Unity Manual
- Unity User Manual 2023.2
- New in Unity 2023.2
- Packages and feature sets
- Released packages
- 2D Animation
- 2D Aseprite Importer
- 2D Pixel Perfect
- 2D PSD Importer
- 2D SpriteShape
- 2D Tilemap Extras
- Adaptive Performance
- Addressables
- Addressables for Android
- Ads Mediation
- Advertisement Legacy
- AI Navigation
- Alembic
- Analytics
- Android Logcat
- Animation Rigging
- Apple ARKit XR Plugin
- AR Foundation
- Authentication
- Build Automation
- Burst
- CCD Management
- Cinemachine
- Cloud Diagnostics
- Cloud Save
- Code Coverage
- Collections
- Deployment
- Device Simulator Devices
- Economy
- Editor Coroutines
- FBX Exporter
- Friends
- Google ARCore XR Plugin
- In App Purchasing
- Input System
- iOS 14 Advertising Support
- JetBrains Rider Editor
- Leaderboards
- Live Capture
- Lobby
- Localization
- Magic Leap XR Plugin
- Matchmaker
- Mathematics
- Memory Profiler
- ML Agents
- Mobile Notifications
- Multiplayer Tools
- Netcode for GameObjects
- Oculus XR Plugin
- OpenXR Plugin
- Player Accounts
- Polybrush
- Post Processing
- ProBuilder
- Profile Analyzer
- Push Notifications
- Python Scripting
- Recorder
- Relay
- Remote Config
- Scriptable Build Pipeline
- Sequences
- Splines
- Sysroot Base
- Sysroot Linux x64
- System Metrics Mali
- Terrain Tools
- Test Framework
- Timeline
- Toolchain Linux x64
- Toolchain MacOS Linux x64
- Toolchain Win Linux x64
- Tutorial Authoring Tools
- Tutorial Framework
- Unity Distribution Portal
- Unity OpenXR Meta
- Unity Profiling Core API
- Unity Transport
- User Generated Content
- User Generated Content Bridge
- User Reporting
- Version Control
- Visual Scripting
- Visual Studio Editor
- WebGL Publisher
- XR Hands
- XR Interaction Toolkit
- XR Plugin Management
- ZivaRT Player
- Release candidates
- Pre-release packages
- Core packages
- Built-in packages
- Accessibility
- AI
- Android JNI
- Animation
- Asset Bundle
- Audio
- Cloth
- Director
- Image Conversion
- IMGUI
- JSONSerialize
- NVIDIA
- Particle System
- Physics
- Physics 2D
- Screen Capture
- Terrain
- Terrain Physics
- Tilemap
- UI
- UIElements
- Umbra
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Web Request
- Unity Web Request Asset Bundle
- Unity Web Request Audio
- Unity Web Request Texture
- Unity Web Request WWW
- Vehicles
- Video
- VR
- Wind
- XR
- Experimental packages
- Packages by keywords
- Deprecated packages
- Unity's Package Manager
- How Unity works with packages
- Concepts
- Configuration
- Package Manager window
- Access the Package Manager window
- Navigation panel
- List panel
- Details panel
- Features (details panel)
- Finding packages and feature sets
- Add and remove UPM packages or feature sets
- Install a feature set from the Unity registry
- Install a UPM package from a registry
- Install a UPM package from the Asset Store
- Install a UPM package from a local folder
- Install a UPM package from a local tarball file
- Install a UPM package from a Git URL
- Install a UPM package by name
- Remove a UPM package from a project
- Switch to another version of a UPM package
- Add and remove asset packages
- Disable a built-in package
- Perform an action on multiple packages
- Finding package documentation
- Inspecting packages
- Scripting API for packages
- Scoped registries
- Resolution and conflict
- Project manifest
- Troubleshooting
- Creating custom packages
- Feature sets
- Released packages
- Install Unity
- Licenses and activation
- Upgrade Unity
- Create with Unity
- 2D or 3D projects
- Unity's interface
- The Project window
- The Scene view
- The Game view
- Device Simulator
- The Hierarchy window
- The Inspector window
- Editing properties
- The Toolbar
- The status bar
- The Background Tasks window
- Console Window
- Additional windows
- Undo
- Search in the Editor
- Customizing your workspace
- Unity shortcuts
- Quickstart guides
- Advanced best practice guides
- Create Gameplay
- Editor Features
- Analysis
- Memory in Unity
- Profiler overview
- Profiling your application
- Common Profiler markers
- The Profiler window
- Asset Loading Profiler module
