Surface Shader lighting examples
This page provides examples of custom Surface Shader lighting models in Surface ShadersUnity’s code generation approach that makes it much easier to write lit shaders than using low level vertex/pixel shader programs. More info
See in Glossary. For more general Surface ShaderA small script that contains the mathematical calculations and algorithms for calculating the Color of each pixel rendered, based on the lighting input and the Material configuration. More info
See in Glossary guidance, see Surface Shader Examples.
Because Deferred Lighting does not play well with some custom per-material lighting models, most of the examples below make the shaders compile to Forward RenderingA rendering path that renders each object in one or more passes, depending on lights that affect the object. Lights themselves are also treated differently by Forward Rendering, depending on their settings and intensity. More info
See in Glossary only.
Diffuse
The following is an example of a shader that uses the built-in Lambert lighting model:
Shader "Example/Diffuse Texture" {
Properties {
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
}
SubShader {
Tags { "RenderType" = "Opaque" }
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf Lambert
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) {
o.Albedo = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex).rgb;
}
ENDCG
}
Fallback "Diffuse"
}
Here’s how it looks like with a Texture and without a Texture, with one directional Light in the SceneA Scene contains the environments and menus of your game. Think of each unique Scene file as a unique level. In each Scene, you place your environments, obstacles, and decorations, essentially designing and building your game in pieces. More info
See in Glossary:
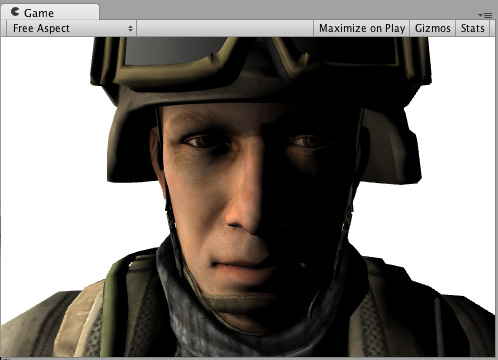
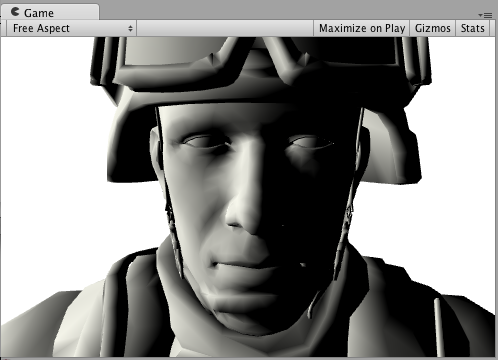
The following example shows how to achieve the same result by writing a custom lighting model instead of using the built-in Lambert model.
To do this, you need to use a number of Surface Shader lighting model functions. Here’s a simple Lambert one. Note that only the CGPROGRAM section changes; the surrounding Shader code is exactly the same:
Shader "Example/Diffuse Texture" {
Properties {
_MainTex ("Texture", 2D) = "white" {}
}
SubShader {
Tags { "RenderType" = "Opaque" }
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf SimpleLambert
half4 LightingSimpleLambert (SurfaceOutput s, half3 lightDir, half atten) {
half NdotL = dot (s.Normal, lightDir);
half4 c;
c.rgb = s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * (NdotL * atten);
c.a = s.Alpha;
return c;
}
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) {
o.Albedo = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex).rgb;
}
ENDCG
}
Fallback "Diffuse"
}
This simple Diffuse lighting model uses the LightingSimpleLambert function. It computes lighting by calculating a dot product between surface normal and light direction, and then applying light attenuation and color.
Diffuse Wrap
The following example shows Wrapped Diffuse, a modification of Diffuse lighting where illumination “wraps around” the edges of objects. It’s useful for simulating subsurface scattering effects. Only the CGPROGRAM section changes, so once again, the surrounding Shader code is omitted:
...ShaderLab code...
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf WrapLambert
half4 LightingWrapLambert (SurfaceOutput s, half3 lightDir, half atten) {
half NdotL = dot (s.Normal, lightDir);
half diff = NdotL * 0.5 + 0.5;
half4 c;
c.rgb = s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * (diff * atten);
c.a = s.Alpha;
return c;
}
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) {
o.Albedo = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex).rgb;
}
ENDCG
...ShaderLab code...
Here’s how it looks like with a Texture and without a Texture, with one directional Light in the Scene:


