手册
- Unity User Manual 2023.2
- New in Unity 2023.2
- Packages and feature sets
- Released packages
- 2D Animation
- 2D Aseprite Importer
- 2D Pixel Perfect
- 2D PSD Importer
- 2D SpriteShape
- 2D Tilemap Extras
- Adaptive Performance
- Addressables
- Addressables for Android
- Ads Mediation
- Advertisement Legacy
- AI Navigation
- Alembic
- Analytics
- Android Logcat
- Animation Rigging
- Apple ARKit XR Plugin
- AR Foundation
- Authentication
- Build Automation
- Burst
- CCD Management
- Cinemachine
- Cloud Code
- Cloud Diagnostics
- Cloud Save
- Code Coverage
- Collections
- Deployment
- Device Simulator Devices
- Economy
- Editor Coroutines
- FBX Exporter
- Friends
- Google ARCore XR Plugin
- In App Purchasing
- Input System
- iOS 14 广告支持
- JetBrains Rider 编辑器
- Leaderboards
- Live Capture
- Lobby
- Localization
- Magic Leap XR Plugin
- Matchmaker
- Mathematics
- 内存性能分析器 (Memory Profiler)
- ML Agents
- Mobile Notifications
- Multiplayer Tools
- Netcode for GameObjects
- Oculus XR Plugin
- OpenXR 插件
- Player Accounts
- Polybrush
- Post Processing
- ProBuilder
- Profile Analyzer
- Push Notifications
- Python Scripting
- Recorder
- Relay
- Remote Config
- Scriptable Build Pipeline
- Sequences
- Splines
- Sysroot Base
- Sysroot Linux x64
- System Metrics Mali
- Terrain Tools
- Test Framework
- 时间轴
- Toolchain Linux x64
- Toolchain MacOS Linux x64
- Toolchain Win Linux x64
- Tutorial Authoring Tools
- Tutorial Framework
- Unity Distribution Portal
- Unity OpenXR Meta
- Unity Profiling Core API
- Unity Transport
- User Generated Content
- User Generated Content Bridge
- User Reporting
- 版本控制
- Visual Scripting
- Visual Studio 编辑器
- WebGL Publisher
- XR Hands
- XR Interaction Toolkit
- XR Plugin Management
- ZivaRT Player
- Release candidates
- Pre-release packages
- 核心包
- 内置包
- Accessibility
- AI
- Android JNI
- 动画
- Asset Bundle
- Audio
- 布料
- Director
- Image Conversion
- IMGUI
- JSONSerialize
- NVIDIA
- Particle System
- 物理 (Physics)
- Physics 2D
- Screen Capture
- Terrain
- Terrain Physics
- Tilemap
- UI
- UIElements
- Umbra
- Unity Analytics
- Unity Web Request
- Unity Web Request Asset Bundle
- Unity Web Request Audio
- Unity Web Request Texture
- Unity Web Request WWW
- Vehicles
- Video
- VR
- Wind
- XR
- Experimental packages
- 按关键字排列的包
- Deprecated packages
- Unity 的 Package Manager
- How Unity works with packages
- 概念
- 配置
- Package Manager 窗口
- Access the Package Manager window
- Navigation panel
- List panel
- Details panel
- Features (details panel)
- Finding packages and feature sets
- Adding and removing
- Install a feature set from the Unity registry
- Install a package from a registry
- Install a package from a local folder
- Install a package from a local tarball file
- Install a package from a Git URL
- Install a package from a registry by name
- Removing an installed package from a project
- 禁用内置包
- 切换到另一个包版本
- 导入 Asset Store 资源包
- Updating an Asset Store package
- Remove imported assets from a project
- Delete a package from the Asset Store cache
- Perform an action on multiple packages
- 查找包文档
- 检查包
- 包的脚本 API
- Scoped registries
- 解析和冲突
- 项目清单
- 故障排除
- 创建自定义包
- Feature sets
- Released packages
- Install Unity
- 许可证和激活
- Upgrade Unity
- Create with Unity
- 2D 还是 3D 项目
- Unity 的界面
- Project 窗口
- Scene 视图
- Game 视图
- Device Simulator
- Hierarchy 窗口
- Inspector 窗口
- 编辑属性
- The Toolbar
- 状态栏
- 后台任务窗口
- Console 窗口
- 其他窗口
- Undo
- Search in the Editor
- 自定义工作空间
- Unity 快捷键
- Quickstart guides
- Advanced best practice guides
- Create Gameplay
- 编辑器功能
- 分析
- Memory in Unity
- 性能分析器概述
- 应用程序性能分析
- 常见性能分析器标记
- Profiler 窗口
- Asset Loading Profiler module
- Audio Profiler 模块
- CPU Usage Profiler 模块
- File Access Profiler module
- Global Illumination Profiler 模块
- GPU Usage Profiler 模块
- Highlights Profiler Module
- Memory Profiler 模块
- Physics Profiler 模块
- Physics 2D Profiler module
- Rendering Profiler 模块
- UI 和 UI Details Profiler
- Video Profiler 模块
- Virtual Texturing Profiler 模块
- Customizing the Profiler
- 低级原生插件 Profiler API
- Profiling tools
- Log files
- 了解 Unity 中的优化
- 资源加载指标
- 资源工作流程
- 输入
- 2D game development
- Introduction to 2D
- 2D game development quickstart guide
- 2D 排序
- Work with sprites
- Tilemaps
- Essential tilemap steps and tools
- Active brush
- Create Tilemaps
- Create Tiles
- Create a Tile Palette
- Tile Palette editor tools
- Using the Select tool
- Move selected tiles with the Move tool
- Paint tiles with the Paint tool
- Use the Box Fill tool to fill an area with duplicated tiles
- Select tiles on the tilemap or Tile Palette with the Pick tool
- Remove tiles from the tilemap with the Eraser tool
- Fill an empty area with tiles with the Flood Fill tool
- Brush Picks
- Tilemap Collider 2D component reference
- 六边形瓦片地图
- 等距瓦片地图
- 可编程瓦片
- 可编程画笔
- Tile Palette visual elements
- Tilemap component reference
- Grid component reference
- Tilemap Renderer component reference
- Tile asset reference
- Tile Palette preferences reference
- Tile Palette editor reference
- Essential tilemap steps and tools
- Physics 2D Reference
- 图形
- 渲染管线
- 摄像机
- 光照
- 模型
- 网格
- 纹理
- 导入纹理
- Texture Import Settings
- Default Import Settings reference
- Normal map Import Settings reference
- Editor GUI and Legacy GUI Import Settings reference
- Sprite (2D and UI) Import Settings reference
- Cursor Import Settings reference
- Cookie Import Settings reference
- Lightmap Import Settings reference
- Directional Lightmap Import Settings reference
- Shadowmask Import Settings reference
- Single Channel Import Settings reference
- Texture Import Settings
- Texture formats
- Mipmaps
- 渲染纹理
- 自定义渲染纹理
- 电影纹理 (Movie Textures)
- 3D 纹理
- 纹理数组
- 立方体贴图
- 立方体贴图数组
- Streaming Virtual Texturing
- 稀疏纹理
- 加载纹理和网格数据
- 导入纹理
- 着色器
- 着色器核心概念
- 内置着色器
- 标准着色器
- 标准粒子着色器
- Autodesk Interactive 着色器
- 旧版着色器
- 内置着色器的用途和性能
- 普通着色器系列
- 透明着色器系列
- 透明镂空着色器系列
- 自发光着色器系列
- 反光着色器系列
- 反射顶点光照 (Reflective Vertex-Lit)
- 反光漫射 (Reflective Diffuse)
- 反光镜面反射 (Reflective Specular)
- 反光凹凸漫射 (Reflective Bumped Diffuse)
- 反光凹凸镜面反射 (Reflective Bumped Specular)
- 反光视差漫射 (Reflective Parallax Diffuse)
- 反光视差镜面反射 (Reflective Parallax Specular)
- 反光法线贴图无光照 (Reflective Normal Mapped Unlit)
- 反光法线贴图顶点光照 (Reflective Normal mapped Vertex-lit)
- 使用 Shader Graph
- 编写着色器
- 编写着色器概述
- ShaderLab
- ShaderLab:定义 Shader 对象
- ShaderLab:定义子着色器
- ShaderLab:定义一个通道
- ShaderLab:添加着色器程序
- ShaderLab: specifying package requirements
- ShaderLab:命令
- ShaderLab:使用 Category 代码块对命令进行分组
- ShaderLab 命令:AlphaToMask
- ShaderLab 命令:Blend
- ShaderLab 命令:BlendOp
- ShaderLab 命令:ColorMask
- ShaderLab 命令:Conservative
- ShaderLab 命令:Cull
- ShaderLab 命令:Offset
- ShaderLab 命令:模板
- ShaderLab 命令:UsePass
- ShaderLab 命令:GrabPass
- ShaderLab 命令:ZClip
- ShaderLab 命令:ZTest
- ShaderLab 命令:ZWrite
- ShaderLab 旧版功能
- Unity 中的 HLSL
- Unity 中的 GLSL
- 着色器示例
- 编写表面着色器
- 为不同的图形 API 编写着色器
- Understanding shader performance
- 材质
- Visual effects
- Post-processing and full-screen effects
- 粒子系统
- 选择粒子系统解决方案
- 内置粒子系统
- 使用内置粒子系统
- 粒子系统顶点流和标准着色器支持
- 粒子系统 GPU 实例化
- 粒子系统 C# 作业系统集成
- 组件和模块
- 粒子系统 (Particle System)
- 粒子系统模块
- Main module
- Emission 模块
- Shape module
- Velocity over Lifetime 模块
- Noise 模块
- Limit Velocity over Lifetime module
- Inherit Velocity 模块
- Lifetime by Emitter Speed module
- Force over Lifetime module
- Color over Lifetime module
- Color by Speed module
- Size over Lifetime 模块
- Size by Speed 模块
- Rotation over Lifetime module
- Rotation by Speed module
- External Forces 模块
- Collision 模块
- Triggers 模块
- Sub Emitters 模块
- Texture Sheet Animation 模块
- Lights 模块
- Trails 模块
- Custom Data 模块
- Renderer 模块
- 粒子系统力场 (Particle System Force Field)
- Visual Effect Graph
- Decals and projectors
- Lens flares and halos
- Lines, trails, and billboards
- 天空
- 颜色
- 图形 API 支持
- Graphics performance and profiling
- World building
- 物理系统
- Built-in 3D Physics
- Character control
- Rigidbody physics
- Collision
- Joints
- Articulations
- Ragdoll physics
- 布料
- 多场景物理
- Built-in 3D Physics
- 脚本
- 多玩家和联网
- Audio
- 视频概述
- 动画
- User interface (UI)
- Unity 中 UI 系统的对比
- UI 工具包
- Get started with UI Toolkit
- UI Builder
- Structure UI
- The visual tree
- Structure UI with UXML
- Structure UI with C# scripts
- Custom controls
- Best practices for managing elements
- Encapsulate UXML documents with logic
- UXML 元素参考
- UXML element BindableElement
- UXML element VisualElement
- UXML element BoundsField
- UXML element BoundsIntField
- UXML element Box
- UXML element Button
- UXML element ColorField
- UXML element CurveField
- UXML element DoubleField
- UXML element DropdownField
- UXML element EnumField
- UXML element EnumFlagsField
- UXML element FloatField
- UXML element Foldout
- UXML element GradientField
- UXML element GroupBox
- UXML element Hash128Field
- UXML element HelpBox
- UXML element IMGUIContainer
- UXML element Image
- UXML element InspectorElement
- UXML element IntegerField
- UXML element Label
- UXML element LayerField
- UXML element LayerMaskField
- UXML element LongField
- UXML element ListView
- UXML element MaskField
- UXML element MinMaxSlider
- UXML element MultiColumnListView
- UXML element MultiColumnTreeView
- UXML element ObjectField
- UXML element PopupWindow
- UXML element ProgressBar
- UXML element PropertyField
- UXML element RadioButton
- UXML element RadioButtonGroup
- UXML element RectField
- UXML element RectIntField
- UXML element RepeatButton
- UXML element ScrollView
- UXML element Scroller
- UXML element Slider
- UXML element SliderInt
- UXML element Tab
- UXML element TabView
- UXML element TagField
- UXML element TextElement
- UXML element TextField
- UXML element TemplateContainer
- UXML element Toggle
- UXML element ToggleButtonGroup
- UXML element Toolbar
- UXML element ToolbarBreadcrumbs
- UXML element ToolbarButton
- UXML element ToolbarMenu
- UXML element ToolbarPopupSearchField
- UXML element ToolbarSearchField
- UXML element ToolbarSpacer
- UXML element ToolbarToggle
- UXML element TreeView
- UXML element TwoPaneSplitView
- UXML element UnsignedLongField
- UXML element UnsignedIntegerField
- UXML element Vector2Field
- UXML element Vector2IntField
- UXML element Vector3Field
- UXML element Vector3IntField
- UXML element Vector4Field
- Structure UI examples
- Create list and tree views
- Create a complex list view
- Create a list view runtime UI
- Wrap content inside a scroll view
- Create a tabbed menu
- Create a pop-up window
- Use Toggle to create a conditional UI
- Create a custom control with two attributes
- Create a slide toggle custom control
- Create a bindable custom control
- Create a custom style for a custom control
- Create a drag-and-drop list and tree views between windows
- Create an aspect ratio custom control
- Style UI
- UI Toolkit Debugger
- Control behavior with events
- UI Renderer
- Data binding
- Comparison of the binding systems
- Runtime data binding
- SerializedObject data binding
- Introduction to SerializedObject data binding
- Bindable elements reference
- Bindable data types and fields
- Binding system implementation details
- Binding examples
- Bind with binding path in C# script
- Bind without the binding path
- Bind with UXML and C# script
- Create a binding with the Inspector
- Bind to nested properties
- Bind to a UXML template
- Receive callbacks when a bound property changes
- Receive callbacks when any bound properties change
- Bind to a list with ListView
- Bind to a list without ListView
- Bind a custom control
- Bind a custom control to custom data type
- Support for Editor UI
- Support for runtime UI
- Work with text
- Examples
- Migration guides
- Unity UI
- 即时模式 GUI (IMGUI)
- Unity 服务
- XR
- Unity Asset Store
- 平台开发
- 将“Unity 用作库”用于其他应用程序
- Deep linking
- Xcode frame debugger Unity integration
- Android
- Introducing Android
- Getting started with Android
- Developing for Android
- Android 移动端脚本
- Input for Android devices
- Android application size restrictions
- Graphics for Android
- Testing and debugging
- Optimization for Android
- Create and use plug-ins in Android
- 将 Unity 集成到 Android 应用程序中
- Android application entry points
- Deep linking on Android
- Device features and permissions
- Handle Android crashes
- Quit a Unity Android application
- Building and delivering for Android
- ChromeOS
- Dedicated Server
- iOS
- Introducing iOS
- Getting started with iOS
- Developing for iOS
- Building and delivering for iOS
- 在 iOS 设备上进行故障排除
- 报告 iOS 上的崩溃错误
- Linux
- macOS
- tvOS
- Web
- Web introduction
- Web development
- Web Player settings
- Interaction with browser scripting
- Web native plug-ins for Emscripten
- Memory in Unity Web
- Cache behavior in Web
- Web graphics
- Audio in Web
- Video playback in Web
- Texture compression in Web
- Embedded resources in Web
- Input in Web
- Configure a Web Canvas size
- Web browser access to device features
- Web networking
- Cursor locking and full-screen mode in Web
- Web performance considerations
- Debug and troubleshoot Web builds
- Build and distribute a Web application
- Windows
- Universal Windows Platform
- Introduction to Universal Windows Platform
- Get started with Universal Windows Platform
- Develop for Universal Windows Platform
- Build and deliver for Universal Windows Platform
- Unity Search
- 术语表
- Unity User Manual 2023.2
- 图形
- 纹理
- Mipmaps
- Mipmaps introduction
Mipmaps introduction
A mipmap level is a version of a texture with a specific resolution. Mipmap levels exist in sets called mipmaps. Mipmaps contain progressively smaller and lower resolution versions of a single texture.
For example, a mipmap might contain four versions of a texture, from the original texture (mipmap level 0), to mipmap level 1, mipmap level 2, and mipmap level 3:
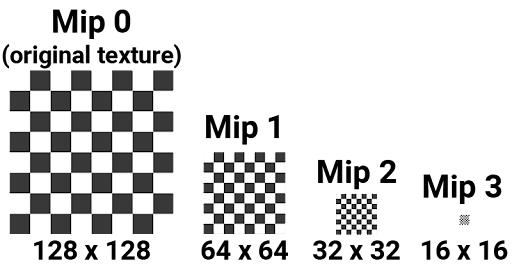
Mipmaps are commonly used for rendering objects in 3D scenes, where textured objects can vary in distance from the camera. A higher mipmap level is used for objects closer to the camera, and lower mipmap levels are used for more distant objects.
Mipmaps can speed up rendering operations and reduce rendering artifacts in situations where the GPU renders a texture at less than its full resolution. A mipmap is effectively a cached, downsampled version of the original texture. Instead of performing many sampling operations on the original, full resolution texture, the GPU can perform a smaller number of operations on the already downsampled version.
Sometimes, mipmaps aren’t beneficial. Mipmaps increase the size of a texture by 33%, both on disk and in memory. They also provide no benefit when a texture is only rendered at its full resolution, such as a UI texture that isn’t scaled.
You can create a mipmap for a texture manually, or you can instruct Unity to generate a mipmap for you. To automatically generate a mipmap, ensure that your original texture’s resolution is a power of two value, as shown in the example mipmap image.
You can enable or disable mipmaps for a texture asset in the Texture Import Settings Inspector.
How the GPU samples mipmap levels
When the GPU samples a texture, it determines which mipmap level to use based on the texture coordinates (UVs) for the current pixel, and two internal values that the GPU calculates: DDX and DDY. DDX and DDY provide information about the UVs of the pixels beside and above the current pixel, including distances and angles.
The GPU uses these values to determine how much of a texture’s detail is visible to the camera. A greater distance and a more extreme angle between the current pixel and its neighbors means that the GPU picks a lower resolution mipmap level; a shorter distance and less extreme angle means that the GPU picks a mipmap level with a higher resolution.
The GPU can also blend the texture information from two mipmap levels together with trilinear filtering. Blending mipmap levels while sampling can make the transition from one mipmap level to another less noticeable. To blend mipmap levels, the GPU takes a specific percentage of texture information from one mipmap level and the rest from another mipmap level.
Mipmap bias
A setting called mipmap bias can do two things while sampling, based on the sampler settings:
- The mipmap bias can change the threshold for the GPU selecting a lower or higher mipmap level for a sample. The GPU selects a specific mipmap level when you use point and linear filtering in a sampler. For example, the GPU’s might decide that the texture at a set of UVs uses a sample from mipmap level 3. With a mipmap bias of –2, the GPU would use the higher resolution mipmap level 1 for the sample, instead.
- The mipmap bias can tell the GPU to prefer one mipmap level over another by an exact percentage when blending samples from different mipmap levels. The GPU blends mipmap levels when you use trilinear filtering in a sampler. For example, the GPU’s calculations might return a value of 0.5. The 0.5 value tells the GPU to take 50% of the texture information it needs from one mipmap level, and the remaining 50% from the next mipmap level. With an added mipmap bias of 0.2, the 0.5 value would change to 0.7, and the GPU would take 70% of the texture information from the first mipmap level and only 30% from the second.
The GPU has a global mipmap bias that it applies to its mipmap level selection by default. Textures can have their own mipmap bias, which Unity adds or subtracts from the global mipmap bias. You can also specify your own mipmap bias for an individual texture sampling operation in a shader.
To set the mipmap bias for an individual texture, see Texture.mipMapBias. To set a mipmap bias for a texture sampling operation in a hand-coded shader, use HLSL functions such as tex2dbias. To set a mipmap bias for a texture sampling operation in Shader Graph, see Sample texture 2D Array node or Sample texture 2D node.
How Unity loads mipmaps
You can control the way that Unity loads mipmaps at runtime with Mipmap Streaming.
Did you find this page useful? Please give it a rating:
Thanks for rating this page!
What kind of problem would you like to report?
Thanks for letting us know! This page has been marked for review based on your feedback.
If you have time, you can provide more information to help us fix the problem faster.
Provide more information
You've told us this page needs code samples. If you'd like to help us further, you could provide a code sample, or tell us about what kind of code sample you'd like to see:
You've told us there are code samples on this page which don't work. If you know how to fix it, or have something better we could use instead, please let us know:
You've told us there is information missing from this page. Please tell us more about what's missing:
You've told us there is incorrect information on this page. If you know what we should change to make it correct, please tell us:
You've told us this page has unclear or confusing information. Please tell us more about what you found unclear or confusing, or let us know how we could make it clearer:
You've told us there is a spelling or grammar error on this page. Please tell us what's wrong:
You've told us this page has a problem. Please tell us more about what's wrong:
Thank you for helping to make the Unity documentation better!
Your feedback has been submitted as a ticket for our documentation team to review.
We are not able to reply to every ticket submitted.