- Audio Profiler module
- CPU Usage Profiler module
- File Access Profiler module
- Global Illumination Profiler module
- GPU Usage Profiler module
- Highlights Profiler Module
- Memory Profiler module
- Physics Profiler module
- Physics 2D Profiler module
- Rendering Profiler module
- UI and UI Details Profiler
- Video Profiler module
- Virtual Texturing Profiler module
- Customizing the Profiler
- Low-level native plug-in Profiler API
- Profiling tools
- Log files
- Understanding optimization in Unity
- Asset loading metrics
- Asset workflow
- Input
- 2D game development
- Introduction to 2D
- 2D game development quickstart guide
- 2D Sorting
- Work with sprites
- Tilemaps
- Essential tilemap steps and tools
- Active brush
- Create Tilemaps
- Create Tiles
- Create a Tile Palette
- Tile Palette editor tools
- Using the Select tool
- Move selected tiles with the Move tool
- Paint tiles with the Paint tool
- Use the Box Fill tool to fill an area with duplicated tiles
- Select tiles on the tilemap or Tile Palette with the Pick tool
- Remove tiles from the tilemap with the Eraser tool
- Fill an empty area with tiles with the Flood Fill tool
- Brush Picks
- Tilemap Collider 2D component reference
- Hexagonal Tilemaps
- Isometric Tilemaps
- Scriptable Tiles
- Scriptable Brushes
- Tile Palette visual elements
- Tilemap component reference
- Grid component reference
- Tilemap Renderer component reference
- Tile asset reference
- Tile Palette preferences reference
- Tile Palette editor reference
- Essential tilemap steps and tools
- Physics 2D Reference
- Graphics
- Render pipelines
- Render pipelines introduction
- Render pipeline feature comparison
- How to get, set, and configure the active render pipeline
- Choosing and configuring a render pipeline and lighting solution
- Using the Built-in Render Pipeline
- Using the Universal Render Pipeline
- Using the High Definition Render Pipeline
- Scriptable Render Pipeline fundamentals
- Creating a custom render pipeline
- Cameras
- Lighting
- Introduction to lighting
- Light sources
- Shadows
- The Lighting window
- Lighting Settings Asset
- The Light Explorer window
- Lightmapping
- Realtime Global Illumination using Enlighten
- Light Probes
- Reflection Probes
- Precomputed lighting data
- Debug Draw Modes for lighting
- Models
- Meshes
- Textures
- Importing Textures
- Texture Import Settings
- Default Import Settings reference
- Normal map Import Settings reference
- Editor GUI and Legacy GUI Import Settings reference
- Sprite (2D and UI) Import Settings reference
- Cursor Import Settings reference
- Cookie Import Settings reference
- Lightmap Import Settings reference
- Directional Lightmap Import Settings reference
- Shadowmask Import Settings reference
- Single Channel Import Settings reference
- Texture Import Settings
- Texture formats
- Mipmaps
- Render Texture
- Custom Render Textures
- Movie Textures
- 3D textures
- Texture arrays
- Cubemaps
- Cubemap arrays
- Streaming Virtual Texturing
- Streaming Virtual Texturing requirements and compatibility
- How Streaming Virtual Texturing works
- Enabling Streaming Virtual Texturing in your project
- Using Streaming Virtual Texturing in Shader Graph
- Cache Management for Virtual Texturing
- Marking textures as "Virtual Texturing Only"
- Virtual Texturing error material
- Sparse Textures
- Loading texture and mesh data
- Importing Textures
- Shaders
- Shaders core concepts
- Built-in shaders
- Standard Shader
- Standard Particle Shaders
- Autodesk Interactive shader
- Legacy Shaders
- Using Shader Graph
- Writing shaders
- Writing shaders overview
- ShaderLab
- ShaderLab: defining a Shader object
- ShaderLab: defining a SubShader
- ShaderLab: defining a Pass
- ShaderLab: adding shader programs
- ShaderLab: specifying package requirements
- ShaderLab: commands
- ShaderLab: grouping commands with the Category block
- ShaderLab command: AlphaToMask
- ShaderLab command: Blend
- ShaderLab command: BlendOp
- ShaderLab command: ColorMask
- ShaderLab command: Conservative
- ShaderLab command: Cull
- ShaderLab command: Offset
- ShaderLab command: Stencil
- ShaderLab command: UsePass
- ShaderLab command: GrabPass
- ShaderLab command: ZClip
- ShaderLab command: ZTest
- ShaderLab command: ZWrite
- ShaderLab legacy functionality
- HLSL in Unity
- GLSL in Unity
- Example shaders
- Writing Surface Shaders
- Writing shaders for different graphics APIs
- Understanding shader performance
- Materials
- Visual effects
- Post-processing and full-screen effects
- Particle systems
- Choosing your particle system solution
- Built-in Particle System
- Using the Built-in Particle System
- Particle System vertex streams and Standard Shader support
- Particle System GPU Instancing
- Particle System C# Job System integration
- Components and Modules
- Particle System
- Particle System modules
- Main module
- Emission module
- Shape module
- Velocity over Lifetime module
- Noise module
- Limit Velocity over Lifetime module
- Inherit Velocity module
- Lifetime by Emitter Speed module
- Force over Lifetime module
- Color over Lifetime module
- Color by Speed module
- Size over Lifetime module
- Size by Speed module
- Rotation over Lifetime module
- Rotation by Speed module
- External Forces module
- Collision module
- Triggers module
- Sub Emitters module
- Texture Sheet Animation module
- Lights module
- Trails module
- Custom Data module
- Renderer module
- Particle System Force Field
- Visual Effect Graph
- Decals and projectors
- Lens flares and halos
- Lines, trails, and billboards
- Sky
- Color
- Graphics API support
- Graphics performance and profiling
- Render pipelines
- World building
- Physics
- Built-in 3D Physics
- Character control
- Rigidbody physics
- Collision
- Joints
- Articulations
- Ragdoll physics
- Cloth
- Multi-scene physics
- Built-in 3D Physics
- Scripting
- Setting Up Your Scripting Environment
- Scripting concepts
- Important Classes
- Unity architecture
- Plug-ins
- Job system
- Unity Properties
- UnityWebRequest
- Multiplayer
- Audio
- Audio overview
- Audio files
- Tracker Modules
- Audio Mixer
- Native audio plug-in SDK
- Audio playlist randomization
- Audio Profiler
- Ambisonic Audio
- Audio Reference
- Audio Clip
- Audio Listener
- Audio Source
- Audio Mixer
- Audio Filters
- Audio Effects
- Audio Low Pass Effect
- Audio High Pass Effect
- Audio Echo Effect
- Audio Flange Effect
- Audio Distortion Effect
- Audio Normalize Effect
- Audio Parametric Equalizer Effect
- Audio Pitch Shifter Effect
- Audio Chorus Effect
- Audio Compressor Effect
- Audio SFX Reverb Effect
- Audio Low Pass Simple Effect
- Audio High Pass Simple Effect
- Reverb Zones
- Microphone
- Audio Settings
- Video overview
- Animation
- Animation system overview
- Rotation in animations
- Animation Clips
- Animator Controllers
- Retargeting of Humanoid animations
- Performance and optimization
- Animation Reference
- Animation FAQ
- Playables API
- A Glossary of animation terms
- Legacy Animation system
- User interface (UI)
- Comparison of UI systems in Unity
- UI Toolkit
- Get started with UI Toolkit
- UI Builder
- Structure UI
- The visual tree
- Structure UI with UXML
- Structure UI with C# scripts
- Custom controls
- Best practices for managing elements
- Encapsulate UXML documents with logic
- UXML elements reference
- UXML element BindableElement
- UXML element VisualElement
- UXML element BoundsField
- UXML element BoundsIntField
- UXML element Box
- UXML element Button
- UXML element ColorField
- UXML element CurveField
- UXML element DoubleField
- UXML element DropdownField
- UXML element EnumField
- UXML element EnumFlagsField
- UXML element FloatField
- UXML element Foldout
- UXML element GradientField
- UXML element GroupBox
- UXML element Hash128Field
- UXML element HelpBox
- UXML element IMGUIContainer
- UXML element Image
- UXML element InspectorElement
- UXML element IntegerField
- UXML element Label
- UXML element LayerField
- UXML element LayerMaskField
- UXML element LongField
- UXML element ListView
- UXML element MaskField
- UXML element MinMaxSlider
- UXML element MultiColumnListView
- UXML element MultiColumnTreeView
- UXML element ObjectField
- UXML element PopupWindow
- UXML element ProgressBar
- UXML element PropertyField
- UXML element RadioButton
- UXML element RadioButtonGroup
- UXML element RectField
- UXML element RectIntField
- UXML element RepeatButton
- UXML element RenderingLayerMaskField
- UXML element ScrollView
- UXML element Scroller
- UXML element Slider
- UXML element SliderInt
- UXML element Tab
- UXML element TabView
- UXML element TagField
- UXML element TextElement
- UXML element TextField
- UXML element TemplateContainer
- UXML element Toggle
- UXML element ToggleButtonGroup
- UXML element Toolbar
- UXML element ToolbarBreadcrumbs
- UXML element ToolbarButton
- UXML element ToolbarMenu
- UXML element ToolbarPopupSearchField
- UXML element ToolbarSearchField
- UXML element ToolbarSpacer
- UXML element ToolbarToggle
- UXML element TreeView
- UXML element TwoPaneSplitView
- UXML element UnsignedLongField
- UXML element UnsignedIntegerField
- UXML element Vector2Field
- UXML element Vector2IntField
- UXML element Vector3Field
- UXML element Vector3IntField
- UXML element Vector4Field
- Structure UI examples
- Create list and tree views
- Create a complex list view
- Create a list view runtime UI
- Wrap content inside a scroll view
- Create a tabbed menu
- Create a pop-up window
- Use Toggle to create a conditional UI
- Create a custom control with two attributes
- Create a slide toggle custom control
- Create a bindable custom control
- Create a custom style for a custom control
- Create a drag-and-drop list and tree views between windows
- Create an aspect ratio custom control
- Style UI
- UI Toolkit Debugger
- Control behavior with events
- UI Renderer
- Data binding
- Comparison of the binding systems
- Runtime data binding
- SerializedObject data binding
- Introduction to SerializedObject data binding
- Bindable elements reference
- Bindable data types and fields
- Binding system implementation details
- Binding examples
- Bind with binding path in C# script
- Bind without the binding path
- Bind with UXML and C# script
- Create a binding with the Inspector
- Bind to nested properties
- Bind to a UXML template
- Receive callbacks when a bound property changes
- Receive callbacks when any bound properties change
- Bind to a list with ListView
- Bind to a list without ListView
- Bind a custom control
- Bind a custom control to custom data type
- Support for Editor UI
- Support for runtime UI
- Work with text
- Examples
- Migration guides
- Unity UI
- Immediate Mode GUI (IMGUI)
- Unity Services
- Setting up your project for Unity services
- Unity Organizations
- Unity Ads
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Cloud Content Delivery
- Unity Build Automation (formerly Cloud Build)
- Unity IAP
- Setting up Unity IAP
- Cross Platform Guide
- Codeless IAP
- Defining products
- Subscription Product support
- Initialization
- Browsing Product Metadata
- Initiating Purchases
- Processing Purchases
- Handling purchase failures
- Restoring Transactions
- Purchase Receipts
- Receipt validation
- Store Extensions
- Cross-store installation issues with Android in-app purchase stores
- Store Guides
- Implementing a Store
- Unity Cloud Diagnostics
- Unity Integrations
- Multiplayer services
- Unity Distribution Portal
- Unity Accelerator
- XR
- Unity's Asset Store
- Asset Store packages
- Publishing to the Asset Store
- Creating your Publisher Account
- Creating a new package draft
- Deleting a package draft
- Uploading assets to your package
- Filling in the package details
- Submitting your package for approval
- Viewing the status of your Asset Store submissions
- Collecting revenue
- Providing support to your customers
- Adding tags to published packages
- Connecting your account to Google Analytics
- Promoting your Assets
- Refunding your customers
- Upgrading packages
- Deprecating your Assets
- Issuing vouchers
- Managing your publishing team
- Asset Store Publisher portal
- Verified Solutions
- Platform development
- Using Unity as a Library in other applications
- Deep linking
- Xcode frame debugger Unity integration
- Android
- Introducing Android