Toon Ramp
The following example shows a “Ramp” lighting model that uses a Texture ramp to define how surfaces respond to the angles between the light and the normal. This can be used for a variety of effects, and is especially effective when used with Toon lighting.
...ShaderLab code...
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf Ramp
sampler2D _Ramp;
half4 LightingRamp (SurfaceOutput s, half3 lightDir, half atten) {
half NdotL = dot (s.Normal, lightDir);
half diff = NdotL * 0.5 + 0.5;
half3 ramp = tex2D (_Ramp, float2(diff)).rgb;
half4 c;
c.rgb = s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * ramp * atten;
c.a = s.Alpha;
return c;
}
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) {
o.Albedo = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex).rgb;
}
ENDCG
...ShaderLab code...
Here’s how it looks like with a Texture and without a Texture, with one directional Light in the Scene:



Simple Specular
The following example shows a simple specular lighting model, similar to the built-in BlinnPhong lighting model.
...ShaderLab code...
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf SimpleSpecular
half4 LightingSimpleSpecular (SurfaceOutput s, half3 lightDir, half3 viewDir, half atten) {
half3 h = normalize (lightDir + viewDir);
half diff = max (0, dot (s.Normal, lightDir));
float nh = max (0, dot (s.Normal, h));
float spec = pow (nh, 48.0);
half4 c;
c.rgb = (s.Albedo * _LightColor0.rgb * diff + _LightColor0.rgb * spec) * atten;
c.a = s.Alpha;
return c;
}
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
sampler2D _MainTex;
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutput o) {
o.Albedo = tex2D (_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex).rgb;
}
ENDCG
...ShaderLab code...
Here’s how it looks like with a Texture and without a Texture, with one directional Light in the Scene:

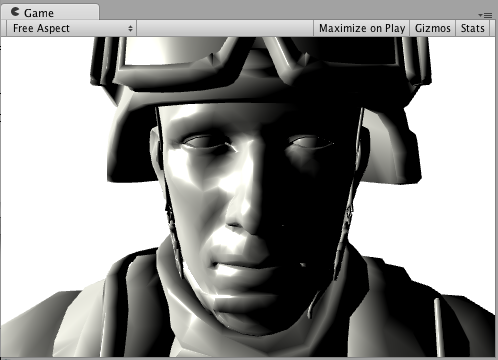
Custom GI
We’ll start with a Shader that mimics Unity’s built-in GI:
Shader "Example/CustomGI_ToneMapped" {
Properties {
_MainTex ("Albedo (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}
}
SubShader {
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf StandardDefaultGI
#include "UnityPBSLighting.cginc"
sampler2D _MainTex;
inline half4 LightingStandardDefaultGI(SurfaceOutputStandard s, half3 viewDir, UnityGI gi)
{
return LightingStandard(s, viewDir, gi);
}
inline void LightingStandardDefaultGI_GI(
SurfaceOutputStandard s,
UnityGIInput data,
inout UnityGI gi)
{
LightingStandard_GI(s, data, gi);
}
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {
o.Albedo = tex2D(_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex);
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Diffuse"
}
Now, let’s add some tone mapping on top of the GI:
Shader "Example/CustomGI_ToneMapped" {
Properties {
_MainTex ("Albedo (RGB)", 2D) = "white" {}
_Gain("Lightmap tone-mapping Gain", Float) = 1
_Knee("Lightmap tone-mapping Knee", Float) = 0.5
_Compress("Lightmap tone-mapping Compress", Float) = 0.33
}
SubShader {
Tags { "RenderType"="Opaque" }
CGPROGRAM
#pragma surface surf StandardToneMappedGI
#include "UnityPBSLighting.cginc"
half _Gain;
half _Knee;
half _Compress;
sampler2D _MainTex;
inline half3 TonemapLight(half3 i) {
i *= _Gain;
return (i > _Knee) ? (((i - _Knee)*_Compress) + _Knee) : i;
}
inline half4 LightingStandardToneMappedGI(SurfaceOutputStandard s, half3 viewDir, UnityGI gi)
{
return LightingStandard(s, viewDir, gi);
}
inline void LightingStandardToneMappedGI_GI(
SurfaceOutputStandard s,
UnityGIInput data,
inout UnityGI gi)
{
LightingStandard_GI(s, data, gi);
gi.light.color = TonemapLight(gi.light.color);
#ifdef DIRLIGHTMAP_SEPARATE
#ifdef LIGHTMAP_ON
gi.light2.color = TonemapLight(gi.light2.color);
#endif
#ifdef DYNAMICLIGHTMAP_ON
gi.light3.color = TonemapLight(gi.light3.color);
#endif
#endif
gi.indirect.diffuse = TonemapLight(gi.indirect.diffuse);
gi.indirect.specular = TonemapLight(gi.indirect.specular);
}
struct Input {
float2 uv_MainTex;
};
void surf (Input IN, inout SurfaceOutputStandard o) {
o.Albedo = tex2D(_MainTex, IN.uv_MainTex);
}
ENDCG
}
FallBack "Diffuse"
}
Did you find this page useful? Please give it a rating: