Description |
|---|---|
h: t:meshrenderer p(castshadows)!="Off" |
Searches all static meshes in a SceneA Scene contains the environments and menus of your game. Think of each unique Scene file as a unique level. In each Scene, you place your environments, obstacles, and decorations, essentially designing and building your game in pieces. More info See in Glossary that cast a shadow. |
h: t:light p(color)=#FFFFFF p(intensity)>7.4 |
Searches all lights in a Scene with a specific color with brightness higher than 7.4. |
h: path:/Collectables t:collectable |
Find all objects with a component Collectable located in the path /Collectables.
|
Search expressions
Search expressions allow you to add to the search query language to express complex queries that cross-reference multiple providers, for example, to search for all objects in a scene that use a shaderA program that runs on the GPU. More info
See in Glossary that doesn’t compile. See Search expressions for more information.