- Getting started with Android
- Developing for Android
- Android mobile scripting
- Input for Android devices
- Android application size restrictions
- Graphics for Android
- Testing and debugging
- Optimization for Android
- Create and use plug-ins in Android
- Integrating Unity into Android applications
- Android application entry points
- Deep linking on Android
- Device features and permissions
- Handle Android crashes
- Quit a Unity Android application
- Building and delivering for Android
- ChromeOS
- Dedicated Server
- iOS
- Introducing iOS
- Getting started with iOS
- Developing for iOS
- iOS Scripting
- Input for iOS devices
- Unity's Device Simulator for iOS
- Unity Remote
- Managed stack traces on iOS
- Optimize performance for iOS
- Native plug-ins for iOS
- Integrating Unity into native iOS applications
- Deep linking on iOS
- iOS authorizations in Unity
- Preparing your application for In-App Purchases (IAP)
- Social API
- Troubleshooting on iOS devices
- Reporting crash bugs on iOS
- Building and delivering for iOS
- Linux
- macOS
- tvOS
- Web
- Web introduction
- Web development
- Web Player settings
- Interaction with browser scripting
- Code examples: Call JavaScript and C/C++/C# functions in Unity
- Set up your JavaScript plug-in
- Call JavaScript functions from Unity C# scripts
- Call Unity C# script functions from JavaScript
- Call C/C++/C# functions from Unity C# scripts
- Compile a static library as a Unity plug-in
- Create callbacks between Unity C#, JavaScript, and C/C++/C# code
- Replace deprecated browser interaction code
- Web native plug-ins for Emscripten
- Memory in Unity Web
- Cache behavior in Web
- Web graphics
- Audio in Web
- Video playback in Web
- Texture compression in Web
- Embedded resources in Web
- Input in Web
- Configure a Web Canvas size
- Web browser access to device features
- Web networking
- Cursor locking and full-screen mode in Web
- Web performance considerations
- Debug and troubleshoot Web builds
- Build and distribute a Web application
- Windows
- Universal Windows Platform
- Introduction to Universal Windows Platform
- Get started with Universal Windows Platform
- Develop for Universal Windows Platform
- Build and deliver for Universal Windows Platform
- Unity Search
- Glossary
- Video overview
- Video Player component
Video Player component
Use the Video Player componentA functional part of a GameObject. A GameObject can contain any number of components. Unity has many built-in components, and you can create your own by writing scripts that inherit from MonoBehaviour. More info
See in Glossary to attach video files to GameObjectsThe fundamental object in Unity scenes, which can represent characters, props, scenery, cameras, waypoints, and more. A GameObject’s functionality is defined by the Components attached to it. More info
See in Glossary, and play them on the GameObject’s TextureAn image used when rendering a GameObject, Sprite, or UI element. Textures are often applied to the surface of a mesh to give it visual detail. More info
See in Glossary at run time.
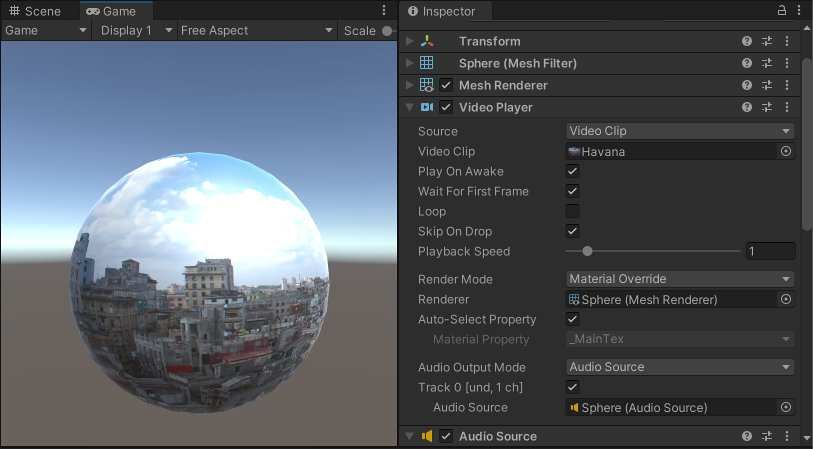
The screenshot below shows a Video Player component attached to a spherical GameObject.
By default, the Material Property of a Video Player component is set to a GameObject’s main texture, which means that when the Video Player component is attached to a GameObject that has a Renderer, it automatically assigns itself to the Texture on that Renderer (because this is the main Texture for the GameObject). Here, the GameObject has a MeshThe main graphics primitive of Unity. Meshes make up a large part of your 3D worlds. Unity supports triangulated or Quadrangulated polygon meshes. Nurbs, Nurms, Subdiv surfaces must be converted to polygons. More info
See in Glossary Renderer component, so the Video Player automatically assigns it to the Renderer field, which means the Video Clip plays on the Mesh RendererA mesh component that takes the geometry from the Mesh Filter and renders it at the position defined by the object’s Transform component. More info
See in Glossary’s Texture.
You can also set a specific target for the video to play on, including:
A CameraA component which creates an image of a particular viewpoint in your scene. The output is either drawn to the screen or captured as a texture. More info
See in Glossary planeA Render TextureA special type of Texture that is created and updated at runtime. To use them, first create a new Render Texture and designate one of your Cameras to render into it. Then you can use the Render Texture in a Material just like a regular Texture. More info
See in GlossaryA MaterialAn asset that defines how a surface should be rendered. More info
See in Glossary Texture parameterAny Texture field in a component
Video Player component reference
| Property | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Source | Choose the source type of your video. | ||
| Video Clip | Select the Video Clip to assign to the Video Player component. This isn’t supported on the Web platform. | ||
| URL | Enter the URL (for example, http:// or file://) of the video you want to assign to the Video Player. | ||
| Update Mode | Set the clock source that the Video Player component uses to update its timing. | ||
| DSP Time | Use the same clock source that processes audio. | ||
| Game Time | Use the same clock source as the game clock. This clock source is affected by the time scaling and capture frame rate settings. | ||
| Unscaled Game Time | Use the same clock source as the game clock but without being affected by time scaling or capture frame rate. | ||
| Play On AwakeSet this to true to make an Audio Source start playing on awake More info See in Glossary |
Play the video when the SceneA Scene contains the environments and menus of your game. Think of each unique Scene file as a unique level. In each Scene, you place your environments, obstacles, and decorations, essentially designing and building your game in pieces. More info See in Glossary launches. Clear it if you want to trigger the video playback at another point during runtime. Trigger it via scripting with the Play() command. |
||
| Wait For First Frame | Wait for the first frame of the source video to be ready for display before the game starts. Clear it to keep the video time in sync with the rest of the game, which might cause the first few frames to be discarded. | ||
| Loop | Loop the source video when it reaches its end. Clear it to stop playing the video when it reaches the end. | ||
| Skip On Drop | When you enable this option, and the Video Player component detects drift between the playback position and the game clock, the Video Player skips ahead. When you disable this option, the Video Player doesn’t correct for drift and systematically plays all frames. | ||
| Playback Speed | Set a multiplier for the playback speed, as a value between 0 and 10. This is set to 1 (normal speed) by default. If the field is set to 2, the video plays at two times its normal speed. | ||
| Render Mode | Choose how the video will render. | ||
| Camera Far Plane | Render the video on the Camera’s far plane. | ||
| Camera Near Plane | Render the video on the Camera’s near plane. | ||
| Render Texture | Render the video into a Render Texture. | ||
| Material Override | Render the video into a selected Texture property of a GameObject through its Renderer’s Material. | ||
| API Only | Render the video into the VideoPlayer.texture Scripting API property. You must use scripting to assign the Texture to its intended destination. | ||
| Camera | Define the Camera receiving the video. | ||
| Alpha | Set the global transparency level to add to the source video. This allows elements behind the plane to be visible through it. For more information about alpha channels, refer to video transparency support. | ||
| 3D Layout | Choose the layout of 3D content in the source video. | ||
| None | Video doesn’t have any 3D content. | ||
| Side by Side | Video has 3D content where the left eye occupies the left half and right eye occupies the right half of video frames. | ||
| Over Under | Video has 3D content where the left eye occupies the upper half and right eye occupies the lower half of video frames. | ||
| Target Texture | Define the Render Texture where the Video Player component renders its images. | ||
| Aspect RatioThe relationship of an image’s proportional dimensions, such as its width and height. See in Glossary |
Set the aspect ratio of the images that fill the Camera Near Plane, Camera Far Plane, or Render Texture when the corresponding Render Mode is used. | ||
| No Scaling | No scaling is used. The video is centered on the destination rectangle. | ||
| Fit Vertically | Scale the source to fit the destination rectangle vertically, cropping the left and right sides or leaving black areas on each side if necessary. The source aspect ratio is preserved. | ||
| Fit Horizontally | Scale the source to fit the destination rectangle horizontally, cropping the top and bottom regions or leaving black areas above and below if needed. The source aspect ratio is preserved. | ||
| Fit Inside | Scale the source to fit the destination rectangle without having to crop. Leaves black areas on the left and right or above and below as needed. The source aspect ratio is preserved. | ||
| Fit Outside | Scale the source to fit the destination rectangle without leaving black areas on the left and right or above and below, cropping as required. The source aspect ratio is preserved. | ||
| Stretch | Scale both horizontally or vertically to fit the destination rectangle. The source aspect ratio isn’t preserved. | ||
| Renderer | Select the Renderer where the Video Player component renders its images. When set to None, the Renderer on the same GameObject as the Video Player component is used. | ||
| Auto-Select Property | When you enable this option, the Video Player component selects the Renderer’s main texture automatically. When you disable this option, you can set the Material Property option manually. | ||
| Material Property | The name of the Material Texture property that receives the Video Player component images. | ||
| Audio Output Mode | Define how the source’s audio tracks are output. | ||
| None | Audio isn’t played. | ||
| Audio Source | Audio samples are sent to selected audio sourcesA component which plays back an Audio Clip in the scene to an audio listener or through an audio mixer. More info See in Glossary, enabling Unity’s audio processing to be applied. |
||
| Direct | Audio samples are sent directly to the audio output hardware, bypassing Unity’s audio processing. | ||
| API Only (Experimental) | Audio samples are sent to the associated AudioSampleProvider. | ||
| Controlled Tracks | The number of audio tracks in the video. Only shown when Source is URL. When Source is Video Clip, the number of tracks is determined by examining the video file. |
||
| Track Number | Enable the associated audio track to use for playback. This must be set prior to playback. The text to the left of the checkbox provides information about the audio track, specifically the track number, language, and number of channels. When the source is a URL, this information is only available during playback. This property only appears if your source is a Video Clip that has an audio track (or tracks), or your source is a URL (allowing you to indicate how many tracks are expected from the URL during playback). |
||
| Audio Source | The audio source through which the audio track is played. The targeted audio source can also play Audio Clips. The audio source’s playback controls ( Play On Awake and Play() in scripting API) don’t apply to the video source’s audio track.This property only appears when the Audio Output Mode is set to Audio Source. |
||
| Mute | Mute the associated audio track. In Audio Source mode, the audio source’s control is used. This property only appears when the Audio Output Mode is set to Direct. |
||
| Volume | Volume of the associated audio track. In Audio Source mode, the audio source’s volume is used. This property only appears when the Audio Output Mode is set to Direct. |
||
Video Player Scripting Example
The following script demonstrates a few of the Video Player component’s features.
// Examples of Video Player function
using UnityEngine;
public class Example : MonoBehaviour
{
void Start()
{
// Will attach a Video Player to the main camera.
GameObject camera = GameObject.Find("Main Camera");
// VideoPlayer automatically targets the camera backplane when it is added
// to a camera object, no need to change videoPlayer.targetCamera.
var videoPlayer = camera.AddComponent<UnityEngine.Video.VideoPlayer>();
// Play on awake defaults to true. Set it to false to avoid the url set
// below to auto-start playback since we're in Start().
videoPlayer.playOnAwake = false;
// By default, Video Players added to a camera will use the far plane.
// Let's target the near plane instead.
videoPlayer.renderMode = UnityEngine.Video.VideoRenderMode.CameraNearPlane;
// This will cause our Scene to be visible through the video being played.
videoPlayer.targetCameraAlpha = 0.5F;
// Set the video to play. URL supports local absolute or relative paths.
// Here, using absolute.
videoPlayer.url = "/Users/graham/movie.mov";
// Skip the first 100 frames.
videoPlayer.frame = 100;
// Restart from beginning when done.
videoPlayer.isLooping = true;
// Each time we reach the end, we slow down the playback by a factor of 10.
videoPlayer.loopPointReached += EndReached;
// Start playback. This means the Video Player may have to prepare (reserve
// resources, pre-load a few frames, etc.). To better control the delays
// associated with this preparation one can use videoPlayer.Prepare() along with
// its prepareCompleted event.
videoPlayer.Play();
}
void EndReached(UnityEngine.Video.VideoPlayer vp)
{
vp.playbackSpeed = vp.playbackSpeed / 10.0F;
}
}
VideoPlayer